Strategic Management - Environmental Analysis and Diagnosis
McKinsey’s 7- s Framework - Competitive Analysis
Posted On :
This framework developed in the 1970’s by US based management consulting firm McKinsey and Company has received attention from strategists.
McKinsey’s
7- s Framework
This framework developed in the 1970’s by US based management consulting firm McKinsey and Company has received attention from strategists. The framework rests on the proposition that effective organizational change is best understood in terms of the complex relationship between the seven S’s. as shown in Figure 7-3. Stated in general terms, the proposition of the7-S model suggests that there are
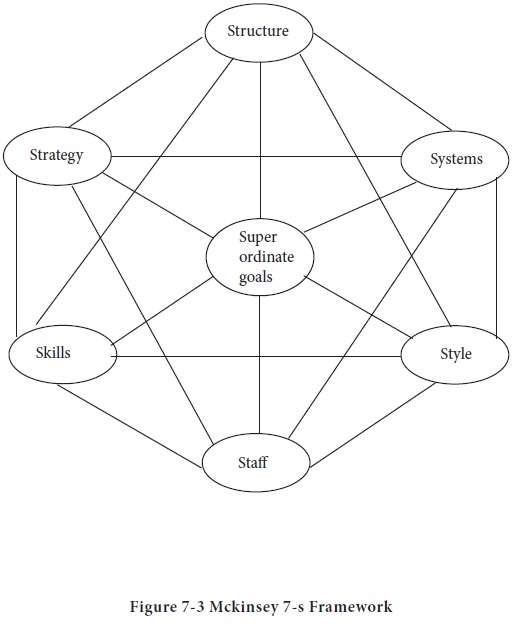
1. Structure refers to the authority relationships, the hierarchical arrangement of positions in the organization.
2. Systems’ may be called the ‘infrastructure’ and include sub-systems relating to production planning and control, cost accounting procedures, capital budgeting, recruitment, training and development, planning and budgeting, performance evolution, etc. Rules, regulations and procedures constitute ‘systems’ in the framework, which complement the organizational structure
3. Strategy refers to the long range plan of action with a set of goals for accomplishment
4. Staff ’ carriers a specific meaning in the 7-S framework. It refers to the way organizations induct young recruits into the mainstream of activities and the manner in which they manage their careers as the new entrants develop into managers.
5. Skills refer to the ‘distinctive competence’ which reflects the dominant skills of an organization, and may consist of competence in terms of engineering skills, or competence in the area of new product development, customer service, quality commitment, market power, and so on.
6. Style is another variable, which may determine the effectiveness of organizational change effort. According to the 7-S framework, the style of an organization becomes evident through the patterns of actions of the top management team over a period of time, the emphasis laid on aspects of business, reporting relationships and aspects of organizational culture.
7. Shared values (or super ordinate goals) in the Mckinsey model refer to the set of values and aspirations that go beyond the formal statement of corporate objectives. In other words, these are fundamental ideas around which a business is built and which constitute its main values. Typical examples are: Hewlett-Packard’s “innovative people at all levels in organization” as the dominant aspiration or value; A T & T’s “universal services” goal; “customer service” which guides IBM’s marketing drive.
Mckinsey’s framework has significance in strategic planning. The following points explain it.
1. It provides a good framework of the seven ‘s’ and align them to energies and executive strategies
2. It is an excellent multivariate model of organizational change
4. Organizational capabilities (strengths and weaknesses may be evaluated along each of the seven dimensions)
Ohmae suggests that in the event of limited resources, it may be wise to concentrate on key functional or operating areas that are the determinants of success for a particular business. This calls for identifying the key factors of success (KFS) for a given industry. There are two approaches to identify the KPS.
1. The first is to dissect the market as imaginatively as possible to identify its key segments.
2. The other is to discover what distinguishes successful companies from losers, and then analyze the differences between them.
