MARKETING MANAGEMENT - Concept Of A Product
Product Classification - Concept Of A Product
Posted On :
The nature of product is found to have considerable impact on the method of product positing.
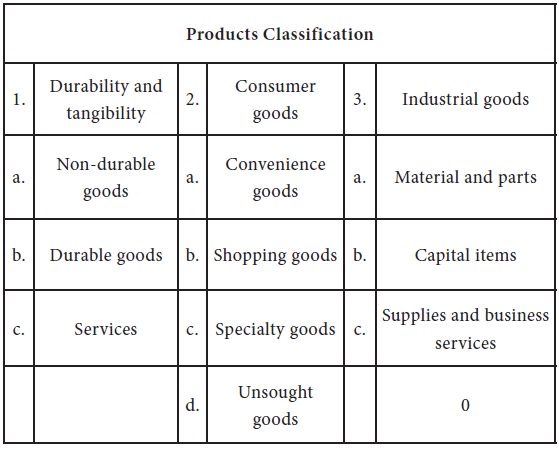
Product Classification
The nature of product is found to have considerable impact on the method of product positing. There are two classes of products consumer goods, and industrial goods, and this classification is useful in product positioning. The table given below shows the categories of consumer and industrial goods. Marketers have traditionally classified products on the basis of there characteristics: durability, tangibility and use. The following figure shows the products classification:
Tangible / Intangible Attributes – key points
Tangible
i. Touch
ii. See
iii. Taste
iv. Smell
Intangible
i. Can’t see
ii. Can’t touch
iii. Can’t smell
iv. Can’t taste
(a)Non – durable goods: Non-durable goods are tangible goods normally consumed in one or a few uses. For example, soap, salt and biscuits.
(b) Durable goods: Durable goods are those which can be used over a period of time. Examples are: Colour TV, Refrigerator, washing machine and Vacuum cleaners.
(c) Services: services rate intangible, inseparable, variable and perishable products, Airlines and Railways offer travel services. Post and telegraph offer communication services. Hospital and diagnostic centers offer medical services.
Exercise: Think of examples of product/services possessing above tangible and intangible attributes
These are goods that the customer usually purchases frequently immediately and with a minimum of efforts, example includes soaps and newspapers.
Convenience goods can be further classification into three categories:
1. Staple goods: consumer purchase on regular basis. Rice,wheat, oils etc.
2. Impulse goods: consumer purchase without any planning or search efforts. Chocolates, soft drinks, biscuits, toys, magazines, etc.
The nature of product is found to have considerable impact on the method of product positing. There are two classes of products consumer goods, and industrial goods, and this classification is useful in product positioning. The table given below shows the categories of consumer and industrial goods. Marketers have traditionally classified products on the basis of there characteristics: durability, tangibility and use. The following figure shows the products classification:

Tangible / Intangible Attributes – key points
Tangible
i. Touch
ii. See
iii. Taste
iv. Smell
Intangible
i. Can’t see
ii. Can’t touch
iii. Can’t smell
iv. Can’t taste
Durability And Tangibility
(a)Non – durable goods: Non-durable goods are tangible goods normally consumed in one or a few uses. For example, soap, salt and biscuits.
(b) Durable goods: Durable goods are those which can be used over a period of time. Examples are: Colour TV, Refrigerator, washing machine and Vacuum cleaners.
(c) Services: services rate intangible, inseparable, variable and perishable products, Airlines and Railways offer travel services. Post and telegraph offer communication services. Hospital and diagnostic centers offer medical services.
Exercise: Think of examples of product/services possessing above tangible and intangible attributes
Consumer Goods Classification
a. Convenience Goods:
These are goods that the customer usually purchases frequently immediately and with a minimum of efforts, example includes soaps and newspapers.
Convenience goods can be further classification into three categories:
1. Staple goods: consumer purchase on regular basis. Rice,wheat, oils etc.
2. Impulse goods: consumer purchase without any planning or search efforts. Chocolates, soft drinks, biscuits, toys, magazines, etc.
3. Emergency goods: consumer purchase on urgent need.
Certain drugs, ambulance services, tatkal reservation of rail tickets, come under this category.
These are goods that the customer, in the process of selection and purchase characteristically compare on such bases as suitability and quality. Example: furniture, kitchen equipment, electrical appliances, clothing, etc.
These are goods with unique characteristic or brand identification for which a sufficient number of buyers are willing to make a special purchasing effort. For example apartments, cars, jewellery, greeting cards, gift articles etc.
These are goods the consumer does not know about or does not normally think of buying. The classic example of known but unsought goods is life insurance and ambulance services.
These are goods that enter the manufacturer’s product completely. They fall into two classes. Raw material and manufactured material parts. Iron,zinc, sulphur, jute, fruits, wheat, nuts, bolts, transistors, chips, etc.
These are long lasting goods that facilitate developing or managing the finished products. They include two groups: installation and equipments. Blast furnaces, lathe machines, computers, fax machines, etc.
These are short-listing goods and services that facilitate developing or managing the finished products. Lubricating oils, cotton, brushes, stationery items, etc.
Certain drugs, ambulance services, tatkal reservation of rail tickets, come under this category.
b. Shopping Goods
These are goods that the customer, in the process of selection and purchase characteristically compare on such bases as suitability and quality. Example: furniture, kitchen equipment, electrical appliances, clothing, etc.
c. Specialty goods
These are goods with unique characteristic or brand identification for which a sufficient number of buyers are willing to make a special purchasing effort. For example apartments, cars, jewellery, greeting cards, gift articles etc.
d. Unsought goods
These are goods the consumer does not know about or does not normally think of buying. The classic example of known but unsought goods is life insurance and ambulance services.
Industrial Goods Classification
a. Material and Parts
These are goods that enter the manufacturer’s product completely. They fall into two classes. Raw material and manufactured material parts. Iron,zinc, sulphur, jute, fruits, wheat, nuts, bolts, transistors, chips, etc.
b. Capital Items
These are long lasting goods that facilitate developing or managing the finished products. They include two groups: installation and equipments. Blast furnaces, lathe machines, computers, fax machines, etc.
C. Supplies and Business Services
These are short-listing goods and services that facilitate developing or managing the finished products. Lubricating oils, cotton, brushes, stationery items, etc.
Tags : MARKETING MANAGEMENT - Concept Of A Product
Last 30 days 3950 views












