Accounting For Managers - Accounting Process
Journal
When a business transaction takes place, the first record of it is done in a book called journal. The journal records all the transactions of a business in the order in which they occur.
The journal may therefore be defined as a chronological record of accounting transactions. It shows names of accounts that are to be debited or credited, the amounts of the debits and credits and any other additional but useful information about the transaction. A journal does not replace but precedes the ledger. A proforma of a journal is given in illustration
Illustration 1:
Journal
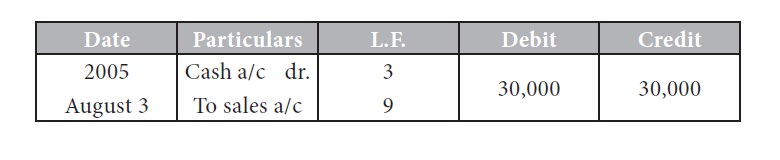
In illustration 1 the debit entry is listed first and the debit amount
appears in the left-hand amount column; the account to be credited appears
below the debit entry and the credit amount appears in the right hand amount
column. The data in the journal entry are transferred to the appropriate
accounts in the ledger by a process known as posting. Any entry in any account
can be made only on the basis of a journal entry. The column l.f. which stands
for ledger folio gives the page number of accounts in the ledger wherein
posting for the journal entry has been made. After all the journal entries are
posted in the respective ledger accounts, each ledger account is balanced by
subtracting the smaller total from the bigger total. The resultant figure may
be either debit or credit balance and vice-versa.
Thus the transactions are recorded first of all in the journal and then
they are posted to the ledger. Hence the journal is called the book of original
or prime entry and the ledger is the book of second entry. While the journal
records transactions in a chronological order, the ledger records transactions
in an analytical order.












