Home | ARTS | Strategic Management
|
Strategy Management outcomes - Strategic Business Unit and Functional Level Strategies
Strategic Management - Concept Of Corporate Strategy
Strategy Management outcomes - Strategic Business Unit and Functional Level Strategies
Posted On :
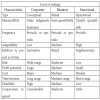
Strategy formulation and strategy implementation when depicted on a matrix form suggests four probable outcomes of the four combinations of variables: Success, roulette, trouble and failure.
Strategy Management outcomes
Strategy formulation and strategy implementation when depicted on a matrix form suggests four probable outcomes of the four combinations of variables: Success, roulette, trouble and failure.

Success is the most likely outcome when an
organization has a good strategy and implements it well. In this case, all that
can be done to ensure success has been done. Environmental factors outside the
company’s control such as competitive reactions or customer changes may still
make a strategy unsuccessful. However, organizational objectives have the best
chance of being achieved in this cell.
Roulette involves situations wherein a poorly formulated strategy is implemented well. Two basic outcomes may ensue. The good execution may overcome the poor strategy or at least give management an early warning of impending failure. Perhaps the field sales force recognizes a problem in the strategy and changes its selling approach to a more successful one. Alternatively, the same good execution can hasten the failure of the poor strategy. Thus, it is impossible to predict exactly what will happen to strategies in the roulette cell, and that’s where it gets its name.
The trouble cell is characterized by situations wherein a well-formulated strategy is poorly implemented. Because managers are more accustomed to focusing on strategy formulation, the real problem with the strategy – faulty implementation-is often not diagnosed. When
Failure is the most likely to occur when a poorly formulated strategy is poorly implemented. In these situations, management has great difficulty getting back on the right track. If the same strategy is retained and implemented in a different way, it is still likely to fail. If the strategy is reformulated and implemented the same way, failure remains the probable result. Strategic problems in this cell of the matrix are very difficult to diagnose and remedy. The analysis of the matrix makes two things clear.
1. First, strategy implementation is at least as important as strategy formulation.
2. Second, the quality of a formulated strategy is
difficult to assess in the absence of effective implementation.
Strategy formulation and strategy implementation when depicted on a matrix form suggests four probable outcomes of the four combinations of variables: Success, roulette, trouble and failure.

Roulette involves situations wherein a poorly formulated strategy is implemented well. Two basic outcomes may ensue. The good execution may overcome the poor strategy or at least give management an early warning of impending failure. Perhaps the field sales force recognizes a problem in the strategy and changes its selling approach to a more successful one. Alternatively, the same good execution can hasten the failure of the poor strategy. Thus, it is impossible to predict exactly what will happen to strategies in the roulette cell, and that’s where it gets its name.
The trouble cell is characterized by situations wherein a well-formulated strategy is poorly implemented. Because managers are more accustomed to focusing on strategy formulation, the real problem with the strategy – faulty implementation-is often not diagnosed. When
Failure is the most likely to occur when a poorly formulated strategy is poorly implemented. In these situations, management has great difficulty getting back on the right track. If the same strategy is retained and implemented in a different way, it is still likely to fail. If the strategy is reformulated and implemented the same way, failure remains the probable result. Strategic problems in this cell of the matrix are very difficult to diagnose and remedy. The analysis of the matrix makes two things clear.
1. First, strategy implementation is at least as important as strategy formulation.
Tags : Strategic Management - Concept Of Corporate Strategy
Last 30 days 972 views