Financial Management - WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT
Other Sources - Sources Of Working Capital
Posted On :
In case of credit sales, it attracts more customers, resulting in increased sales and higher profit, but it has a cost also.
Other Sources
In case of credit sales, it attracts more customers, resulting in increased sales and higher profit, but it has a cost also. This cost may be of two types, namely investment cost and administrative cost. Moreover, the sellers have to raise funds from various sources in order to finance the receivables. While maintaining receivables, a firm may have to face two types of problems. First, the problem of raising funds to finance the receivables, and second the problem relating to collection, delay and defaults of the receivables. If the firm concentrates on managing funds and receivables, it cannot concentrate on other functions like finance, production, marketing, personal etc. Under this situation a firm can avail the services of a specialist organization engaged in receivables management. These specialist firms are known as factoring firms.
Factoring is a service that covers the financing and collection of account receivables in domestic and international trade.
Factoring may be defined as the relationship between the seller of the goods and a financial firm, called the factor, whereby the latter purchases the receivables from the former and also administers the receivables of the former.
Factoring is an ongoing arrangement between client and factor, where invoices raised on open account sales of goods and services are regularly assigned to ‘the Factor’ for financing, collection and sales ledger administration.
Factoring is a financing technique in which a business sells invoiced receivables at a discount to a bank or a financing house or to an internal finance company. The factor may or may not accept the incumbent credit risk. This is a service offered by a factoring company that enables companies to sell their outstanding book debts for cash.
Companies that typically benefit from factoring include those that rapidly grow, seasonal, in start up mode, under capitalized, those that have a lengthy manufacturing cycle, those strained by slow turnovers of
The factor fully manages your sales ledger and provides you with credit control and collection services of all your outstanding debts. The invoices you issue upon a sale are sent to the factor that typically advances upto 80% to 90% of the invoice amount to you. The balance, less charge, is paid when the customer makes payment directly to the factor. These services are disclosed to your customer who typically receives a letter from the factor, or attached note to your invoice, containing payment instructions to the factor. Funds are typically released to you with in 24 hours of issuing the invoices.
The factors are providing advances to their client upto 80% to 90% of the invoice amount within 24 hours of issuing invoices. For this cash advance they are charging interest. The interest charges calculated on the daily usage of funds are typically comparable to normal secured bank overdraft rates.

The charge, which is known as service charge, is expressed as a percentage of sales factored. The service charge, covering sale ledger management, collection services, and bad debts protection can range between 0.60% and 3.0% of turnover.
Factoring is a financial service provided by a factor firm to the client seller. The type of factoring depends upon the terms and conditions on which the services are provided, it is classified as follows:
This refers to those situations where factor firms assume only the work of collection of the receivables. They do not take any responsibility of bad debts i.e. any loss due to delay or default by the receivables is borne by the selling firms. In case the factor firm has already given advance to the selling firm against the receivable, then the seller firm should reduce the advance to the factor firm in case of default by the customer.
It is also known as full factoring. Non-recourse factoring protects against customers who fail to pay. The basic feature of non-recourse factoring is that the risk of default is born by the factor firm and the selling firm in any case receives the sales amount. Thus the factor typically covers this risk by taking out credit insurance. The cost of the credit insurance is passed on to the selling firm and depends on the risk profile of your customer and the amount of your factor is typically between 0.3% and 0.7% of turnover. The coverage limit with the factor is normally 80% - 95% of the factored amount.
Factoring may be advanced factoring or maturity factoring. In the case of advance factoring 80 – 90% of the receivable is paid by the factor to the seller within 24 hours of issue of invoice and the balance less charges payable at the time of collection of receivables. In the case of maturity factoring no advance is payable to the seller, rather the payment is made only after collection from the customers.
If, the business has sufficient staff and information system to manage the outstanding invoices efficiently and then the firm may want to consider an invoice discounting rather than factoring. It is identical to factoring except that in the sales ledger management the collection responsibility remains with the firm and the service is undisclosed to the customer.
Many factoring companies provide Internet access to the seller, allowing you to constantly monitor your sales ledger, balances, and
Better working capital management: Since there is instant cash and 80-90% of issued invoices are prepaid within 24 hours the problem of additional working capital required to match sales growth does not arise at all.

