Strategic Management - Environmental Analysis and Diagnosis
Competitive Strategies - Competitive Analysis
Posted On :
We will now discuss the generic strategies given by Porter and the generally found marketing warfare strategies.
Competitive Strategies
We will now discuss the generic strategies given by Porter and the generally found marketing warfare strategies.
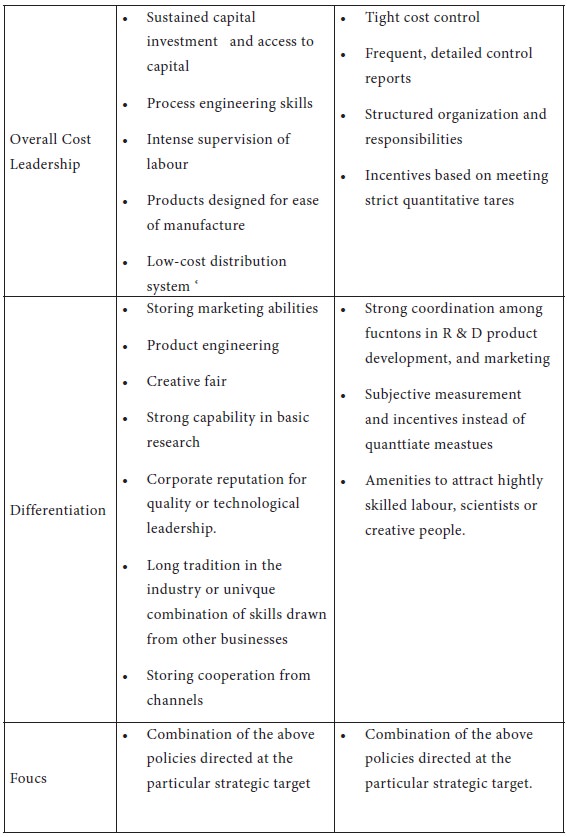
tAccording to Porter there are three potentially successful generic strategies (see Figure 7-3) to cope up with the five competitive forces as well as gain advantage (See Figure 7-2and Table 7- 3). These are:
1. Overall cost leadership
2. Differentiation and
3. Focus
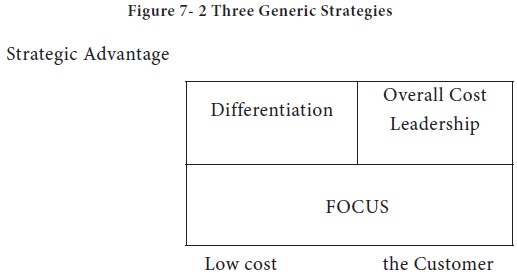
In this strategy company makes all possible attempts to achieve the lowest costs in production and marketing. The aim is to gain a large market share. Efficiency is the keyword guiding all decisions to keep the costs low.
Here the aim is to achieve class leadership by creating something, which is perceived as unique. Creating highly differentiated products and marketing programmes-like design or brand image, customer service or dealer network, or any other feasible dimension can achieve it. Companies pursuing this strategy have major strengths in R&D design, quality control and marketing.
Chiragh Din Shirts, Bata Shoes, OTIS Elevators, Cini Fans are some examples where this strategy seems to be the dominant guiding force.
The underlying assumption in ‘Focus’ is that a firm should be able to serve a narrow strategic target effectively and efficiently. As a result the firm achieves either differentiation from meeting the need of a particular target, on both.
Genteel’, a liquid detergent for expensive clothes by Swastik, and Ponds Talcum Powder are some handy examples for this strategy.
We will now discuss the generic strategies given by Porter and the generally found marketing warfare strategies.
Generic Strategies
tAccording to Porter there are three potentially successful generic strategies (see Figure 7-3) to cope up with the five competitive forces as well as gain advantage (See Figure 7-2and Table 7- 3). These are:
1. Overall cost leadership
2. Differentiation and
3. Focus

Overall Cost Leadership
In this strategy company makes all possible attempts to achieve the lowest costs in production and marketing. The aim is to gain a large market share. Efficiency is the keyword guiding all decisions to keep the costs low.
Differentiation
Here the aim is to achieve class leadership by creating something, which is perceived as unique. Creating highly differentiated products and marketing programmes-like design or brand image, customer service or dealer network, or any other feasible dimension can achieve it. Companies pursuing this strategy have major strengths in R&D design, quality control and marketing.
Chiragh Din Shirts, Bata Shoes, OTIS Elevators, Cini Fans are some examples where this strategy seems to be the dominant guiding force.
Focus
The underlying assumption in ‘Focus’ is that a firm should be able to serve a narrow strategic target effectively and efficiently. As a result the firm achieves either differentiation from meeting the need of a particular target, on both.
Genteel’, a liquid detergent for expensive clothes by Swastik, and Ponds Talcum Powder are some handy examples for this strategy.


Source: Adaped/reprinted with permission of The Free Press, an important of Simon & Schuster, from Competitive strategy. Techniques for Analyzing Industries and Competitors by Michael E. Porter, pp 40-41. Copyright © 1980, by The Free Press.
Tags : Strategic Management - Environmental Analysis and Diagnosis
Last 30 days 701 views













