Home | ARTS | Strategic Management
|
Marketing Strategies—Competition Based - Finance Marketing, Human Resource, Management Information Systems and logistics
Strategic Management - Functional Strategy
Marketing Strategies—Competition Based - Finance Marketing, Human Resource, Management Information Systems and logistics
Posted On :
Marketers have to evolve strategies to fight competition, to gain and retain market shares. The right tool for analyzing market situation is SWOT analysis.
Marketing Strategies—Competition
Based
Marketers have to evolve strategies to fight competition, to gain and retain market shares. The right tool for analyzing market situation is SWOT analysis. Based on the SWOT analysis competitors can be classified as follows:
1. Based on the ability to engage and sustain warfare—strong and weak
2. Based on the percentage of market share—close and distant held by a competitor
These competitors can, in turn, be assigned following competitive positions.
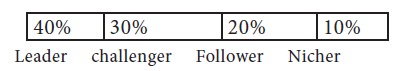
Market shares of the competitive firms are:
What are the moves of the competitors? Are they preemptive or predatory? Are they defensive or offensive? Companies in different competitive positions work different strategies. The possible moves of a leader, challenger, follower and nicher are:
Grow strong—become invincible
Defend—develop protection against attack
Offend—weaken or destroy competitor
Play safe—select less competitive areas and cultivate.
1. Market penetration strategy
Increase use of the product
Find new uses for the product
2. Market development strategy
Convert non-users to users
Find new markets in other places
3. Product development strategies
Create new products/services
Modify existing products
• Continuous innovation and quality platform
1. Position defense - Product—Line complete
2. Flanking defense - Varieties of Variants
3. Preemptive defense - Price reduction through sales promotion
Counter offensive defense - Match with ads and others at tacks
1. Mobile defense - Concentrate in successful markets
Contraction defense - Prune brands
A market challenger may choose to attack
The leader
The followers
The nichers.
By pass attack — Diversifying into unrelated products Diversifying into new geographic markets Leap frogging into new technologies
Frontal attack — Price and promotion aggressiveness
Flank attack — find gaps in product line and set up variety competition Encirclement
attack - Wide range of products with heavy advertising and promotion
Guerilla attack — New product or promotions of short life cycle with marketing blitzkrieg
The options are:
Following closely — imitate immediately
Following at a distance — slow imitation
Following selectively — imitation in select areas
The companies are generally small in size. Some companies in the unorganized sector may follow ‘fakes’ strategy.
The niche is sufficient size in size and purchasing power to be profitable.
The niche has growth potential
The niche is of negligible interest to major competitors
The firm has the required skills and resources to serve the niche effectively
The firm can defend itself against and attacking major competitor through the customer good will it has built up.
Computer companies are among the newest converts to the “end user” type of niche marketing, but they call it vertical marketing. For years, computer fought to sell general hardware and software systems horizontally across many markets, and the price battles got rougher. Smaller companies started to specialize by vertical slices—law firms, medical practices, banks, etc,--studying the specific hardware and software needs of their target group and designing high-value added products that had a competitive advantage over more general products. Their sales forces were trained to understand and service the particular vertical market. Computer companies also worked with independent value-added resellers (VARS), who customized the computer hardware and software for individual clients or customer segments and earned a price premium in the process.
There are many successful companies which proved professional with faster growth due to high power promotion. A good example is reliance group in India. It has built brand loyalty with a different mix of a media.
Reliance has a high budget promotion for all its textile brands. It has specific promotion strategies for suiting, dress materials and saris. “ONLY VIMAL” ‘ONLY’ concept in the promotion made Reliance a super success. Effective media selection and 80% budget for press and after 1978 more focus on TV ads made their promotion No.1. Miss Universe Contest’ ‘Oscar awards nite’ etc were sponsored including the ‘Reliance cup’
Choosing Pull or Push Strategy for sales promotion:
Push strategy – A promotion strategy mainly aimed at channels of distribution is called a push strategy. Marketers promote their products heavily among distributors wholesalers and retailers. Retailer promotes to customers. This includes trade shows, personal selling and contests.