a. Factoring
In case of credit sales, it attracts more customers, resulting in increased sales and higher profit, but it has a cost also. This cost may be of two types, namely investment cost and administrative cost. Moreover, the sellers have to raise funds from various sources in order to finance the receivables. While maintaining receivables, a firm may have to face two types of problems. First, the problem of raising funds to finance the receivables, and second the problem relating to collection, delay and defaults of the receivables. If the firm concentrates on managing funds and receivables, it cannot concentrate on other functions like finance, production, marketing, personal etc. Under this situation a firm can avail the services of a specialist organization engaged in receivables management. These specialist firms are known as factoring firms.
Definition
Factoring is a service that covers the financing and collection of account receivables in domestic and international trade.
Factoring may be defined as the relationship between the seller of the goods and a financial firm, called the factor, whereby the latter purchases the receivables from the former and also administers the receivables of the former.
Factoring is an ongoing arrangement between client and factor, where invoices raised on open account sales of goods and services are regularly assigned to ‘the Factor’ for financing, collection and sales ledger administration.
Factoring is a financing technique in which a business sells invoiced receivables at a discount to a bank or a financing house or to an internal finance company. The factor may or may not accept the incumbent credit risk. This is a service offered by a factoring company that enables companies to sell their outstanding book debts for cash.
Companies Benefiting from Factoring
Companies that typically benefit from factoring include those that rapidly grow, seasonal, in start up mode, under capitalized, those that have a lengthy manufacturing cycle, those strained by slow turnovers of
How it works
The factor fully manages your sales ledger and provides you with credit control and collection services of all your outstanding debts. The invoices you issue upon a sale are sent to the factor that typically advances upto 80% to 90% of the invoice amount to you. The balance, less charge, is paid when the customer makes payment directly to the factor. These services are disclosed to your customer who typically receives a letter from the factor, or attached note to your invoice, containing payment instructions to the factor. Funds are typically released to you with in 24 hours of issuing the invoices.
Cost involvement in factoring
Monetary Costs
The factors are providing advances to their client upto 80% to 90% of the invoice amount within 24 hours of issuing invoices. For this cash advance they are charging interest. The interest charges calculated on the daily usage of funds are typically comparable to normal secured bank overdraft rates.
Service Charges
The charge, which is known as service charge, is expressed as a percentage of sales factored. The service charge, covering sale ledger management, collection services, and bad debts protection can range between 0.60% and 3.0% of turnover.
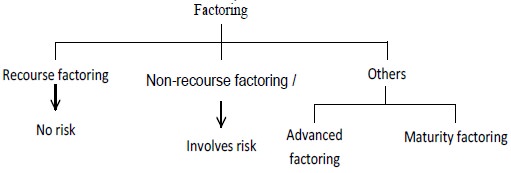
Types of Factoring
Factoring is a financial service provided by a factor firm to the client seller. The type of factoring depends upon the terms and conditions on which the services are provided, it is classified as follows:

1. Recourse Factoring
This refers to those situations where factor firms assume only the work of collection of the receivables. They do not take any responsibility of bad debts i.e. any loss due to delay or default by the receivables is borne by the selling firms. In case the factor firm has already given advance to the selling firm against the receivable, then the seller firm should reduce the advance to the factor firm in case of default by the customer.
2. Non-Recourse Factoring
It is also known as full factoring. Non-recourse factoring protects against customers who fail to pay. The basic feature of non-recourse factoring is that the risk of default is born by the factor firm and the selling firm in any case receives the sales amount. Thus the factor typically covers this risk by taking out credit insurance. The cost of the credit insurance is passed on to the selling firm and depends on the risk profile of your customer and the amount of your factor is typically between 0.3% and 0.7% of turnover. The coverage limit with the factor is normally 80% - 95% of the factored amount.
3. Other Types of Factoring
Factoring may be advanced factoring or maturity factoring. In the case of advance factoring 80 – 90% of the receivable is paid by the factor to the seller within 24 hours of issue of invoice and the balance less charges payable at the time of collection of receivables. In the case of maturity factoring no advance is payable to the seller, rather the payment is made only after collection from the customers.
