Home | ARTS | Strategic Management
|
Types of Organization Structures - Strategic Business Unit and Functional Level Strategies
Strategic Management - Concept Of Corporate Strategy
Types of Organization Structures - Strategic Business Unit and Functional Level Strategies
Posted On :
Two basic kinds of organizational structures exist-Formal and informal.
Types of Organization Structures
Two basic kinds of organizational structures exist-Formal and informal. There is the formal organizational structure which represents the relationships between resources as designed by management. The formal organizational structure is conveyed in the organization chart. Then there is the informal organizational structure, which represents the social relationships based on friendships or interests shared among various members of an organization. The informal organizational structure is evidenced in the patterns of communication commonly called the “grapevine.” The informal network can be used to encourage rapid execution of strategies.
In formal organization structure there is the question of what management levels and personnel with the organization will be responsible for various implementation tasks. The five types of organizational structures that are commonly seen are the simple, functional, divisional, strategic business unit (SBU), and matrix structures. A schematic diagram of each of these structures is shown in Figure 4-1
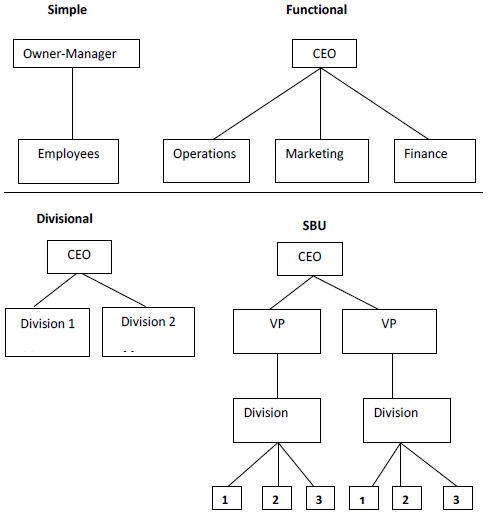
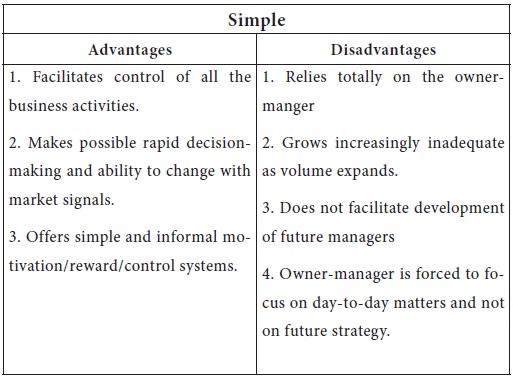
A simple organizational structure has only two
levels, the owner-manager and the employees. Small firms with one product or
only a few related ones usually exhibit this structure.
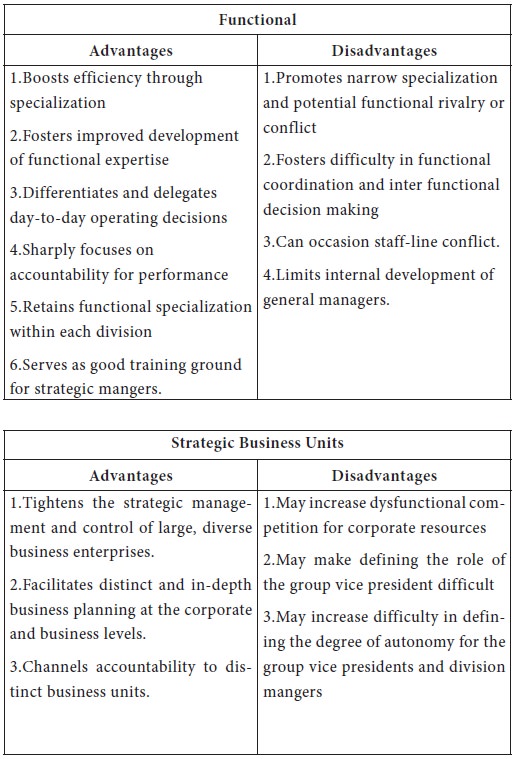
As organizations grow and develop a number of related products and markets, their structures frequently change to reflect greater special-ization in functional business areas. Such line functions as production and operations, marketing and research and development (R&D) may be organized in departments.