Producer Distributor Wholesaler Retailer Consumer
Pull Strategy – Here promotion is directed towards ultimate consumers. Manufacture tries to stimulate demand and attracts consumers to buy his product.
Manufacturer Consumer
This includes advertising, publicity and sales promotion like discounts, free goods and contests.
Tools of Sales Promotion
The most commonly used sales promotion tools in India are
i. Prize schemes
A prize scheme is designed for both the public and the dealers. Sales competition is arranged, prizes are announced or special offers are made.
ii. Trade Fairs and Exhibitions
These exhibitions attract a lot of people especially from rural areas who find them as a very convenient place to make their purchases of consumer goods. Many state Governments announce relief or concession in sales Tax; for example, a passenger car can be purchased in Gwalior Mela without payment of any sales tax.
Marketers have to evolve strategies to fight competition, to gain and retain market shares. The right tool for analyzing market situation is SWOT analysis. Based on the SWOT analysis competitors can be classified as follows:
1. Based on the ability to engage and sustain warfare—strong and weak
2. Based on the percentage of market share—close and distant held by a competitor
These competitors can, in turn, be assigned following competitive positions.
- Market leader—the firm with largest market share
and strong in designing and implementation plans.
- Market challenger—close and strong competitors to
market leader, who aggressively or mildly challenge him
- Market follower—the distant and weak competitor who
is content in following leaders and challenger.
- Market Nicher—the independent, non-fighter, who
carves his niche for peaceful and profitable specialized operations.
Market shares of the competitive firms are:

What are the moves of the competitors? Are they preemptive or predatory? Are they defensive or offensive? Companies in different competitive positions work different strategies. The possible moves of a leader, challenger, follower and nicher are:
Grow strong—become invincible
Defend—develop protection against attack
Offend—weaken or destroy competitor
Play safe—select less competitive areas and cultivate.
Leader
Expansion strategy
1. Market penetration strategy
Increase use of the product
Find new uses for the product
2. Market development strategy
Convert non-users to users
Find new markets in other places
3. Product development strategies
Create new products/services
Modify existing products
Defending strategy
• Continuous innovation and quality platform
1. Position defense - Product—Line complete
2. Flanking defense - Varieties of Variants
3. Preemptive defense - Price reduction through sales promotion
Counter offensive defense - Match with ads and others at tacks
1. Mobile defense - Concentrate in successful markets
Contraction defense - Prune brands
Market Challenger
A market challenger may choose to attack
The leader
The followers
The nichers.
By pass attack — Diversifying into unrelated products Diversifying into new geographic markets Leap frogging into new technologies
Frontal attack — Price and promotion aggressiveness
Flank attack — find gaps in product line and set up variety competition Encirclement
attack - Wide range of products with heavy advertising and promotion
Guerilla attack — New product or promotions of short life cycle with marketing blitzkrieg
Market follower
The options are:
Following closely — imitate immediately
Following at a distance — slow imitation
Following selectively — imitation in select areas
The companies are generally small in size. Some companies in the unorganized sector may follow ‘fakes’ strategy.
Market—Nicher
The niche is sufficient size in size and purchasing power to be profitable.
The niche has growth potential
The niche is of negligible interest to major competitors
The firm has the required skills and resources to serve the niche effectively
The firm can defend itself against and attacking major competitor through the customer good will it has built up.
Computer companies are among the newest converts to the “end user” type of niche marketing, but they call it vertical marketing. For years, computer fought to sell general hardware and software systems horizontally across many markets, and the price battles got rougher. Smaller companies started to specialize by vertical slices—law firms, medical practices, banks, etc,--studying the specific hardware and software needs of their target group and designing high-value added products that had a competitive advantage over more general products. Their sales forces were trained to understand and service the particular vertical market. Computer companies also worked with independent value-added resellers (VARS), who customized the computer hardware and software for individual clients or customer segments and earned a price premium in the process.
Designing a Promotion Strategy
There are many successful companies which proved professional with faster growth due to high power promotion. A good example is reliance group in India. It has built brand loyalty with a different mix of a media.
