Accounting For Managers - Management Accounting-Marginal Costing
Accepting Foreign Order-Application Of Marginal Costing
Posted On :
Marginal costing technique can also be used to take a decision as to whether to accept a foreign offer or not.
7.
Accepting Foreign Order
Marginal costing technique can also be used to take a decision as to whether to accept a foreign offer or not. The speciality of this situation is that normally foreign order is requiring the manufacturer to supply the product at a price lower than the inland selling price. Here the decision is taken by comparing the marginal cost of the product with the foreign price offered. If the foreign order offers a price higher than the marginal cost then the offer can be accepted subject to availability of sufficient installed production capacity. The following illustration highlights this decision:
Due to industrial depression, a plant is running at present at 50% of the capacity. The following details are available:
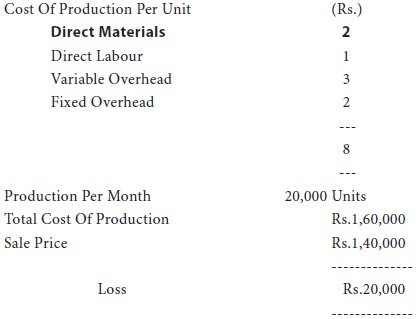
An exporter offers to buy 5000 units per month at the rate of rs.6.50 per unit and the company is hesitant to accept the order for fear of increasing its already large operating losses. Advise whether the company should accept or decline this offer.
Solution:
At present the selling price per unit is Rs.7/- and the marginal cost per unit is Rs.6/- (Material Rs.2 + Labour Re.1 + Variable Overhead Rs.3). The foreign order offers a price of Rs.6.50 and there is ample production capacity (50%) available. Since the foreign offer is at a price higher than marginal cost the offer can be accepted. This is proved hereunder:

Marginal costing technique can also be used to take a decision as to whether to accept a foreign offer or not. The speciality of this situation is that normally foreign order is requiring the manufacturer to supply the product at a price lower than the inland selling price. Here the decision is taken by comparing the marginal cost of the product with the foreign price offered. If the foreign order offers a price higher than the marginal cost then the offer can be accepted subject to availability of sufficient installed production capacity. The following illustration highlights this decision:
Illustration 15:
Due to industrial depression, a plant is running at present at 50% of the capacity. The following details are available:

An exporter offers to buy 5000 units per month at the rate of rs.6.50 per unit and the company is hesitant to accept the order for fear of increasing its already large operating losses. Advise whether the company should accept or decline this offer.
Solution:
At present the selling price per unit is Rs.7/- and the marginal cost per unit is Rs.6/- (Material Rs.2 + Labour Re.1 + Variable Overhead Rs.3). The foreign order offers a price of Rs.6.50 and there is ample production capacity (50%) available. Since the foreign offer is at a price higher than marginal cost the offer can be accepted. This is proved hereunder:

Thus by accepting the foreign order the present loss of Rs.20,000 would
be reduced to Rs.17,500 I.E., Rs.20000 Loss – Rs.2,500 Profit.
Tags : Accounting For Managers - Management Accounting-Marginal Costing
Last 30 days 1711 views












