Strategic Management - Concept Of Corporate Strategy
Objectives - Mission and Objectives
Posted On :
An organization’s mission gives a framework or direction to a firm.
Objectives
An organization’s mission gives a framework or direction to a firm. The next step in planning is focusing on estab-lishing progressively more specific organizational direction by setting objectives. An organizational objective is a target toward which the organization directs its efforts. Objectives in organizations, as shown in Figure 3.3 exhibit a hierarchy.
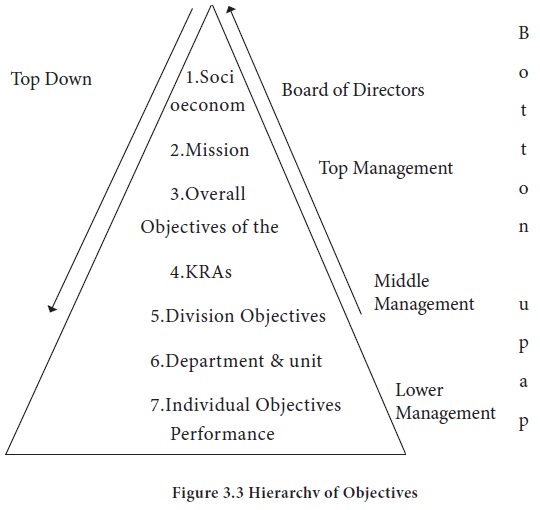
The BOD are more concerned with mission, purpose
and overall objectives. Middle managers are involved in key result areas(KRAs),
division and department objectives. At the lower level, group personal
Managers should develop organizational objectives that are
1. Specific
2. Require a desirable level of effort
3. Flexible
4. Measurable and operational
5. Consistent in the long and short run
Peter Drucker, perhaps the most influential business writer of modern times, has pointed out that it is a mistake to manage organizations by focusing primarily on one and only one objective. According to Drucker, organizations should aim at achieving several objectives instead of just one. Enough objectives should be set so that all areas important to the operation of the firm are covered. Eight key areas in which organizational objectives should normally be set are:
Market standing: The position of an organization – where it stands – relative to its competitors
Innovation: Any change made to improve methods of conducting organizational business.
Productivity: The level of goods or services produced by an organization relative to the resources used in the production process. Organizations that use fewer resources to produce a specified level of products are said to be more ‘productive than organizations that require more resources to produce at the same level.
Resource levels: the relative amounts of various resources held by an organization, such as inventory, equipment, and cash. Most organizations should set objectives indicating the relative amount of each of these assets that should be held.
Profitability: The ability of an organization to earn revenue dollars beyond the expenses necessary to generate the revenue. Organizations commonly have objectives indicating the level of profitability they seek.
Manager performance and development: The quality of managerial performance and the rate at which managers are developing personally. Because both of these areas are critical to the long-term success of an organization, emphasizing them by establishing and striving to reach related organizational objectives is very important.
Worker performance and attitude: The quality of non-management performance and such employee’s feelings about their work. These areas are also crucial to long-term organizational success. The importance of these considerations should be stressed through the establishment of organizational objectives.
Social responsibility: The obligation of business to help improve the welfare of society while it strives to reach organizational objectives.
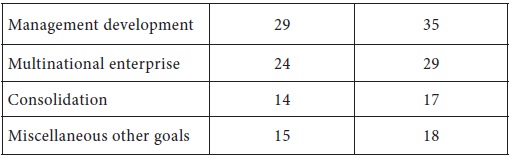
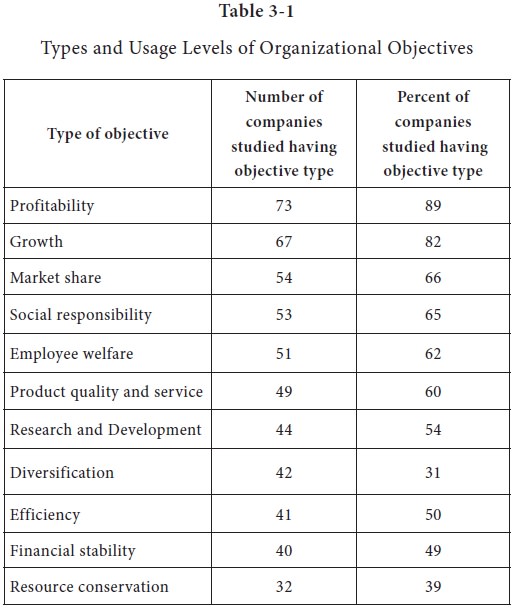
Table 3.1 shows the usage of the different objectives by various companies.
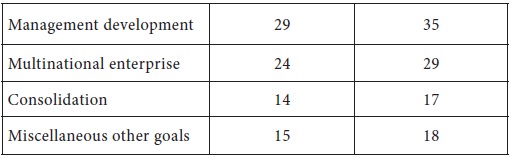
*Adds to more than 100 percent because most companies have more than one goal
Source : Y.K. Shetty, New Look at Corporate Goals,” California Manage-ment Review, 22 , No.2 (Winter 1979).
An organization’s mission gives a framework or direction to a firm. The next step in planning is focusing on estab-lishing progressively more specific organizational direction by setting objectives. An organizational objective is a target toward which the organization directs its efforts. Objectives in organizations, as shown in Figure 3.3 exhibit a hierarchy.

Managers should develop organizational objectives that are
1. Specific
2. Require a desirable level of effort
3. Flexible
4. Measurable and operational
5. Consistent in the long and short run
Market standing: The position of an organization – where it stands – relative to its competitors
Innovation: Any change made to improve methods of conducting organizational business.
Productivity: The level of goods or services produced by an organization relative to the resources used in the production process. Organizations that use fewer resources to produce a specified level of products are said to be more ‘productive than organizations that require more resources to produce at the same level.
Resource levels: the relative amounts of various resources held by an organization, such as inventory, equipment, and cash. Most organizations should set objectives indicating the relative amount of each of these assets that should be held.
Profitability: The ability of an organization to earn revenue dollars beyond the expenses necessary to generate the revenue. Organizations commonly have objectives indicating the level of profitability they seek.
Manager performance and development: The quality of managerial performance and the rate at which managers are developing personally. Because both of these areas are critical to the long-term success of an organization, emphasizing them by establishing and striving to reach related organizational objectives is very important.
Worker performance and attitude: The quality of non-management performance and such employee’s feelings about their work. These areas are also crucial to long-term organizational success. The importance of these considerations should be stressed through the establishment of organizational objectives.
Social responsibility: The obligation of business to help improve the welfare of society while it strives to reach organizational objectives.
Table 3.1 shows the usage of the different objectives by various companies.


*Adds to more than 100 percent because most companies have more than one goal
Source : Y.K. Shetty, New Look at Corporate Goals,” California Manage-ment Review, 22 , No.2 (Winter 1979).
Tags : Strategic Management - Concept Of Corporate Strategy
Last 30 days 845 views













