Strategic Management - Environmental Analysis and Diagnosis
Approaches for internal analysis
Posted On :
We will now consider the three approaches to internal analysis
Approaches for internal analysis
We will now consider the three approaches to internal analysis
Sustainability of an advantage can be determined by considering two factors
1. Durability—rate at which a firm’s resources and capabilities depreciate or become obsolete Ex: Intel’s R&D weakness & mere imitation.
2. Imitability—Rate at which others can duplicate a firm’s core competencies. It can duplicated early when it is
i. Transparent Ex: Gillette’s sensor blades, difficult to copy, expensive manufacturing equipment.
ii. Transferable Ex: French winery’s land and climate.
iii. Replicable Ex: Brand Mgt of P&G cannot be replicable
We will now consider the three approaches to internal analysis
1. VRIO
framework
2. Grant’s
approach
3. Continuum
of sustainability
The framework help raise the following questions.
VALUE: Does it provide competitive advantage?
RARENESS: Do other competitors posses it?
IMITABILITY: Is it costly for others to imitate?
Vrio Framework
The framework help raise the following questions.
VALUE: Does it provide competitive advantage?
RARENESS: Do other competitors posses it?
IMITABILITY: Is it costly for others to imitate?
ORGANISATION:
Is the firm organized to exploit the resource?
If the answer is ‘yes’, there is
distinctive competence. Measure these with
1. The
company’s past performance,
2. The
company’s key competitors, and
3. The
industry as a whole
It is a five step approach
1. Identify and classify a firm’s strengths & weaknesses
2. Combine the strengths to core competencies
3. Appraise the profit potential of these resources and capabilities.
4. Select the strategy that exploits the firms resources and capabilities to external opportunities
5. Identify resource gaps and invest in upgrading weaknesses.
United Airlines is a very successful, full service international airline. However, South West Airlines was dominating in California due to low cost carriers. UA tried to imitate SWA and had to reduce flying costs form 10.5/- to 7.4/-, speed up boarding and take offs and reduce idle time on the ground. The same being 737 was introduced in 1994. By Feb, 1996 only 8/- cost per passenger mile could be discounted compared to SWAS 7.1/-. It had to pull out from all routes that did not connect with carrier’s hubs in San Francisco and Los Angels. For shorter flights like San Francisco to California UA’s tariff was higher by $30 while SWA’s was $ 69. Slowly UA lost its loyal customers for short route flights to SWA.
So far, no one knows the competitive advantage of SWA. SWA had two capabilities:
1. low costs per passenger mile
2. Energizing its people to provide safe, on time flight service.
Grant’s Approach
It is a five step approach
1. Identify and classify a firm’s strengths & weaknesses
2. Combine the strengths to core competencies
3. Appraise the profit potential of these resources and capabilities.
4. Select the strategy that exploits the firms resources and capabilities to external opportunities
5. Identify resource gaps and invest in upgrading weaknesses.
United Airlines is a very successful, full service international airline. However, South West Airlines was dominating in California due to low cost carriers. UA tried to imitate SWA and had to reduce flying costs form 10.5/- to 7.4/-, speed up boarding and take offs and reduce idle time on the ground. The same being 737 was introduced in 1994. By Feb, 1996 only 8/- cost per passenger mile could be discounted compared to SWAS 7.1/-. It had to pull out from all routes that did not connect with carrier’s hubs in San Francisco and Los Angels. For shorter flights like San Francisco to California UA’s tariff was higher by $30 while SWA’s was $ 69. Slowly UA lost its loyal customers for short route flights to SWA.
So far, no one knows the competitive advantage of SWA. SWA had two capabilities:
1. low costs per passenger mile
2. Energizing its people to provide safe, on time flight service.
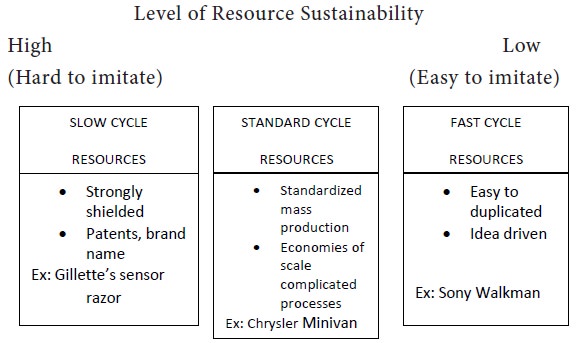
Continuum of Sustainability
Sustainability of an advantage can be determined by considering two factors
1. Durability—rate at which a firm’s resources and capabilities depreciate or become obsolete Ex: Intel’s R&D weakness & mere imitation.
2. Imitability—Rate at which others can duplicate a firm’s core competencies. It can duplicated early when it is
i. Transparent Ex: Gillette’s sensor blades, difficult to copy, expensive manufacturing equipment.
ii. Transferable Ex: French winery’s land and climate.
iii. Replicable Ex: Brand Mgt of P&G cannot be replicable
An organization’s resources and capabilities can be
placed on a continuum as follows –

Tags : Strategic Management - Environmental Analysis and Diagnosis
Last 30 days 1547 views













