Home | ARTS | Marketing Management
|
Segmenting the Consumer Markets and Industrial Markets - Market Segmentation, Targeting and Positioning
MARKETING MANAGEMENT - Market Segmentation, Targeting and Positioning
Segmenting the Consumer Markets and Industrial Markets - Market Segmentation, Targeting and Positioning
Posted On :
Consumer markets are those where the products are purchased by ultimate consumers for personal use.
Segmenting the Consumer Markets
Consumer markets are those where the products are purchased by ultimate consumers for personal use. Industrial markets are those where the goods and services are purchased for use either directly or indirectly in the production of other goods and services for resale. Market segmentation of these markets use different variables.
The consumer market segmentation variables appear to fall into two broad classes: consumers’ background characteristics and consumers’ market history. The following tables illustrate the most important factors and variables that have been found useful for market segmentation.
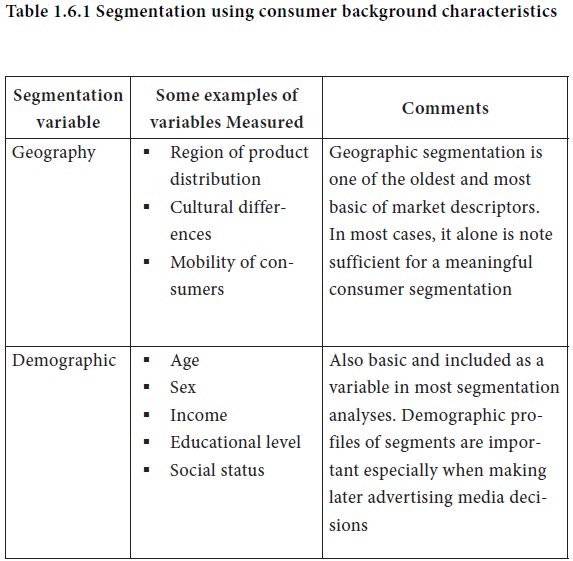
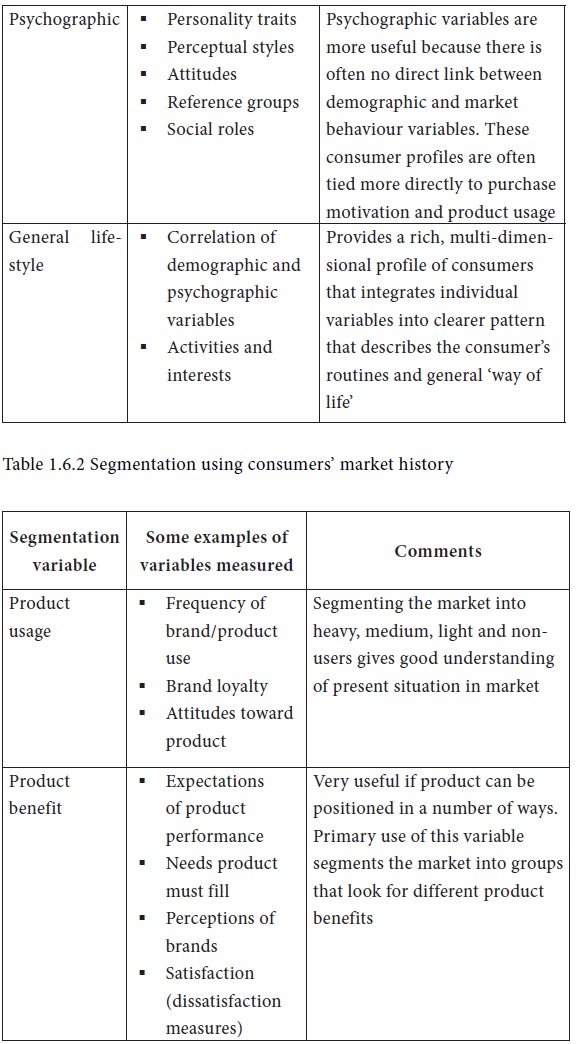
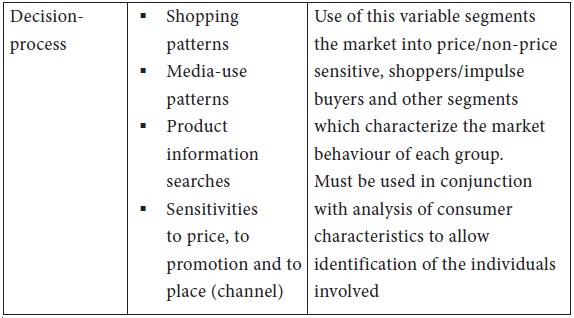
Activity 1.6.2
Refer to the activity 1.6.1. From what you had noted down as the ‘wants’ of toothpaste consumers, match each of those wants with the segmentation variables listed below
1. Consumer background characteristics
1.1 | Geography | - |
1.2 | Demographic | - |
1.3 | Psychographic | - |
