Financial Management - WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT
Spontaneous Sources - Sources Of Working Capital
Posted On :
Some sources of funds, which are created during the course of normal business activity have zero cost and are termed as spontaneous sources.
Spontaneous Sources
Some sources of funds, which are created during the course of normal business activity have zero cost and are termed as spontaneous sources. For example suppliers supply goods; employees provide services where the payment are made at a latter stage. To an extent, the payment
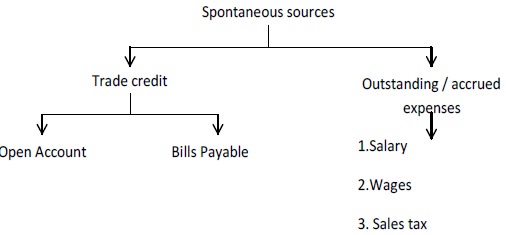
The credit extended in connection with the goods purchased for resale by a retailer or a wholesaler for materials used by manufacturers in producing its products is called the trade credit.
Trade credit is a form of short-term financing common is almost all types of business firm. As a matter of fact, it is the largest source of short-term funds. The amount of such financing depends on the volume of purchase and the payment timings. Small and new firms are usually more dependent on the trade credit, as they find it difficult to obtain funds from other sources. This trade credit may be extended to the customers in the form of
1. An opening account credit and
2. Acceptance credit management / bills payable.
Trade credit is mostly an informal arrangement, and is granted on an open account basis. Open account is usually extended only after the seller conducts a fairly extensive investigation of the buyer’s standard and reputation. In the case of open account credit arrangement the buyer does not sign any formal debt instrument as an evidence of the amount due by him to the seller. The only evidence is the copy of the invoice that goods have been delivered. Open account trade credit appears as Sundry creditors
on the buyer’s balance sheet in the liability side.
Trade credit may also take the form of Bills payable. In such a case the buyer accepts a bill of exchange or gives a promissory note for the amount due by him to the seller. This bill has specified future date, and is usually used when the supplier is less sure about buyers’ willingness and ability to pay or when the suppliers’ wants cash by discounting the bill from a bank. Thus, it is an arrangement by which the indebtedness of the buyer is recognized formally. This appears in the buyer’s balance sheet as accounts payable or bills payable.
Easy availability: Unlike other sources of finance trade credit as a source of finance relatively easy to obtain. The easy availability is very important in the case of small and medium firms where they cannot raise funds in the capital market.
Flexibility: The trade credit increases or decreases depending upon the growth of the firm. Moreover it need not pledge securities or adhere to strict payment schedule.
Informality: Trade credit is an informal spontaneous source of finance. It does not require signing in the negotiable instruments to obtain the credit.
Increased cost: The trade credit is usually very high when compared to cash sales. The seller while fixing the selling price will consider all explicit and implicit costs.
Overtrading: Trade credit facility may induce the buyer to buy a large quantity as a result it may occur in over trade.
Another spontaneous source of short-term financing is the accrued expenses as the outstanding expense liabilities. Accrued expenses refer to services received by the firm but the payment for which has not been made. The accrued expenses represent an interest free source of finance.
There is no explicit and implicit cost included in the accrued expenses. The most common accrued expenses are salary, wages and taxes. In these cases the amount may be due but the payments are not paid immediately. For example a firm may have a policy of paying salary and wages on a monthly basis. Similarly, the sales commission or target incentives, sales tax etc. are always payable with a time lag. The interest on debentures and borrowings is also payable periodically and thereby provide funds to the firms for the intervening period between two interest rates.
The accrued expenses are interest free sources of financing. It is consistent with the general philosophy of paying the creditors as late as possible as long as the firm does not damage its credit rating.
Postponement of salary and wages beyond normal level will affect the morale of the employees, resulting in reduced efficiency and higher labour turnover.
Some sources of funds, which are created during the course of normal business activity have zero cost and are termed as spontaneous sources. For example suppliers supply goods; employees provide services where the payment are made at a latter stage. To an extent, the payment

A. Trade Credit
(i) Open Account
(ii) Acceptance credit / Bills payable
Trade credit may also take the form of Bills payable. In such a case the buyer accepts a bill of exchange or gives a promissory note for the amount due by him to the seller. This bill has specified future date, and is usually used when the supplier is less sure about buyers’ willingness and ability to pay or when the suppliers’ wants cash by discounting the bill from a bank. Thus, it is an arrangement by which the indebtedness of the buyer is recognized formally. This appears in the buyer’s balance sheet as accounts payable or bills payable.
Merits of Trade Credit
Easy availability: Unlike other sources of finance trade credit as a source of finance relatively easy to obtain. The easy availability is very important in the case of small and medium firms where they cannot raise funds in the capital market.
Flexibility: The trade credit increases or decreases depending upon the growth of the firm. Moreover it need not pledge securities or adhere to strict payment schedule.
Informality: Trade credit is an informal spontaneous source of finance. It does not require signing in the negotiable instruments to obtain the credit.
Demerits of Trade Credit
Increased cost: The trade credit is usually very high when compared to cash sales. The seller while fixing the selling price will consider all explicit and implicit costs.
Overtrading: Trade credit facility may induce the buyer to buy a large quantity as a result it may occur in over trade.
Accrued Expenses
Another spontaneous source of short-term financing is the accrued expenses as the outstanding expense liabilities. Accrued expenses refer to services received by the firm but the payment for which has not been made. The accrued expenses represent an interest free source of finance.
There is no explicit and implicit cost included in the accrued expenses. The most common accrued expenses are salary, wages and taxes. In these cases the amount may be due but the payments are not paid immediately. For example a firm may have a policy of paying salary and wages on a monthly basis. Similarly, the sales commission or target incentives, sales tax etc. are always payable with a time lag. The interest on debentures and borrowings is also payable periodically and thereby provide funds to the firms for the intervening period between two interest rates.
Merits
Interest free cost
The accrued expenses are interest free sources of financing. It is consistent with the general philosophy of paying the creditors as late as possible as long as the firm does not damage its credit rating.
Demerits
Postponement of salary and wages beyond normal level will affect the morale of the employees, resulting in reduced efficiency and higher labour turnover.
Tags : Financial Management - WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT
Last 30 days 3344 views












