Home | ARTS | Accounting For Managers
|
Meaning of Concepts of Cash, Cash Flow And Cash Flow Analysis
Accounting For Managers - Funds Flow Analysis And Cash Flow Analysis
Meaning of Concepts of Cash, Cash Flow And Cash Flow Analysis
Posted On :
While explaining the concept of `fund’ it was mentioned that in a narrower sense the term `fund’ is also used to denote cash.
The term `cash’ in the context of cash flow analysis stands for cash and bank balances. Cash flow refers to the actual movement of cash in and out of an organisation. When cash flows into the organisation it is called cash inflow or positive cash flow. In the same way when cash flows out of the organisation, it is called cash outflow or negative cash flows. Cash flow analysis is an analysis based on the movement of cash and bank balances. Under cash flow analysis, all movements of cash would be considered.
Cash Flow Statement
A cash flow statement is a statement depicting changes in cash position from one period to another i.e. The result of cash flow analysis is given in the cash flow statement. For example if the cash balance of a concern as per its balance sheet as on 31st march 2004 is rs.90,000 and the cash balance as per its balance sheet as on 31st march 2005 is rs.1,20,000, there has been an inflow of cash of rs.30,000 in the year 2004-05 as compared to the year 2003-04. The cash flow statement explains the reasons for such inflows or outflows of cash as the case may be.
Normally the following are principal sources of inflows of cash:
- Issue Of Shares And Debentures For Cash
- Sale Of Fixed Assets And Investments For Cash
- Borrowings From Banks And Other Financial Institution 169
- Cash From Operations Outflows of cash generally include:
- Redemption Of Shares And Debentures By Cash
- Purchase Of Fixed Assets And Investments By Cash
- Repayment Of Loans
- Cash Lost In Operations
The following is the format of a cash flow statement: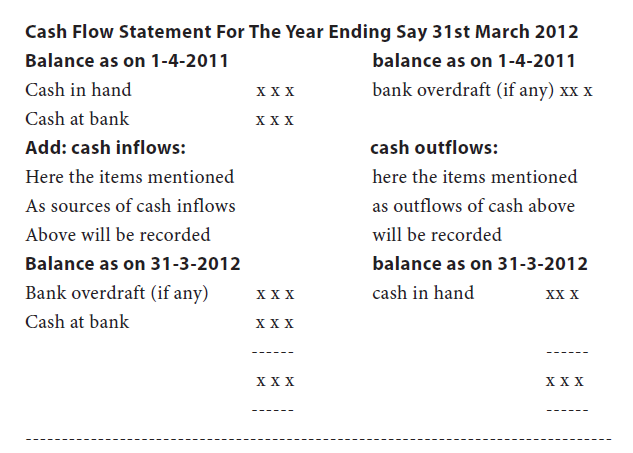

The accounting standard 3 issued by the institute of chartered accountants of india requires the companies to prepare cash flow statement and present them as part of their annual reports.
Tags : Accounting For Managers - Funds Flow Analysis And Cash Flow Analysis
Last 30 days 955 views