1.4 | General
life-style | - |
2. Consumers’ market history
2.1 | Product
usage | - |
2.2 | Product
benefit | - |
2.3 | Decision-process | - |
Segmenting the Industrial Markets
Industrial marketing needs to consider two important sets of characteristics of the business buyers: (1) the characteristics of the buyer as a consuming organization and (2) the behavioural characteristics of the
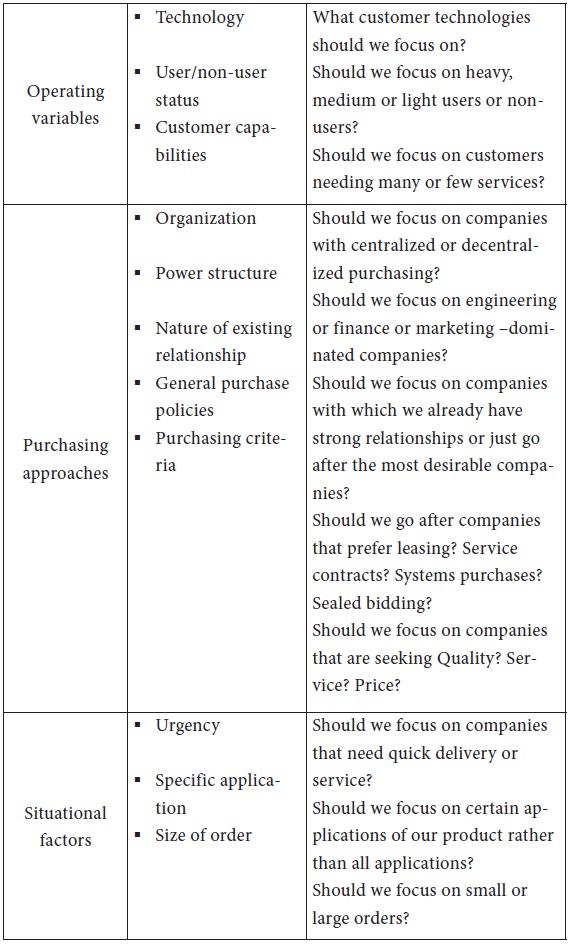
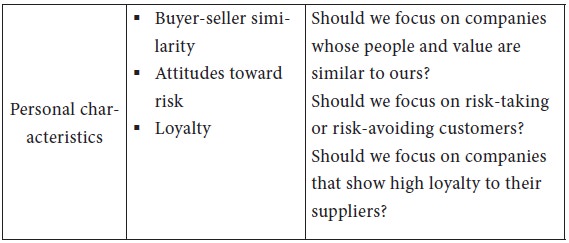
These characteristics have led to a two-stage approach to industrial market segmentation starting with a macro segmentation and then going into a micro segmentation. Between the macro and micro bases of industrial market segmentation, there lie some useful bases of segmentation, as suggested by Shapiro and Bonoma in the Nested approach to segmenting the industrial markets.
These intermediate bases of segmentation, viz., demographics, operating variables, purchasing approaches, situational factors and personal characteristics, are explained in Table 1.6.3. The table lists major questions that business marketers should ask in determining which customers they want to serve. By targeting these segments instead of the whole market, companies have a much better chance to deliver value to customers and to receive maximum rewards for close attention to their needs.
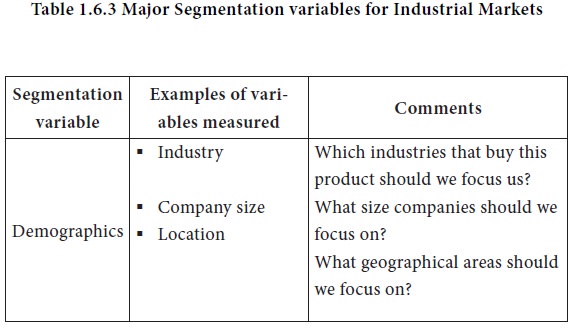
Tags : MARKETING MANAGEMENT - Market Segmentation, Targeting and Positioning
Last 30 days 2862 views












