Home | ARTS | Management Concepts & Organisational Behaviour
|
The Matrix Structure - Organisation Structure And Design
Management Concepts & Organisational Behaviour - Organisation Structure And Design
The Matrix Structure - Organisation Structure And Design
Posted On :
The matrix structure is a hybrid organization form, containing of characteristics of both project and functional structures.
The
Matrix Structure
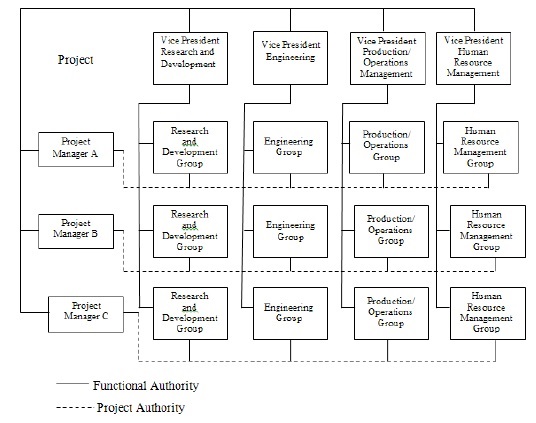
The matrix structure is a hybrid organization form, containing of characteristics of both project and functional structures. In consumer goods industries, it could contain the characteristics of both product and functional departments. This structure allows operational responsibilities to be divided into two parts. One part contains all the responsibilities associated with the management of an independent business and it’s given to an individual who is called “business manager” or “product manger”. The other part contains all the responsibilities related to the management of resources needed to get the job done. The person responsible for these is the “functional manager” or “resource manager” in charge of the functions like production, marketing, finance, personnel and so on. The matrix is built around a cooperative relationship between the project/ product manager and the functional/ resource manager. Thus, project staff members in a matrix structure have a dual responsibility. First, they are responsible to the head of their line superior and will continue to be so. But the project manager exercises what is called project authority over the project staff. Figure presents these dual responsibilities in a matrix form of organization.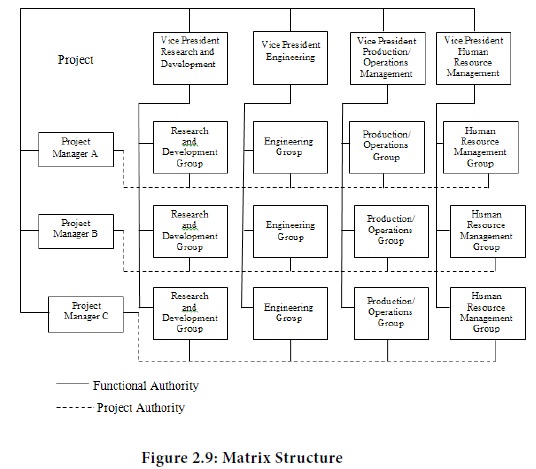
When the concepts of functional and project authority are brought together, the result is an organization structure that is both vertical and horizontal. The vertical pattern is brought about by the typical line authority flowing down from superior to subordinate. The horizontal authority flow runs through both the scalar principle.
Companies like Larsen & Tourbro (L&T), U.P. Construction Corporation, Afcons-Pauling, etc., adopt this structure for the execution of various projects. For instance, L&T’s construction of Jawaharlal Football Stadium in Chennai and Afcons-Pauling’s laying the East Coast Road are big projects themselves. The execution of such projects is entrusted to a team drawn from the functional departments of the headquarters. The overall responsibility for the project lies with project manager. The people who work in the project are responsible to the project manager as well as their functional head from whom they are drawn. The matrix may be temporary or permanent. In construction and turnkey activities, project is disbanded after the execution, whereas it may take a permanent form in the case of consumer goods company.
-- Specialized knowledge is available to all projects or products on an equal basis. Knowledge and experience can be transferred from one project to another;
-- Utilization of manpower can be flexible because a reservoir of specialists is maintained in functional departments. These specialists can be deployed to the various projects for optimum use of their services;
-- Responsibility for the overall execution, management, and profit is with the project manager who acts like a chief executive;
-- Project people have a functional home when they are no longer needed on a given projects; and
-- A better balance between time, cost and performance can be obtained through the built-in checks and balances and the continuous negotiations carried on between the project and the functional organization.
