Home | ARTS | Strategic Management
|
Information Systems Strategies - Logistics And Information Strategies
Strategic Management - Functional Strategy
Information Systems Strategies - Logistics And Information Strategies
Posted On :
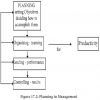
A management information system is complex and therefore needs an overall plan to guide its initial development and subsequent change.
Information
Systems Strategies
A management information system is complex and therefore needs an overall plan to guide its initial development and subsequent change. The plan will be referred to as an information systems plan, master development plan or information resources plan. The need for planning is obvious as companies that plan tend to achieve better results than companies that do not plan.
Contents of Information system plan
What does an MIS plan contain?
The master plan typically has two components-a long range plan for three to five years or longer, and a short range plan for one year. The long range plan provides general guidelines for direction and the short range portion provides a basis for specific accountability as to operational and financial performance.
The master development plan contains four major sections:
1. Information system goals, objectives and architecture.
2. Inventory of current capabilities
3. forecast of developments affecting the plan
4. The specific plan.
A very important fundamental concept of information system planning is that the corporate strategic plan should be the basis for the MIS strategic plan. Alignment of MIS strategy with organizational strategy is one of the central problems of MIS planning. That is why MIS plan is referred to as derivative of corporate plan.
The goals section as such might contain descriptions of the following:
1. Organizational goals, objectives and strategies
2. External environment (industry, government regulation, customers and suppliers)
3. Internal organizational constraints such as management philosophy
4. Assumptions about business risks and potential consequences
5. Overall goals, objectives and strategy for the information system
6. Architecture of the information system (categories of information or applications)
This is a summary of the current status of an information system. It includes the following.
1. Inventory of hardware, general purpose soft were, applications
2. Analysis of expense, hardware utilization, software utilization, personnel utilization
3. Status of projects in process
4. Assessment of strengths and weaknesses.
Planning is affected by current and anticipated technology. Broad technological changes can be perceived several years before they become generally available. The impact of such developments as personal computers, local area net works, data base management systems and office automation should be reflected in the long range plan.
The plan should include:
1) Hard ware acquisition schedule
2) Purchased soft ware schedule
• Systems
• Applicationss
3) Application development schedule
4) Soft ware maintenance and conversion schedule
5) Personnel resources required and schedule of hiring and training
6) Financial resources required
By object of expenditure (hardware, software, personnel)
By purpose of expenditure (operations, maintenance and development)
How is MIS planning made?
Bowman, Davis and Wetherbe developed a three-stage model of information system planning process. It is as given below:
1. Strategic Planning Stage
In this stage, objectives, goals and strategies of information system will be defined in such a way that they align with the organizations objectives, goals and strategies.
a. Derivation of information systems strategy from organizational planning.
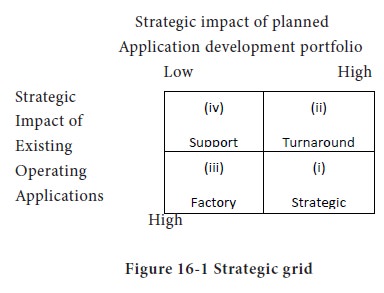
For example, if the organization’s objective is to implement quality circles the objective of MIS is to provide data base on quality control and provide access to quality circles in the required form. Strategic grid is a useful tool in this regard.
The grid is a diagnostic tool to understand the role of MIS in an organization. The position in the grid explains the needed level of top management involvement and the relationship of the MIS plan and organizational plan (i) & (ii) Integration of corporate Planning &MIS planning(iii) Guidance from corporate plan for alignment; Detailed operational and capacity planning by MIS function.(iv) No guidance from corporate plan
b)
Strategic fit with organization culture
MIS should fit with culture of organization which reinforces values, norms and beliefs about the organization. If the culture is not clear to information system planners, clues can be obtained from the following sources
• Stories --- particular stories or incidents popular with organization
• Meetings --- Items in agenda considered important by managers
• Top management behavior --- the concern shown by top management shall be concern through out the organization
• Physical layout --- the location of activities and relative positions and size of facilities, offices etc
• Rituals --- Banquets, parties, orientations—reflect values
• Documents --- What is written by Whom and to whom can help understand ends and means of an organization.
