Strategic Management - Concept Of Corporate Strategy
Role of strategists - Strategic Management Process
Posted On :
Strategists are individuals or groups who are primarily involved in the formulation, implementation, and evaluation of strategy.
Role of
strategists
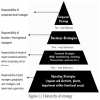
Strategists are individuals or groups who are primarily involved in the formulation, implementation, and evaluation of strategy. In a lim-ited sense, all managers are strategists. There are persons outside the organization who are also involved in various aspects of strategic man-agement. They too are referred to as strategists. We can identify nine strategists who, as individuals or in groups, are concerned with and play a role in strategic management.
1. Consultants
2. Entrepreneurs
3. Board of Directors
4. Chief Executive Officer
5. Senior management
6. Corporate planning staff
7. Strategic business unit (SBU) level executives
8. Middle level managers
9. Executive Assistant
1. Consultants: Many organizations which do not have a corporate planning
department owing to reasons like small size, infrequent require-ments,
financial constraints, and so on, take the help of external consult-ants in
strategic management. Besides the Indian consultancy firms, such as,
A.F.Ferguson, S.B. Billimoria and several others, now there are many foreign
consultancy firms. They offer a variety of services.
McKinsey and Company, specializes in offering consultancy in the areas of fundamental change management and strategic visioning; Andreson Consulting, is in business restructuring, and info tech and systems; Boston Consulting helps in building competitive advantage; and KPMG Peat Marwick is in strategic financial management and feasi-bility studies for strategy implementation.
2. Entrepreneurs are promoters who conceive the idea of starting a business enterprise for getting maximum returns on their investment. They are waiting for an environment change and thereby for an opportu-nity to exploit the situation in their best interest. Thus they start playing their role right from the promotion of the proposed venture. So, their strategic role to make the venture a success is very conspicuous in a new business enterprise. Therefore, it is expected of an entrepreneur that he should posses foresight, sense of responsibility, desire to work hard and dashing spirit to bear any future contingencies. According to Drucker, “the entrepreneur always searches for change, responds to it and exploits it as an opportunity”. Here is an example of a successful women entre-preneur.
Kiran Mazumdar Shaw, a young entrepreneur, set up an export-oriented unit manufacturing a range of enzymes. As an expert in brew-ing technology, Mazumdur entered the field of biotechnology after ex-periencing problems in getting a job. Later she set up another plant for manufacturing two new enzymes created by her own research and development (R&D) department. As managing director, Mazumdar was actively involved in all aspects of policy formulation and implementa-tion for her companies.
3. Board of Directors are professionals elected on the Board of Di-rectors (BOD) by the shareholders of the company as per rules and regu-lations of the Companies Act, 1956. They are responsible for the general administration of the organization. They are supposed to guide the top management in framing business strategies for accomplishing predeter-mined objectives. It is also the responsibility of the Board to review and evaluate organizational performance whether it is as per the strategy laid down or not. The Board is also empowered to make appointments of senior executives. In this connection, it should be noted that the success of strategies much depends on the relative strength in terms of power held by the Board and the Chief Executive (CE).
Strategic planning at MRF Ltd. used senior management expertise by dividing them into five groups dealing with products and markets, environment, technology, resources, and manpower. Each group had a leader who helped to prepare position papers for presentation to the board. The executive directors in the company were actively involved in SWOT analysis through the help of managers and assistant managers.
6. SBU level executives: “SBU” stands for strategic business unit. Under this approach, the main business unit is divided into different independent units and is allowed to form their own respective strategies. In fact, the business is diversified and thus the departmental heads are supposed to act as the main strategist, keeping an eye on optimum ben-efit for their departments. Hence strategists i.e., the departmental heads enjoy the maximum amount of authority and responsibility within their strategic business units.
At Shriram Fibres, the strategic planning system covered the dif-ferent businesses ranging from nylon yarn manufacture to the provision of financial services. Strategic plans were formulated at the level of each SBU as well as at the corporate level. The corporate planning depart-ment at the head office coordinated the strategic planning exercise at the SBU-level. Each SBU had its own strategic planning cell.
7. Corporate-planning staff plays a supporting role in strategic management. It assists the management in all aspects of strategy for-mulation, implementation and evaluation. Besides this, they are respon-sible for the preparation and communication of strategic plans, and for conducting special studies and research pertaining to strategic manage-ment. It is important to note that the corporate planning department is not responsible for strategic management and usually does not initiate the process on its own. By providing administrative support, it fulfills its functions of assisting the introduction, working, and maintenance of the strategic management system.
8. Middle level managers: They are basically operational planners they may, at best, be involved as ‘sounding boards’ for departmental plans, as implementers of the decisions taken above, followers of policy guidelines, and passive receivers of communication about functional strategic plans. As they are basically involved in the implementation of functional strategies, the middle-level mangers are rarely employed for any other purpose in strategic management.
9. Executive Assistant: An executive assistant is a person who as-sists the chief executive in the performance of his duties in various ways. These could be : to assist the chief executive in data collection and analy-sis, suggesting alternatives where decisions are required, preparing briefs of various proposals, projects and reports, helping in public relations and liaison functions, coordinating activities with the internal staff and outsiders, and acting as a filter for the information coming from differ-ent sources. Among these “the most important and what one manager
Strategists are individuals or groups who are primarily involved in the formulation, implementation, and evaluation of strategy. In a lim-ited sense, all managers are strategists. There are persons outside the organization who are also involved in various aspects of strategic man-agement. They too are referred to as strategists. We can identify nine strategists who, as individuals or in groups, are concerned with and play a role in strategic management.