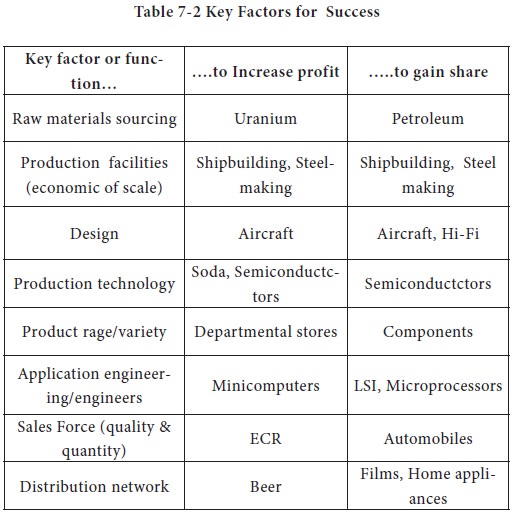
The key factors for success of different industries may live in different functions, areas, distribution, channels and so on. These can be identified along the various functional activities of business starting from raw material to customer servicing. Table 7-2 provides the key factors for success to increase profit and gain market share for various industries.
Business history indicates that the “most effective shortcut to major success appears to be to jump quickly to the top by concentrating major resources early on a single strategically significant function, become really good and competitive at it, and then move to consolidate a lead in the other functions by using the profit structure that the early top status has been made possible. All of to-day’s industry leaders without exception began by bold deployment of strategies based on KFS.
This framework developed in the 1970’s by US based management consulting firm McKinsey and Company has received attention from strategists. The framework rests on the proposition that effective organizational change is best understood in terms of the complex relationship between the seven S’s. as shown in Figure 7-3. Stated in general terms, the proposition of the7-S model suggests that there are

1. Structure refers to the authority relationships, the hierarchical arrangement of positions in the organization.
2. Systems’ may be called the ‘infrastructure’ and include sub-systems relating to production planning and control, cost accounting procedures, capital budgeting, recruitment, training and development, planning and budgeting, performance evolution, etc. Rules, regulations and procedures constitute ‘systems’ in the framework, which complement the organizational structure
3. Strategy refers to the long range plan of action with a set of goals for accomplishment
4. Staff ’ carriers a specific meaning in the 7-S framework. It refers to the way organizations induct young recruits into the mainstream of activities and the manner in which they manage their careers as the new entrants develop into managers.
5. Skills refer to the ‘distinctive competence’ which reflects the dominant skills of an organization, and may consist of competence in terms of engineering skills, or competence in the area of new product development, customer service, quality commitment, market power, and so on.
6. Style is another variable, which may determine the effectiveness of organizational change effort. According to the 7-S framework, the style of an organization becomes evident through the patterns of actions of the top management team over a period of time, the emphasis laid on aspects of business, reporting relationships and aspects of organizational culture.
7. Shared values (or super ordinate goals) in the Mckinsey model refer to the set of values and aspirations that go beyond the formal statement of corporate objectives. In other words, these are fundamental ideas around which a business is built and which constitute its main values. Typical examples are: Hewlett-Packard’s “innovative people at all levels in organization” as the dominant aspiration or value; A T & T’s “universal services” goal; “customer service” which guides IBM’s marketing drive.
Mckinsey’s framework has significance in strategic planning. The following points explain it.
1. It provides a good framework of the seven ‘s’ and align them to energies and executive strategies
2. It is an excellent multivariate model of organizational change
3. It provides a convenient means of checking whether
an organization has the necessary conditioning for implementing strategy
4. Organizational capabilities (strengths and weaknesses may be evaluated along each of the seven dimensions)
Ohmae’s Key factors for success
Ohmae suggests that in the event of limited resources, it may be wise to concentrate on key functional or operating areas that are the determinants of success for a particular business. This calls for identifying the key factors of success (KFS) for a given industry. There are two approaches to identify the KPS.
1. The first is to dissect the market as imaginatively as possible to identify its key segments.
2. The other is to discover what distinguishes successful companies from losers, and then analyze the differences between them.
The key factors for success of different industries may live in different functions, areas, distribution, channels and so on. These can be identified along the various functional activities of business starting from raw material to customer servicing. Table 7-2 provides the key factors for success to increase profit and gain market share for various industries.

Ohmae Observes
Business history indicates that the “most effective shortcut to major success appears to be to jump quickly to the top by concentrating major resources early on a single strategically significant function, become really good and competitive at it, and then move to consolidate a lead in the other functions by using the profit structure that the early top status has been made possible. All of to-day’s industry leaders without exception began by bold deployment of strategies based on KFS.
Tags : Strategic Management - Environmental Analysis and Diagnosis
Last 30 days 1117 views












