Research Methodology - Experiments
Informal Experimental Designs - Experiments
Posted On :
In this design, a single test group or area is selected and the dependent variable is measured before introduction of the treatment.
Informal
Experimental Designs
Before and after without control design:
In this design, a single test group or area is selected and the dependent variable is measured before introduction of the treatment. Then the treatment is introduced and the dependent variable is measured again after the treatment has been introduced. The effect of the treatment would be equal to the level of the phenomenon after the treatment minus the level of the phenomenon before the treatment. Thus, the design can be presented in the following manner:
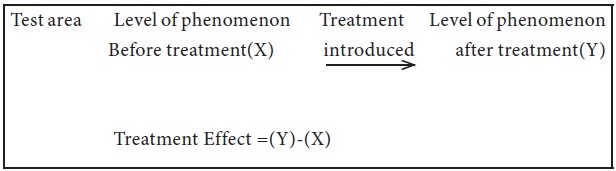
The main difficulty of such a design is that with the passage of time considerable extraneous variations may be there in its treatment effect.
After-only with control design:
Two groups or areas are selected in this design and the treatment is introduced into the test area only. Then the dependent variable is measured in both the areas at the same time. Treatment impact is assessed by subtracting the value of the dependent variable in the control area from its value in the test area. The design can be presented in the following manner:
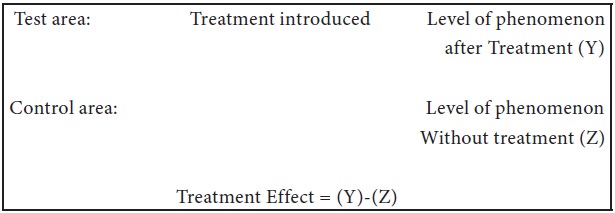
The basic assumption in this type of design is that the two areas are identical with respect to their behavior towards the phenomenon considered. If this assumption is not true, there is the possibility of extraneous variation entering into the treatment effect.
Before and after with control design:
In this design, two areas are selected and the dependent variable is measured in both the areas for an identical time-period before the treatment. Thereafter, the treatment is introduced into the test area only
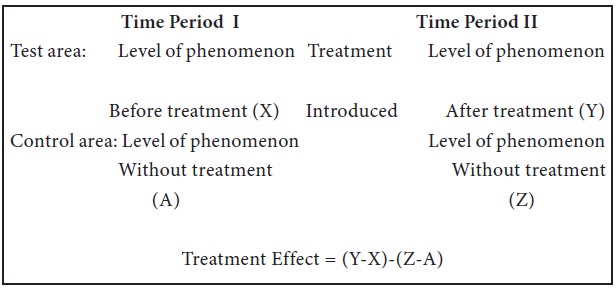
This design is superior to the
previous two designs because it avoids extraneous variation resulting both from
the passage of time and from non-comparability of the rest and control areas.
But at times, due to lack of historical data time or a comparable control area,
we should prefer to select one of the first two informal designs stated above.
Tags : Research Methodology - Experiments
Last 30 days 7702 views