2. Entrepreneurs
3. Board of Directors
4. Chief Executive Officer
5. Senior management
6. Corporate planning staff
9. Executive Assistant
A brief description of how the different strategists approach the
process is outlined here.
McKinsey and Company, specializes in offering consultancy in the areas of fundamental change management and strategic visioning; Andreson Consulting, is in business restructuring, and info tech and systems; Boston Consulting helps in building competitive advantage; and KPMG Peat Marwick is in strategic financial management and feasi-bility studies for strategy implementation.
2. Entrepreneurs are promoters who conceive the idea of starting a business enterprise for getting maximum returns on their investment. They are waiting for an environment change and thereby for an opportu-nity to exploit the situation in their best interest. Thus they start playing their role right from the promotion of the proposed venture. So, their strategic role to make the venture a success is very conspicuous in a new business enterprise. Therefore, it is expected of an entrepreneur that he should posses foresight, sense of responsibility, desire to work hard and dashing spirit to bear any future contingencies. According to Drucker, “the entrepreneur always searches for change, responds to it and exploits it as an opportunity”. Here is an example of a successful women entre-preneur.
Kiran Mazumdar Shaw, a young entrepreneur, set up an export-oriented unit manufacturing a range of enzymes. As an expert in brew-ing technology, Mazumdur entered the field of biotechnology after ex-periencing problems in getting a job. Later she set up another plant for manufacturing two new enzymes created by her own research and development (R&D) department. As managing director, Mazumdar was actively involved in all aspects of policy formulation and implementa-tion for her companies.
3. Board of Directors are professionals elected on the Board of Di-rectors (BOD) by the shareholders of the company as per rules and regu-lations of the Companies Act, 1956. They are responsible for the general administration of the organization. They are supposed to guide the top management in framing business strategies for accomplishing predeter-mined objectives. It is also the responsibility of the Board to review and evaluate organizational performance whether it is as per the strategy laid down or not. The Board is also empowered to make appointments of senior executives. In this connection, it should be noted that the success of strategies much depends on the relative strength in terms of power held by the Board and the Chief Executive (CE).
4. Chief Executive Officer: In the management circle, the chief ex-ecutive is the top man, next to the directors of the Board. He occupies the most sensitive post, being held responsible for all aspects of strategic management right from formulation to evaluation of strategy. He is des-ignated in some companies as the managing director, executive director or as a general manager. Whatever the designation be, he is considered the most important strategist being responsible to play major role in strategic decision-making.
5. Senior Management: Starting from the chief executive to the lev-el of functional or profit-centre heads, these managers are involved in various aspects of strategic management. Some of the members of the senior management act as directors on the board usually on a rotational basis. All of them serve on different top-level committees set up by the board to look after matters of strategic importance and other policy is-sues. Executive committees, consisting of senior managers, are respon-sible for implementing strategies and plans, and for a periodic evaluation of performance.
Strategic planning at MRF Ltd. used senior management expertise by dividing them into five groups dealing with products and markets, environment, technology, resources, and manpower. Each group had a leader who helped to prepare position papers for presentation to the board. The executive directors in the company were actively involved in SWOT analysis through the help of managers and assistant managers.
6. SBU level executives: “SBU” stands for strategic business unit. Under this approach, the main business unit is divided into different independent units and is allowed to form their own respective strategies. In fact, the business is diversified and thus the departmental heads are supposed to act as the main strategist, keeping an eye on optimum ben-efit for their departments. Hence strategists i.e., the departmental heads enjoy the maximum amount of authority and responsibility within their strategic business units.
At Shriram Fibres, the strategic planning system covered the dif-ferent businesses ranging from nylon yarn manufacture to the provision of financial services. Strategic plans were formulated at the level of each SBU as well as at the corporate level. The corporate planning depart-ment at the head office coordinated the strategic planning exercise at the SBU-level. Each SBU had its own strategic planning cell.
7. Corporate-planning staff plays a supporting role in strategic management. It assists the management in all aspects of strategy for-mulation, implementation and evaluation. Besides this, they are respon-sible for the preparation and communication of strategic plans, and for conducting special studies and research pertaining to strategic manage-ment. It is important to note that the corporate planning department is not responsible for strategic management and usually does not initiate the process on its own. By providing administrative support, it fulfills its functions of assisting the introduction, working, and maintenance of the strategic management system.
8. Middle level managers: They are basically operational planners they may, at best, be involved as ‘sounding boards’ for departmental plans, as implementers of the decisions taken above, followers of policy guidelines, and passive receivers of communication about functional strategic plans. As they are basically involved in the implementation of functional strategies, the middle-level mangers are rarely employed for any other purpose in strategic management.
9. Executive Assistant: An executive assistant is a person who as-sists the chief executive in the performance of his duties in various ways. These could be : to assist the chief executive in data collection and analy-sis, suggesting alternatives where decisions are required, preparing briefs of various proposals, projects and reports, helping in public relations and liaison functions, coordinating activities with the internal staff and outsiders, and acting as a filter for the information coming from differ-ent sources. Among these “the most important and what one manager
Tags : Strategic Management - Concept Of Corporate Strategy
Last 30 days 13054 views