Home | ARTS | Marketing Management
|
The Technology / Market Matrix - New Products Development Strategies
MARKETING MANAGEMENT - New Products Development Strategies
The Technology / Market Matrix - New Products Development Strategies
Posted On :
Another way to look at new products is through one of strategic planning’s most useful analytical devices – an array of future options or alternative such as that shown in figure 1.1.
The Technology / Market Matrix
Another way to look at new products is through one of strategic planning’s most useful analytical devices – an array of future options or alternative such as that shown in figure 1.1, A firm has roughly four way to gain new business – see quadrants A, B, C and D in the figure 13.1
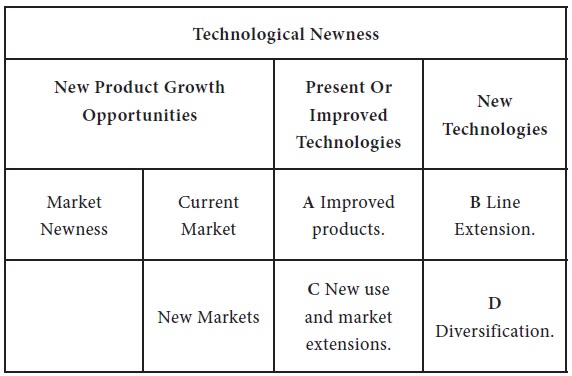
This is the easiest strategy – selling more of the product line to current customers. This involves product improvement, smarter marketing and increasing market shares. New products management plays a minor role and the activity is often called market development, not product development.
It involves capitalizing on the firm’s current strengths. If the strengths is franchise with a particular customer group, quadrant B’s strategy is to develop more product t sell to them. Such products don’t have to be unique because the franchise will help sell them.
This is suitable when the firm’s strength is technology –something the firm known or does especially well.
Example are coca-cola’s bottling system. Coming’s glass skills and Hewlett packand’s electronics capabilities.
Such firms try to develop new products that exploit their technology.
It involves leaving both the firm’s customer base and its technology base. This high-risk strategy should be used only under special circumstances. The new products may come by acquisition rather than through internal product development.
DCM’S entry into the LCV market fits into this category.
Another way to look at new products is through one of strategic planning’s most useful analytical devices – an array of future options or alternative such as that shown in figure 1.1, A firm has roughly four way to gain new business – see quadrants A, B, C and D in the figure 13.1

Product improvement
This is the easiest strategy – selling more of the product line to current customers. This involves product improvement, smarter marketing and increasing market shares. New products management plays a minor role and the activity is often called market development, not product development.
Line Extension
It involves capitalizing on the firm’s current strengths. If the strengths is franchise with a particular customer group, quadrant B’s strategy is to develop more product t sell to them. Such products don’t have to be unique because the franchise will help sell them.
New use and market extensions
This is suitable when the firm’s strength is technology –something the firm known or does especially well.
Example are coca-cola’s bottling system. Coming’s glass skills and Hewlett packand’s electronics capabilities.
Such firms try to develop new products that exploit their technology.
Diversification
It involves leaving both the firm’s customer base and its technology base. This high-risk strategy should be used only under special circumstances. The new products may come by acquisition rather than through internal product development.
DCM’S entry into the LCV market fits into this category.
Tags : MARKETING MANAGEMENT - New Products Development Strategies
Last 30 days 690 views