These clues can be organized into “rules of the game” and classified into organizational tasks and relationships.
c) Strategy Set transformation
It is used to produce objectives, goals and strategy for MIS by the following steps
3. Resource allocation
The last stage is the resource allocation to determine which application shall be implemented and in what order. Since information system resource are limited not all projects can be done at once. Each project is to be analyzed in terms of the following factors.
i. Expected Profit improvements or cost savings -quantitative and qualitative.
ii. Need basis –need of the system to have the development proceed in an orderly fashion
iii. System management factors---priority projects.
Four approaches are generally used in resource allocation
A management information system is complex and therefore needs an overall plan to guide its initial development and subsequent change. The plan will be referred to as an information systems plan, master development plan or information resources plan. The need for planning is obvious as companies that plan tend to achieve better results than companies that do not plan.
Contents of Information system plan
What does an MIS plan contain?
The master plan typically has two components-a long range plan for three to five years or longer, and a short range plan for one year. The long range plan provides general guidelines for direction and the short range portion provides a basis for specific accountability as to operational and financial performance.
The master development plan contains four major sections:
1. Information system goals, objectives and architecture.
2. Inventory of current capabilities
3. forecast of developments affecting the plan
4. The specific plan.
Goals
A very important fundamental concept of information system planning is that the corporate strategic plan should be the basis for the MIS strategic plan. Alignment of MIS strategy with organizational strategy is one of the central problems of MIS planning. That is why MIS plan is referred to as derivative of corporate plan.
The goals section as such might contain descriptions of the following:
1. Organizational goals, objectives and strategies
2. External environment (industry, government regulation, customers and suppliers)
3. Internal organizational constraints such as management philosophy
4. Assumptions about business risks and potential consequences
5. Overall goals, objectives and strategy for the information system
6. Architecture of the information system (categories of information or applications)
Current Capabilities
This is a summary of the current status of an information system. It includes the following.
1. Inventory of hardware, general purpose soft were, applications
2. Analysis of expense, hardware utilization, software utilization, personnel utilization
3. Status of projects in process
4. Assessment of strengths and weaknesses.
Forecasts
Planning is affected by current and anticipated technology. Broad technological changes can be perceived several years before they become generally available. The impact of such developments as personal computers, local area net works, data base management systems and office automation should be reflected in the long range plan.
The specific plan
The plan should include:
1) Hard ware acquisition schedule
2) Purchased soft ware schedule
• Systems
• Applicationss
3) Application development schedule
4) Soft ware maintenance and conversion schedule
5) Personnel resources required and schedule of hiring and training
6) Financial resources required
By object of expenditure (hardware, software, personnel)
By purpose of expenditure (operations, maintenance and development)
MIS Planning process
How is MIS planning made?
Bowman, Davis and Wetherbe developed a three-stage model of information system planning process. It is as given below:

1. Strategic Planning Stage
In this stage, objectives, goals and strategies of information system will be defined in such a way that they align with the organizations objectives, goals and strategies.
a. Derivation of information systems strategy from organizational planning.
For example, if the organization’s objective is to implement quality circles the objective of MIS is to provide data base on quality control and provide access to quality circles in the required form. Strategic grid is a useful tool in this regard.
The grid is a diagnostic tool to understand the role of MIS in an organization. The position in the grid explains the needed level of top management involvement and the relationship of the MIS plan and organizational plan (i) & (ii) Integration of corporate Planning &MIS planning(iii) Guidance from corporate plan for alignment; Detailed operational and capacity planning by MIS function.(iv) No guidance from corporate plan

MIS should fit with culture of organization which reinforces values, norms and beliefs about the organization. If the culture is not clear to information system planners, clues can be obtained from the following sources
• Stories --- particular stories or incidents popular with organization
• Meetings --- Items in agenda considered important by managers
• Top management behavior --- the concern shown by top management shall be concern through out the organization
• Physical layout --- the location of activities and relative positions and size of facilities, offices etc
• Rituals --- Banquets, parties, orientations—reflect values
• Documents --- What is written by Whom and to whom can help understand ends and means of an organization.