Reliance has a high budget promotion for all its textile brands. It has specific promotion strategies for suiting, dress materials and saris. “ONLY VIMAL” ‘ONLY’ concept in the promotion made Reliance a super success. Effective media selection and 80% budget for press and after 1978 more focus on TV ads made their promotion No.1. Miss Universe Contest’ ‘Oscar awards nite’ etc were sponsored including the ‘Reliance cup’
Choosing Pull or Push Strategy for sales promotion:
Push strategy – A promotion strategy mainly aimed at channels of distribution is called a push strategy. Marketers promote their products heavily among distributors wholesalers and retailers. Retailer promotes to customers. This includes trade shows, personal selling and contests.
Producer Distributor Wholesaler Retailer Consumer
Pull Strategy – Here promotion is directed towards ultimate consumers. Manufacture tries to stimulate demand and attracts consumers to buy his product.
This includes advertising, publicity and sales promotion like discounts, free goods and contests.
Tools of Sales Promotion
The most commonly used sales promotion tools in India are
i. Prize schemes
A prize scheme is designed for both the public and the dealers. Sales competition is arranged, prizes are announced or special offers are made.
ii. Trade Fairs and Exhibitions
These exhibitions attract a lot of people especially from rural areas who find them as a very convenient place to make their purchases of consumer goods. Many state Governments announce relief or concession in sales Tax; for example, a passenger car can be purchased in Gwalior Mela without payment of any sales tax.
iii. Free Samples
Free samples are generally used to introduce a new product and as a sales tool to attract the attention of prospects, not only much time is saved, but it also eliminates the need for inspection or testing of goods by the buyer.
iv. Correspondence
Sending letters or brochures. A specialized correspondence section can communicate very effectively with prospects as well as potential customers.
v. Catalogues
Catalogues are largely used when a firm manufactures different types of products which are distinguished by size, shape and other features. The following purpose can be served by catalogues:
To get orders
To make the customers aware about the specifications
To
provide detailed information
To solicit product sales
Free samples are generally used to introduce a new product and as a sales tool to attract the attention of prospects, not only much time is saved, but it also eliminates the need for inspection or testing of goods by the buyer.
iv. Correspondence
Sending letters or brochures. A specialized correspondence section can communicate very effectively with prospects as well as potential customers.
v. Catalogues
Catalogues are largely used when a firm manufactures different types of products which are distinguished by size, shape and other features. The following purpose can be served by catalogues:
To get orders
To make the customers aware about the specifications
To solicit product sales
vi. Advertising Novelties
Small, interesting, or personally useful items, etc., can be used for sales promotion. To be effective an advertising novelty should meet the following requirements:
It should not be a high cost item
The novelty item should be usually eye-catching
The item should be useful.
Small, interesting, or personally useful items, etc., can be used for sales promotion. To be effective an advertising novelty should meet the following requirements:
It should not be a high cost item
The novelty item should be usually eye-catching
The item should be useful.
vii. Entertainment of Customers
Entertainment of customers acts as a primary promotional device. But when the product is sold on a routine basis, customer entertainment is neither necessary nor justified.
Entertainment of customers acts as a primary promotional device. But when the product is sold on a routine basis, customer entertainment is neither necessary nor justified.
viii. Sales Contests
The main aim of sales contests is to motivate the sales personnel and increase sales, and bring more profit to the company. Under this scheme special incentives in the form of prizes or awards are offered.
The main aim of sales contests is to motivate the sales personnel and increase sales, and bring more profit to the company. Under this scheme special incentives in the form of prizes or awards are offered.
ix. Price—off
A price-off is simply a reduction in the price of the product to increase sales and is very often used in introducing a new product. Price-offs should generally be considered:
For introducing new brands or existing brands with new uses
For products/brands which are already doing better than the competing brands
In conjunction with sales activities aimed at increasing retail distribution
Henkel, the German toiletries major, gave Rs. 10 off on a Rs. 40 pack when it introduced Pril scouring concentrate
x. Refunds
It is an offer made by a manufacturer to give back a certain amount of money to a consumer.
xi. Point-of-sales materials
The POS display persuades reminds and gives details to the consumers about a specific brand. Companies using this method are Procter and Gamble, Nestle and Parle.
xii. Boosters for Dealers
In a bid to reduce its mounting inventories and boost the sagging morale of its dealers, Telco offered a 2 per cent discount to dealers on purchase of a truck if payment is made up-front. Also confessional interest rates were offered to expedite payments.
