Home | ARTS | Management Concepts & Organisational Behaviour
|
HERZBERG’S Two Factor theory of MOTIVATION
Management Concepts & Organisational Behaviour - Motivation
HERZBERG’S Two Factor theory of MOTIVATION
Posted On :
A significant development in motivation theory was distinction between motivational and maintenance factors in job situation.
HERZBERG’S Two Factor
theory of MOTIVATION
A significant development in motivation theory was distinction between motivational and maintenance factors in job situation. A research was conducted by Herzberg and his associates based on the interview of 200 engineers and accountants who worked for eleven different firms in Pittsburgh area. These men were asked to recall specific incidents in their experience which made them feel particularly bad about jobs. The findings of the research led to draw a distinction between what are called as ‘motivators’ and ‘hygiene factors’. To this group of engineers and accountants, the real motivators were opportunities to gain expertise and to handle more demanding assignments. Hygiene factors served to prevent loss of money and efficiency. Thus, hygiene factors provide no motivation to the employees, but the absence of these factors serves as dissatisfies.
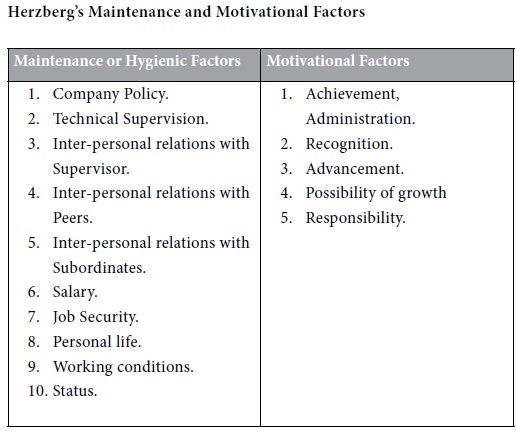
Some job conditions operate primarily to dissatisfy employees. Their presence does not motivate employees in a strong way. Many of these factors are traditionally perceived by management as motivators, but the factors are really more potent as dissatisfiers. They are called maintenance factors in job because they are necessary to maintain a reasonable level of satisfaction among the employees. Their absence proves to be strong dissatisfiers. They are also known as ‘dissatisfiers’ or ‘hygienic factors’ because they support employees’ mental health. Another set of job conditions operates primarily to build strong motivation and high job satisfaction among the employees. These conditions are ‘Motivational Factors’. Herzberg’s maintenance and motivational factors have been shown in the table given below.
A significant development in motivation theory was distinction between motivational and maintenance factors in job situation. A research was conducted by Herzberg and his associates based on the interview of 200 engineers and accountants who worked for eleven different firms in Pittsburgh area. These men were asked to recall specific incidents in their experience which made them feel particularly bad about jobs. The findings of the research led to draw a distinction between what are called as ‘motivators’ and ‘hygiene factors’. To this group of engineers and accountants, the real motivators were opportunities to gain expertise and to handle more demanding assignments. Hygiene factors served to prevent loss of money and efficiency. Thus, hygiene factors provide no motivation to the employees, but the absence of these factors serves as dissatisfies.
Some job conditions operate primarily to dissatisfy employees. Their presence does not motivate employees in a strong way. Many of these factors are traditionally perceived by management as motivators, but the factors are really more potent as dissatisfiers. They are called maintenance factors in job because they are necessary to maintain a reasonable level of satisfaction among the employees. Their absence proves to be strong dissatisfiers. They are also known as ‘dissatisfiers’ or ‘hygienic factors’ because they support employees’ mental health. Another set of job conditions operates primarily to build strong motivation and high job satisfaction among the employees. These conditions are ‘Motivational Factors’. Herzberg’s maintenance and motivational factors have been shown in the table given below.

Hygienic factors include such
things as wages, fringe benefits, Physical conditions and overall company
policy and administration. The presence of these factors at a satisfactory
level prevents job dissatisfaction, but they do not provide motivation to the
employees. So they are not considered as motivational factors, on the other
hand, are essential for increasing the productivity of the employees. They are
also known as satisfiers and include such factors as recognition, feeling of
accomplishment and achievement, opportunity of advancement and potential for
personal growth, responsibility and sense of job and individual importance, new
experience and challenging work etc.
Tags : Management Concepts & Organisational Behaviour - Motivation
Last 30 days 1021 views