Inspite of its advantages, matrix structure suffers from some disadvantages. Mangers have to learn to deal effectively with them.
-- If the organization has too many projects, the result may be severe layering of matrixes. Uncontrolled growth of matrix structures often results in power struggles between managers;
-- The major disadvantage relates to power struggles. Since use of the matrix means use of dual command, managers often end up in conflicts;
-- Matrix entails wide use of group decision making because group cooperation is required for success. The inevitability of group cooperation at times delays decision making; and
-- Matrix structure may be expensive. The dual chain of command may cause management costs to double.
Despite the drawbacks, matrix structure is preferred by many organizations because of the overriding advantages. In addition to construction and engineering, consumer goods, banking, insurance and computer companies are now using it. Variations of matrix are also used by hospitals and other professional organizations.
The matrix structure is a hybrid organization form, containing of characteristics of both project and functional structures. In consumer goods industries, it could contain the characteristics of both product and functional departments. This structure allows operational responsibilities to be divided into two parts. One part contains all the responsibilities associated with the management of an independent business and it’s given to an individual who is called “business manager” or “product manger”. The other part contains all the responsibilities related to the management of resources needed to get the job done. The person responsible for these is the “functional manager” or “resource manager” in charge of the functions like production, marketing, finance, personnel and so on. The matrix is built around a cooperative relationship between the project/ product manager and the functional/ resource manager. Thus, project staff members in a matrix structure have a dual responsibility. First, they are responsible to the head of their line superior and will continue to be so. But the project manager exercises what is called project authority over the project staff. Figure presents these dual responsibilities in a matrix form of organization.

When the concepts of functional and project authority are brought together, the result is an organization structure that is both vertical and horizontal. The vertical pattern is brought about by the typical line authority flowing down from superior to subordinate. The horizontal authority flow runs through both the scalar principle.
Companies like Larsen & Tourbro (L&T), U.P. Construction Corporation, Afcons-Pauling, etc., adopt this structure for the execution of various projects. For instance, L&T’s construction of Jawaharlal Football Stadium in Chennai and Afcons-Pauling’s laying the East Coast Road are big projects themselves. The execution of such projects is entrusted to a team drawn from the functional departments of the headquarters. The overall responsibility for the project lies with project manager. The people who work in the project are responsible to the project manager as well as their functional head from whom they are drawn. The matrix may be temporary or permanent. In construction and turnkey activities, project is disbanded after the execution, whereas it may take a permanent form in the case of consumer goods company.
Advantages of Matrix Organization:
-- Specialized knowledge is available to all projects or products on an equal basis. Knowledge and experience can be transferred from one project to another;
-- Utilization of manpower can be flexible because a reservoir of specialists is maintained in functional departments. These specialists can be deployed to the various projects for optimum use of their services;
-- Responsibility for the overall execution, management, and profit is with the project manager who acts like a chief executive;
-- Project people have a functional home when they are no longer needed on a given projects; and
-- A better balance between time, cost and performance can be obtained through the built-in checks and balances and the continuous negotiations carried on between the project and the functional organization.
Disadvantages:
Inspite of its advantages, matrix structure suffers from some disadvantages. Mangers have to learn to deal effectively with them.
-- If the organization has too many projects, the result may be severe layering of matrixes. Uncontrolled growth of matrix structures often results in power struggles between managers;
-- The major disadvantage relates to power struggles. Since use of the matrix means use of dual command, managers often end up in conflicts;
-- Matrix entails wide use of group decision making because group cooperation is required for success. The inevitability of group cooperation at times delays decision making; and
-- Matrix structure may be expensive. The dual chain of command may cause management costs to double.
Despite the drawbacks, matrix structure is preferred by many organizations because of the overriding advantages. In addition to construction and engineering, consumer goods, banking, insurance and computer companies are now using it. Variations of matrix are also used by hospitals and other professional organizations.
Tags : Management Concepts & Organisational Behaviour - Organisation Structure And Design
Last 30 days 1564 views