As firms acquire or develop new products in different industries and markets, they may evolve a divisional organizational structure. Each division may operate autonomously under the direction of a division manager, who reports directly to the CEO. Divisions may be formed on the basis of product lines (automotive, aircraft), markets (customer, in-dustrial buyers), geographic areas (north, south, international), or chan-nels of distribution (retail store, catalog sales). Each division not only has its own line and staff functions to mange but also formulates and implements strategies on its own with the approval of the CEO.
When a divisional structure becomes unwieldy because a CEO has too many divisions to manage effectively, organizations may reor-ganize in the form of strategic business units (SBUs) or strategic groups. This structure groups a number of divisions together on the basis of such things as the similarity of product lines or markets. Vice presidents are appointed to oversee the operations of the newly formed strategic busi-ness units, and these executives report directly to the CEO.
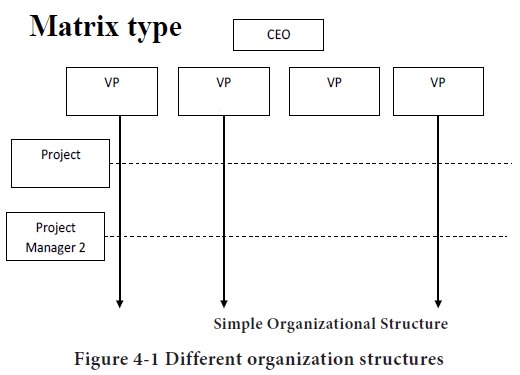
A matrix organizational structure is used to facilitate the develop-ment and execution of various programs or projects. Each of the depart-ment vice presidents listed at the top has functional responsibility for all the projects, whereas each of the project managers listed down the side has project responsibility for completing and implementing the strategy. This approach allows project mangers to cut across departmental lines and can promote efficient implementation of strategies.
Two basic kinds of organizational structures exist-Formal and informal. There is the formal organizational structure which represents the relationships between resources as designed by management. The formal organizational structure is conveyed in the organization chart. Then there is the informal organizational structure, which represents the social relationships based on friendships or interests shared among various members of an organization. The informal organizational structure is evidenced in the patterns of communication commonly called the “grapevine.” The informal network can be used to encourage rapid execution of strategies.
In formal organization structure there is the question of what management levels and personnel with the organization will be responsible for various implementation tasks. The five types of organizational structures that are commonly seen are the simple, functional, divisional, strategic business unit (SBU), and matrix structures. A schematic diagram of each of these structures is shown in Figure 4-1


Functional Organizational Structure
As organizations grow and develop a number of related products and markets, their structures frequently change to reflect greater special-ization in functional business areas. Such line functions as production and operations, marketing and research and development (R&D) may be organized in departments.
Divisional Organizational Structure
As firms acquire or develop new products in different industries and markets, they may evolve a divisional organizational structure. Each division may operate autonomously under the direction of a division manager, who reports directly to the CEO. Divisions may be formed on the basis of product lines (automotive, aircraft), markets (customer, in-dustrial buyers), geographic areas (north, south, international), or chan-nels of distribution (retail store, catalog sales). Each division not only has its own line and staff functions to mange but also formulates and implements strategies on its own with the approval of the CEO.
Strategic Business Unit Structure
When a divisional structure becomes unwieldy because a CEO has too many divisions to manage effectively, organizations may reor-ganize in the form of strategic business units (SBUs) or strategic groups. This structure groups a number of divisions together on the basis of such things as the similarity of product lines or markets. Vice presidents are appointed to oversee the operations of the newly formed strategic busi-ness units, and these executives report directly to the CEO.
Matrix Organizational Structure
A matrix organizational structure is used to facilitate the develop-ment and execution of various programs or projects. Each of the depart-ment vice presidents listed at the top has functional responsibility for all the projects, whereas each of the project managers listed down the side has project responsibility for completing and implementing the strategy. This approach allows project mangers to cut across departmental lines and can promote efficient implementation of strategies.
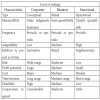
The advantages and disadvantages of the different structures are presented below.
Tags : Strategic Management - Concept Of Corporate Strategy
Last 30 days 3859 views