Home | ARTS | Management Concepts & Organisational Behaviour
|
Theories of Personality - Personality And Individual Differences
Management Concepts & Organisational Behaviour - Personality And Individual Differences
Theories of Personality - Personality And Individual Differences
Posted On :
Trait theory presents an approach to understand personality. Many traits are common to most people.
Theories
of Personality
Trait theory presents an approach to understand personality. Many traits are common to most people. However, there are many other traits that are unique to a person. It may be remembered that traits are reactions and not what a person possesses. A person does not possess emotion but he acts emotionally in some circumstances. One the basis of the traits, people may be described as emotional, aggressive, loyal, creative, flexible, humorous, sentimental, and impulsive and so on. Traits are the basic elements of personality and can be used to summarize the behaviour of a person. However, determining basic traits is rather difficult because thousands of descriptive words are there.
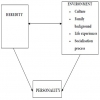
The psychoanalytical theory of personality is based on the Freudian concept of unconscious nature of personality. On the basis of his clinical experience, Freud noted that his patient’s behaviour could not always be consciously explained. This prompted him to believe that the personality structure is primarily founded on unconscious framework and that human behaviour and motivation are the outcomes of such conflicting psychoanalytic concepts as the id, the ego and the super ego. Id is the foundation of the unconscious and is the basis of libido drives. It strives for sexual and other biological pleasures and has animal instincts of aggression, power and domination. Ego is conscious in nature and is a mechanism to relate our conscious urges to the outside real world. It keeps the id in check through the realities of the external environment. While id demands immediate pleasure, regardless of costs, ego controls it so that these pleasures are granted at an appropriate time and in an acceptable manner. Because of difficulty in keeping the id under control, ego is supported by super ego. The super ego is the higher level restraining force and can be described as the conscience of the person. The conscience creates standards of what is right and what is wrong and is generally subconsciously developed by the absorption of cultural and ethical values of the social environment. All these three Freudian elements are inter-related and each cannot exist in isolation from others. In order to create a “normal” personality, there must be a balance in the relationship among these three forces.
The social learning theory differs from the psychoanalytical theory in two ways. First, it is believed that personality development is more a result of social variables than biological drives. Secondly, motives can be traced to known and conscious needs and wants rather than unconscious and latent desires. Thus, learning theory looks at personality as the sum total of all that a person has learned. The social learning theory focuses on behaviour patterns and cognitive activities in relation to the specific conditions that evoke maintain or modify them. The social learning theory uses “reinforcement and punishment” approach in understanding personality. For example, good behaviour is rewarded by management in terms of praise that further reinforces good behaviour. Thus, behaviour and
Learning may also take place simply from observation rather than interaction with the environment. We watch the behaviour of other people, draw conclusions from it and come out with our own behaviour. Unlike trait theory or psychoanalytical theory, social learning theory considers situation as an important variable in determining human behaviour.
Trait Theory
Trait theory presents an approach to understand personality. Many traits are common to most people. However, there are many other traits that are unique to a person. It may be remembered that traits are reactions and not what a person possesses. A person does not possess emotion but he acts emotionally in some circumstances. One the basis of the traits, people may be described as emotional, aggressive, loyal, creative, flexible, humorous, sentimental, and impulsive and so on. Traits are the basic elements of personality and can be used to summarize the behaviour of a person. However, determining basic traits is rather difficult because thousands of descriptive words are there.
Psychoanalytical Theory
The psychoanalytical theory of personality is based on the Freudian concept of unconscious nature of personality. On the basis of his clinical experience, Freud noted that his patient’s behaviour could not always be consciously explained. This prompted him to believe that the personality structure is primarily founded on unconscious framework and that human behaviour and motivation are the outcomes of such conflicting psychoanalytic concepts as the id, the ego and the super ego. Id is the foundation of the unconscious and is the basis of libido drives. It strives for sexual and other biological pleasures and has animal instincts of aggression, power and domination. Ego is conscious in nature and is a mechanism to relate our conscious urges to the outside real world. It keeps the id in check through the realities of the external environment. While id demands immediate pleasure, regardless of costs, ego controls it so that these pleasures are granted at an appropriate time and in an acceptable manner. Because of difficulty in keeping the id under control, ego is supported by super ego. The super ego is the higher level restraining force and can be described as the conscience of the person. The conscience creates standards of what is right and what is wrong and is generally subconsciously developed by the absorption of cultural and ethical values of the social environment. All these three Freudian elements are inter-related and each cannot exist in isolation from others. In order to create a “normal” personality, there must be a balance in the relationship among these three forces.
Social Learning Theory
The social learning theory differs from the psychoanalytical theory in two ways. First, it is believed that personality development is more a result of social variables than biological drives. Secondly, motives can be traced to known and conscious needs and wants rather than unconscious and latent desires. Thus, learning theory looks at personality as the sum total of all that a person has learned. The social learning theory focuses on behaviour patterns and cognitive activities in relation to the specific conditions that evoke maintain or modify them. The social learning theory uses “reinforcement and punishment” approach in understanding personality. For example, good behaviour is rewarded by management in terms of praise that further reinforces good behaviour. Thus, behaviour and
Learning may also take place simply from observation rather than interaction with the environment. We watch the behaviour of other people, draw conclusions from it and come out with our own behaviour. Unlike trait theory or psychoanalytical theory, social learning theory considers situation as an important variable in determining human behaviour.
Tags : Management Concepts & Organisational Behaviour - Personality And Individual Differences
Last 30 days 870 views