Home | ARTS | Management Concepts & Organisational Behaviour
|
Product/ Market Departmentation - Organisation Structure And Design
Management Concepts & Organisational Behaviour - Organisation Structure And Design
Product/ Market Departmentation - Organisation Structure And Design
Posted On :
As organizations are not static, they grow in size either by broadening its product line, or by expanding geographically.
Product/
Market Departmentation
As organizations are not static, they grow in size either by broadening its product line, or by expanding geographically. Further, as the size of the organization increases, some of the disadvantages become more apparent. The organization is rather forced to look for other models in tune with the requirements. In such situations, managements opt for various other types of departmentation, in order to have the right focus on the product or market or the process. Three patterns are adopted generally by organizations depending on the specific requirements to overcome the limitations of functional structure. They are product, territorial and customer departmentation.
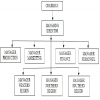
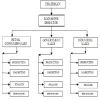
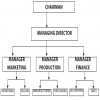
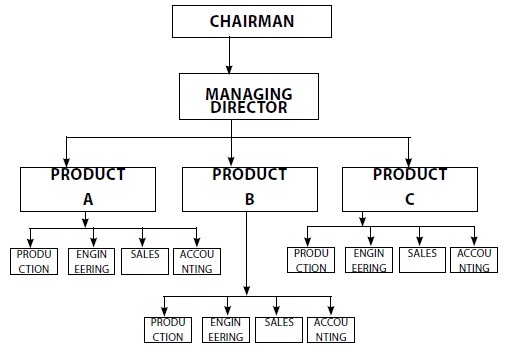
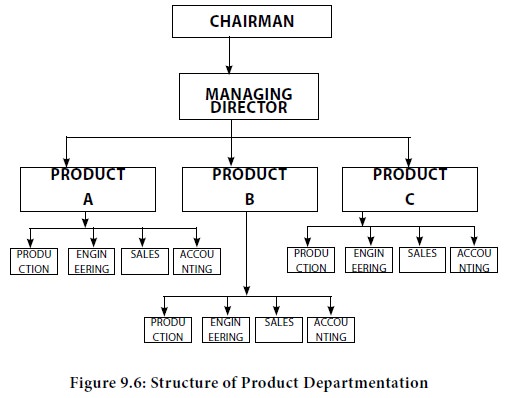
One of the most common ways in which businesses grow is by expanding the product mix. If the organization is successful in expansion, several product lines may attain such high sales volume that each product category or line may be a separate division. Large organizations like Kirloskar, Hindustan Unilever, Godrej have managed such expansion of product lines effectively by creating separate departments or divisions for the various products. Under product departmentation, a single manager, often referred to as the product manager, is delegated authority over all activities required to produce and market that product. The focus in the product departmentation, therefore, shifts on to the product and all the activities related to the production and marketing of the product. As against functions in the functional departmentation, basic products or services become the primary or major departments in the product departmentation as could be seen in the following figure.
-- Product departmentation places emphasis on the basic products, the success of which is critical to the survival of the organization;
-- Since all revenues and costs are assigned to a particular product, cost centres can be established. High profit areas can be encouraged and low/unprofitable product lines can be dropped. Thus, responsibility for cost reduction and profits can be established at the division level;
As organizations are not static, they grow in size either by broadening its product line, or by expanding geographically. Further, as the size of the organization increases, some of the disadvantages become more apparent. The organization is rather forced to look for other models in tune with the requirements. In such situations, managements opt for various other types of departmentation, in order to have the right focus on the product or market or the process. Three patterns are adopted generally by organizations depending on the specific requirements to overcome the limitations of functional structure. They are product, territorial and customer departmentation.
Product Departmentation
One of the most common ways in which businesses grow is by expanding the product mix. If the organization is successful in expansion, several product lines may attain such high sales volume that each product category or line may be a separate division. Large organizations like Kirloskar, Hindustan Unilever, Godrej have managed such expansion of product lines effectively by creating separate departments or divisions for the various products. Under product departmentation, a single manager, often referred to as the product manager, is delegated authority over all activities required to produce and market that product. The focus in the product departmentation, therefore, shifts on to the product and all the activities related to the production and marketing of the product. As against functions in the functional departmentation, basic products or services become the primary or major departments in the product departmentation as could be seen in the following figure.

Advantages:
-- Product departmentation places emphasis on the basic products, the success of which is critical to the survival of the organization;
-- Since all revenues and costs are assigned to a particular product, cost centres can be established. High profit areas can be encouraged and low/unprofitable product lines can be dropped. Thus, responsibility for cost reduction and profits can be established at the division level;
-- Proper coordination
of all functional areas can be achieved as all the functional managers work as
a team under close supervision of the product manager. Since the department or division is
multifunctional, it often operates like an independent division or company
within the large company;
-- Enables quick-response to changes in environment as compared to functionally organized firm;
-- Provide managers a training ground in general management which is useful in overcoming narrow functional perspective; and
-- Expansion and diversification of business is made easy by creating new departments for the new products that are added to the existing business.
-- Requires adequate availability of persons with general management abilities as more and more departments are created for the various products;
-- The product departments may try to become too autonomous thereby making top management control difficult; and
-- It is also common to find product departments engaged in the duplication of efforts. Each product unit has its own functional departments. These may not be sufficiently large to make maximum use of facilities. Thus product departmentation becomes an expensive organizational form, if adopted without proper justification in terms of the products strengths and market potential.
-- Enables quick-response to changes in environment as compared to functionally organized firm;
-- Provide managers a training ground in general management which is useful in overcoming narrow functional perspective; and
-- Expansion and diversification of business is made easy by creating new departments for the new products that are added to the existing business.
Disadvantages:
-- Requires adequate availability of persons with general management abilities as more and more departments are created for the various products;
-- The product departments may try to become too autonomous thereby making top management control difficult; and
-- It is also common to find product departments engaged in the duplication of efforts. Each product unit has its own functional departments. These may not be sufficiently large to make maximum use of facilities. Thus product departmentation becomes an expensive organizational form, if adopted without proper justification in terms of the products strengths and market potential.
Tags : Management Concepts & Organisational Behaviour - Organisation Structure And Design
Last 30 days 2816 views