Train salesmen about the product, familiarize with the market segment and integrate advertising & sales promotion
Let the dealer be given details of the new product, his margins and promotion support
Ensure sufficient quantity to get orders from dealers
Deliver the merchandise at the retail outlets
Arrange to advertise in media
Sample the product door to door with coupons
Promotion strategy should be focused on
1. Sales force promotion
Bonuses
Sales rallies
Best salesman award
2. Trade promotion
Discounts
Displays
Force good
Best dealer awards
A price-off is simply a reduction in the price of the product to increase sales and is very often used in introducing a new product. Price-offs should generally be considered:
For introducing new brands or existing brands with new uses
For products/brands which are already doing better than the competing brands
In conjunction with sales activities aimed at increasing retail distribution
Henkel, the German toiletries major, gave Rs. 10 off on a Rs. 40 pack when it introduced Pril scouring concentrate
x. Refunds
It is an offer made by a manufacturer to give back a certain amount of money to a consumer.
xi. Point-of-sales materials
The POS display persuades reminds and gives details to the consumers about a specific brand. Companies using this method are Procter and Gamble, Nestle and Parle.
xii. Boosters for Dealers
In a bid to reduce its mounting inventories and boost the sagging morale of its dealers, Telco offered a 2 per cent discount to dealers on purchase of a truck if payment is made up-front. Also confessional interest rates were offered to expedite payments.
Strategy for new products
Train salesmen about the product, familiarize with the market segment and integrate advertising & sales promotion
Let the dealer be given details of the new product, his margins and promotion support
Ensure sufficient quantity to get orders from dealers
Deliver the merchandise at the retail outlets
Arrange to advertise in media
Sample the product door to door with coupons
Promotion strategy should be focused on
1. Sales force promotion
Bonuses
Sales rallies
Best salesman award
2. Trade promotion
Discounts
Displays
Force good
Best dealer awards
3. Consumer
promotion
Point of purchase promotion
Free samples
Cash discounts
Free trials
Demonstrations
Prizes
Contests
Industrial products require different promotion strategies due to varied price range
Point of purchase promotion
Free samples
Cash discounts
Free trials
Demonstrations
Contests
Promotion Strategy for Industrial Products
Industrial products require different promotion strategies due to varied price range
1. Documentation
Documentation is essential for improving the marketing effectiveness of a company. Documentation may include;
Product literature
Selection and performance charts
Technical manuals
Operation manuals
Installation manuals
Price lists
Documentation is essential for improving the marketing effectiveness of a company. Documentation may include;
Product literature
Selection and performance charts
Technical manuals
Operation manuals
Installation manuals
Price lists
2. Working models
Many firms supply the working or cutout models of their products to the dealers for display. This helps the customer understand the product easily. In addition, the companies also supply photographs and other display material.
Many firms supply the working or cutout models of their products to the dealers for display. This helps the customer understand the product easily. In addition, the companies also supply photographs and other display material.
3. Exhibitions
Participation in a technical exhibition gives a higher visibility to a company. It is a meeting place for sellers and the buyers. Participation in India Machine Tools Exhibition (IMTEX). Hanover (Germany) Engineering Trade Fair and many other such exhibitions has proved beneficial to many engineering units.
Participation in a technical exhibition gives a higher visibility to a company. It is a meeting place for sellers and the buyers. Participation in India Machine Tools Exhibition (IMTEX). Hanover (Germany) Engineering Trade Fair and many other such exhibitions has proved beneficial to many engineering units.
Tags : Strategic Management - Functional Strategy
Last 30 days 563 views