These clues can be organized into “rules of the game” and classified into organizational tasks and relationships.
c) Strategy Set transformation
It is used to produce objectives, goals and strategy for MIS by the following steps
i. Explicate
the organizations strategy set
• Identify the stake holders and their goals and identify organizational goals and strategies of organization for each group
• Validate the organizational goals & strategies by asking management.
ii. Transform the organization strategy set into MIS objectives in the light of identified constraints and formulating MIS strategies.
2. Organizational Information Requirements
Information requirements are essential organization wide level for information system planning, identifying applications and planning Information architecture. There are four strategies for determining information requirements.
1. Asking
Closed questions; open questions, Brain storming guided brainstorming and group consensus.
2. Deriving from an existing information system
• Identify the stake holders and their goals and identify organizational goals and strategies of organization for each group
• Validate the organizational goals & strategies by asking management.
ii. Transform the organization strategy set into MIS objectives in the light of identified constraints and formulating MIS strategies.
2. Organizational Information Requirements
Information requirements are essential organization wide level for information system planning, identifying applications and planning Information architecture. There are four strategies for determining information requirements.
1. Asking
Closed questions; open questions, Brain storming guided brainstorming and group consensus.
2. Deriving from an existing information system
1. in the
organization
2. in other organization
3. in text books or studies
4. Proprietary system or package
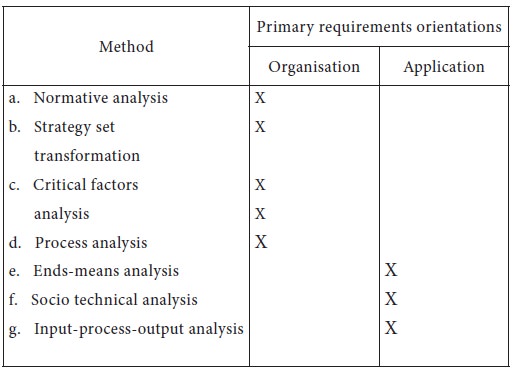
3. Study of utilizing system (object system analysis)
Several methods have been proposed as given below:
2. in other organization
3. in text books or studies
4. Proprietary system or package
3. Study of utilizing system (object system analysis)
Several methods have been proposed as given below:

3. Resource allocation
The last stage is the resource allocation to determine which application shall be implemented and in what order. Since information system resource are limited not all projects can be done at once. Each project is to be analyzed in terms of the following factors.
i. Expected Profit improvements or cost savings -quantitative and qualitative.
ii. Need basis –need of the system to have the development proceed in an orderly fashion
iii. System management factors---priority projects.
Four approaches are generally used in resource allocation
1).
Comparative cost or Benefit
a. ROI- A simple traditional approach to evaluating profitability of investment is return on investment method.
b. Zero based budgeting-It implied budgeting investment from scratch without consideration of previous evaluations.
2). Portfolio approach –Considering a set of investment proposals and evaluating them together to arrive at right combination.
3). Charge out- It is the method of charging the users. Based on utility the proposal is considered.
4). Steering committee ranking-Top level committee that is set up for evaluation and development ranks the proposals.
a. ROI- A simple traditional approach to evaluating profitability of investment is return on investment method.
b. Zero based budgeting-It implied budgeting investment from scratch without consideration of previous evaluations.
2). Portfolio approach –Considering a set of investment proposals and evaluating them together to arrive at right combination.
3). Charge out- It is the method of charging the users. Based on utility the proposal is considered.
4). Steering committee ranking-Top level committee that is set up for evaluation and development ranks the proposals.
Tags : Strategic Management - Functional Strategy
Last 30 days 482 views