Management Concepts & Organisational Behaviour - Communication
The Communication Process
Posted On :
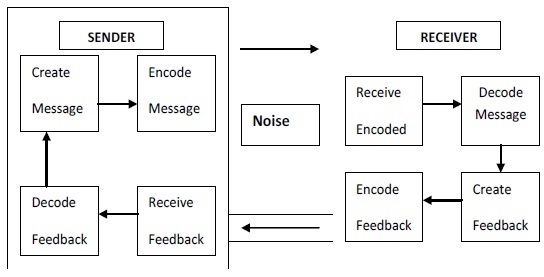
Communication process contains the following elements:
The Communication Process
Communication process contains the following elements:
Communication commences with the communicator. He is the sender of the message. He realizes the need for conveying something to someone else. A communicator or the sender is the source of
Encoding means putting message into code. A message is initiated by encoding a thought. The communicator encodes the information to be transmitted. It is done by translating into a series of symbols or gestures. Encoding is essential because information can be conveyed only through representations or symbols. The sender of the message should establish mutuality of meaning with the receiver. Coded messages may be oral or written words or gestures.
A message is the output of encoding process. It is the physical form of the encoded message. The message may be in any form- oral, written or gesture. But it must be unambiguously understood by the receiver. Speech may be heard. Written words may be read. Gestures may be seen or felt. Message must be clear and precise.
The communicator can communicate the message through a medium. The medium is the carrier of communication. The communication channel is the mode of transmission. Air is the medium for oral message. The medium is inseparable from the message. It links the sender with the receiver. The message may be conveyed through a memorandum, letter, telegram, the telephone, a computer or T.V., but the channel or the medium must be appropriate for the message. At times, multiple media are used for effective communication. A telephone talk may be confirmed by a letter later. Since the choices of channels are many, proper choice of the channel is vital for effective communication.
Decoding refers to the finding of the meaning of something conveyed in code. It is the process by which the receiver interprets the message. It
Communication requires atleast a couple of people, the sender and the receiver. One “encodes” and the other “decodes” the message. It will be complete only when the receiver perceives the message intact. The receiver must decode the message without distortion. If the message does not reach a receiver, communication cannot be said to have taken place.
Feedback refers to the reaction of the receiver. It is a reversal of the communication process. Feedback enables the communicator to know whether his message is received and interpreted correctly or not. Further, Feedback enables the communicator to know the reaction of the receiver so that future communication can be modified, if necessary. The importance of Feedback is incalculable. It helps to check the effectiveness of communication. It makes communication a two-way process.
“Noise” is the enemy of Feedback. It refers to any factor that interferes with communication. Interference may occur in all the above stages of the communication process. It hinders or blocks communication.
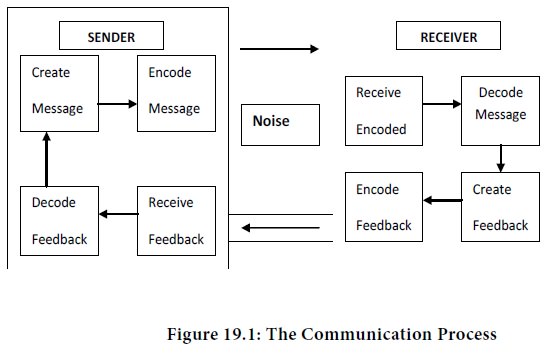
Communication process contains the following elements:

1.The Communicator
Communication commences with the communicator. He is the sender of the message. He realizes the need for conveying something to someone else. A communicator or the sender is the source of
2.Encoding
Encoding means putting message into code. A message is initiated by encoding a thought. The communicator encodes the information to be transmitted. It is done by translating into a series of symbols or gestures. Encoding is essential because information can be conveyed only through representations or symbols. The sender of the message should establish mutuality of meaning with the receiver. Coded messages may be oral or written words or gestures.
3.The message
A message is the output of encoding process. It is the physical form of the encoded message. The message may be in any form- oral, written or gesture. But it must be unambiguously understood by the receiver. Speech may be heard. Written words may be read. Gestures may be seen or felt. Message must be clear and precise.
4.The Medium
The communicator can communicate the message through a medium. The medium is the carrier of communication. The communication channel is the mode of transmission. Air is the medium for oral message. The medium is inseparable from the message. It links the sender with the receiver. The message may be conveyed through a memorandum, letter, telegram, the telephone, a computer or T.V., but the channel or the medium must be appropriate for the message. At times, multiple media are used for effective communication. A telephone talk may be confirmed by a letter later. Since the choices of channels are many, proper choice of the channel is vital for effective communication.
5.Decoding
Decoding refers to the finding of the meaning of something conveyed in code. It is the process by which the receiver interprets the message. It
6.The Receiver
Communication requires atleast a couple of people, the sender and the receiver. One “encodes” and the other “decodes” the message. It will be complete only when the receiver perceives the message intact. The receiver must decode the message without distortion. If the message does not reach a receiver, communication cannot be said to have taken place.
7.Feed Back
Feedback refers to the reaction of the receiver. It is a reversal of the communication process. Feedback enables the communicator to know whether his message is received and interpreted correctly or not. Further, Feedback enables the communicator to know the reaction of the receiver so that future communication can be modified, if necessary. The importance of Feedback is incalculable. It helps to check the effectiveness of communication. It makes communication a two-way process.
8.Noise
“Noise” is the enemy of Feedback. It refers to any factor that interferes with communication. Interference may occur in all the above stages of the communication process. It hinders or blocks communication.
Tags : Management Concepts & Organisational Behaviour - Communication
Last 30 days 2193 views