Strategic Management - Environmental Analysis and Diagnosis
Core Competence Identification - Internal Analysis
Posted On :
A detailed discussion on the concept of core competence is given in lesson 4 of Unit I in this material.
Core Competence
Identification
A detailed discussion on the concept of core competence is given in lesson 4 of Unit I in this material.After identifying the resources and relating them to strategic purpose through value chain analysis, the next step is identification of company’s core competence. The core competence refers to unique strength of the company that competitors cannot easily match or imitate.
To Gary Hamel and C.K. Prahalad,
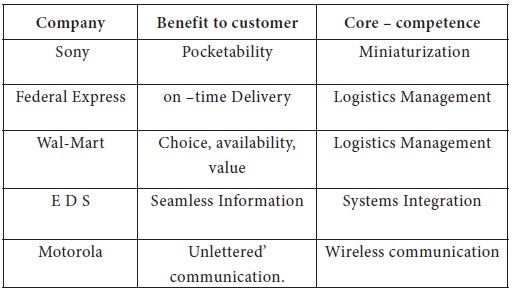
“A core- competence is a bundle of skills and technologies that enables a company to provide a particular benefit to customers”. Following are the examples of core-competence at global level:
“The diversified corporation is a large tree. The trunk and major limbs are core products, the smaller branches are business units; the leaves, flowers and fruit are end products. The root system that provided nourishment, sustenance, and stability is the core competence. You can miss the strength of competition by looking only at their end products in the same way you miss the strength of a tree if you look only at its leaves.”
Core competence provides strategic advantage to the company. In the short run, a company can achieve competitiveness from its price / Performance attributes; but in the long run core competence will provide profitability. With its core – competence, company can produce at lower
Core competence exhibits the following features(Gary Hamel and C.K.Prahalad ).
1. Core competence does not reside in one particular product or business unit. It underlies leadership in a range of products or services. “Core competencies transcend any single business unit within the corporation. Core competences are also longer lasting than any individual product or service.” Sony’s miniaturization competence is not only confined to walkman, but also other products like portable CD player, pocket television, etc.
2. As Core – competence contributes to competitiveness as winning or losing the battle for leadership is highly dependent upon it. “If Motorola lost its leadership position in wireless competencies, a broad spectrum of business would suffer including pagers, two – way mobile radios and cellular telephones.”
3. A Core – competence is not a single discrete skill or technology, rather a bundle of skills and technologies. Thus a core competence “represents the sum of learning across individual skill sets and individual organizational units unlikely to reside in its entirety in a single individual or small team.” This Core-competence has to be nurtured through collective learning of the team members.
Some of the Indian companies with ability to use internal strengths to make strategies effective are explained here.
Use vertical integration to control the market
Attain global scales in each and every product –line
Build production capacities ahead of demand
Leverage technology for process efficiencies
Manage project engineering to control costs
Service the customer at his door- step.
Benchmark costs globally to keep them in check
Focus relentlessly on only some chosen products
Seek out niches unprofitable for the bigger players
Use R &D to build unique, unmatched skills
Seek differentiation in delivery, not product
Integrate vertically to attain economies of scale
Focus on only one segment of customers
Adopt the customer’s quality standards to avoid rejection
Use demanding customers to raise quality levels
Seek out large customers to operate on a global scale
Develop a full range of products to meet complete buyer needs
Build unique skills that are expensive to duplicate
Create global capacities quickly to attack older players
Target large commodity buyers for the benefits of scale
Focus on one basic product, but diversify into new markets
Use value – addition to provide a basket of related products
Keep every element of cost below the level of competitors
Integrate forward to cash in on low-cost in –house supplies
Control costs to keep the product affordable
Reengineer processes to improve time utilization
Forge relationships with vendors to minimize costs
Build global capacities if the domestic market is large enough
Steer clear of diversification even if synergies are available
Focus on chosen segments without straying into new ones
A detailed discussion on the concept of core competence is given in lesson 4 of Unit I in this material.After identifying the resources and relating them to strategic purpose through value chain analysis, the next step is identification of company’s core competence. The core competence refers to unique strength of the company that competitors cannot easily match or imitate.
To Gary Hamel and C.K. Prahalad,
“A core- competence is a bundle of skills and technologies that enables a company to provide a particular benefit to customers”. Following are the examples of core-competence at global level:

According to C.K. Prahalad and Gary Hamel,
“The diversified corporation is a large tree. The trunk and major limbs are core products, the smaller branches are business units; the leaves, flowers and fruit are end products. The root system that provided nourishment, sustenance, and stability is the core competence. You can miss the strength of competition by looking only at their end products in the same way you miss the strength of a tree if you look only at its leaves.”
Core competence provides strategic advantage to the company. In the short run, a company can achieve competitiveness from its price / Performance attributes; but in the long run core competence will provide profitability. With its core – competence, company can produce at lower
Features of Core Competence
Core competence exhibits the following features(Gary Hamel and C.K.Prahalad ).
1. Core competence does not reside in one particular product or business unit. It underlies leadership in a range of products or services. “Core competencies transcend any single business unit within the corporation. Core competences are also longer lasting than any individual product or service.” Sony’s miniaturization competence is not only confined to walkman, but also other products like portable CD player, pocket television, etc.
2. As Core – competence contributes to competitiveness as winning or losing the battle for leadership is highly dependent upon it. “If Motorola lost its leadership position in wireless competencies, a broad spectrum of business would suffer including pagers, two – way mobile radios and cellular telephones.”
3. A Core – competence is not a single discrete skill or technology, rather a bundle of skills and technologies. Thus a core competence “represents the sum of learning across individual skill sets and individual organizational units unlikely to reside in its entirety in a single individual or small team.” This Core-competence has to be nurtured through collective learning of the team members.
Competitive Cannons of Indian Companies
Some of the Indian companies with ability to use internal strengths to make strategies effective are explained here.
Reliance
Use vertical integration to control the market
Attain global scales in each and every product –line
Build production capacities ahead of demand
Leverage technology for process efficiencies
Manage project engineering to control costs
Service the customer at his door- step.
Ranbaxy Laboratories
Benchmark costs globally to keep them in check
Focus relentlessly on only some chosen products
Seek out niches unprofitable for the bigger players
Use R &D to build unique, unmatched skills
Seek differentiation in delivery, not product
Integrate vertically to attain economies of scale
Sundram Fasteners
Focus on only one segment of customers
Adopt the customer’s quality standards to avoid rejection
Use demanding customers to raise quality levels
Seek out large customers to operate on a global scale
Develop a full range of products to meet complete buyer needs
Build unique skills that are expensive to duplicate
Arvind Mills
Create global capacities quickly to attack older players
Target large commodity buyers for the benefits of scale
Focus on one basic product, but diversify into new markets
Use value – addition to provide a basket of related products
Keep every element of cost below the level of competitors
Integrate forward to cash in on low-cost in –house supplies
Bajaj Auto
Control costs to keep the product affordable
Reengineer processes to improve time utilization
Forge relationships with vendors to minimize costs
Build global capacities if the domestic market is large enough
Steer clear of diversification even if synergies are available
Focus on chosen segments without straying into new ones
Tags : Strategic Management - Environmental Analysis and Diagnosis
Last 30 days 1168 views