Factoring Vs. Invoice Discounting
If, the business has sufficient staff and information system to manage the outstanding invoices efficiently and then the firm may want to consider an invoice discounting rather than factoring. It is identical to factoring except that in the sales ledger management the collection responsibility remains with the firm and the service is undisclosed to the customer.
Factoring and Internet
Many factoring companies provide Internet access to the seller, allowing you to constantly monitor your sales ledger, balances, and
Benefits of Factoring
Better working capital management: Since there is instant cash and 80-90% of issued invoices are prepaid within 24 hours the problem of additional working capital required to match sales growth does not arise at all.
Management of receivables: Sales ledger management and debt collection is done by the factoring company.
Improved growth: Firm borrows based on sales activity so firm can automatically set up to finance the growth of the company.
Flexibility with financing: Factoring reveals and often replaces the traditional bank overdraft. In addition to all the credit management services, a factoring facility grows with the business and does not need renegotiating every time an increase is required.
Better risk management: In case of non - recourse factoring, the risk of default is born by the factor firm and the selling firm does not assume any risk in connection with collection of money from the customers.
Factoring in India is of recent origin. In order to study the feasibility of factoring services in India the RBI constituted a committee in January 1988. The committee submitted its response in January 1989 and RBI accepted its recommendation with specific guidelines permitting banks to start factoring in India through their subsidiaries.
Factoring in India
Factoring in India is of recent origin. In order to study the feasibility of factoring services in India the RBI constituted a committee in January 1988. The committee submitted its response in January 1989 and RBI accepted its recommendation with specific guidelines permitting banks to start factoring in India through their subsidiaries.
In India, factoring is still not
very common and only a few commercial banks have established factoring
agencies. The first factoring i.e. the SBI commercial and factoring services
Ltd started working in April 1991. This company looks after the business of
Western India. The business of Northern India, Southern India and Eastern India
are being looked after by Punjab national bank, Canara bank and Allahabad bank
respectively. Honkong and Shangai Banking Corporation (HSBC) currently offer
both domestic and international factoring. When such banks are fully in operation, it will be a boon to
specially small and medium sections.
In February 1992, the RBI issued guidelines for the introduction of forfaiting, which refers to factoring of export receivables. It refers to discounting of future trade related receivables under credit, made available by exporters to the customers.
Commercial Papers are debt instruments issued by corporates for raising short-term resources from the money market. These are unsecured debts of corporates. They are issued in the form of promissory notes, redeemable at par to the holder at maturity. Only corporates who get an investment grade rating can issue CPs as per RBI rules. Though CPs are issued by corporates, they could be good investments if proper caution is exercised.
Sometimes, the companies borrow funds for a short-term period; say up to six months, from other companies, which have surplus liquidity for the time being. The ICD are generally unsecured and are arranged by a financier. The ICD are very common and popular in practice, as these are not influenced by the legal hassles. The convenience is the basic virtue of this method of financing. There is no regulation at present in India to regulate these ICD. Moreover, these are not covered by the section 58A of the companies Act, 1956, as the ICD are not for long term.
Forfaiting
In February 1992, the RBI issued guidelines for the introduction of forfaiting, which refers to factoring of export receivables. It refers to discounting of future trade related receivables under credit, made available by exporters to the customers.
b. Commercial Papers (CPs)
Commercial Papers are debt instruments issued by corporates for raising short-term resources from the money market. These are unsecured debts of corporates. They are issued in the form of promissory notes, redeemable at par to the holder at maturity. Only corporates who get an investment grade rating can issue CPs as per RBI rules. Though CPs are issued by corporates, they could be good investments if proper caution is exercised.
c. Inter Corporate Deposits (ICD)
Sometimes, the companies borrow funds for a short-term period; say up to six months, from other companies, which have surplus liquidity for the time being. The ICD are generally unsecured and are arranged by a financier. The ICD are very common and popular in practice, as these are not influenced by the legal hassles. The convenience is the basic virtue of this method of financing. There is no regulation at present in India to regulate these ICD. Moreover, these are not covered by the section 58A of the companies Act, 1956, as the ICD are not for long term.
Tags : Financial Management - WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT
Last 30 days 401 views












