MARKETING MANAGEMENT - Retailers And Wholesalers
Classification Of Retail Formats - Retailers And Wholesalers
Posted On :
Retailers have changed dramatically according to the changing trends and the evolving needs of the consumers.
Classification Of Retail Formats
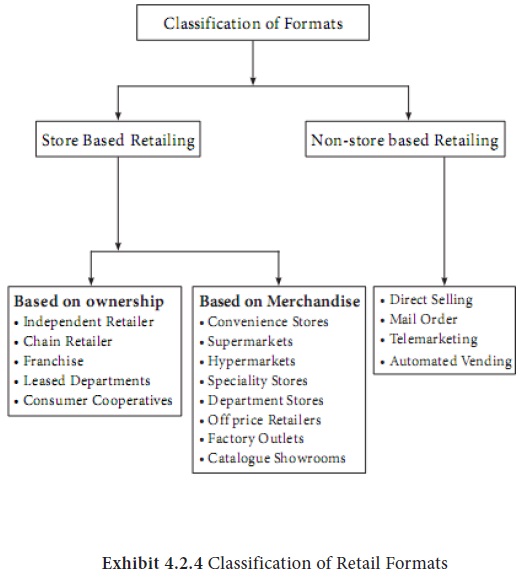
Retail formats are broadly classified into store based and non-store based retail formats. The store based formats are the traditional models where you have brick and motor stores while a direct relationship with the customer is the trust area of the non-store based. The store based is further divided based on the ownership and the merchandise held by the stores.
An independent Retailer- these are retail stores which owns only one retail outlet. Usually the format is passed from generation to generation and this is has a proprietor who owns the store. 80 percent of the retail stores fall under this class in our country. From the paan shops to the kirana stores we find this type of stores in our country. Saravana stores is a good example.
They are otherwise known as the corporate chain where we find two or more outlets under a common ownership. These stores have commonality in merchandise, store layout, ambience etc. The advantage of this particular type of format is the economies of scale they enjoy. Here since they are scattered all over consumer preference may not be given greater importance. Some of the chain retailers are Mega mart and Nilgris.
This is a contractual agreement between two parties where the franchiser allows the franchisee to conduct the business under an established name in return for a fee. Some of the well-known franchisers are Mc Donald’s, Archie’s stores, Pizza Hut etc
These is otherwise known as shops in shops. In this particular type a portion of a store is rented or leased to a third party. We see Coffee Day having outlets in Crossword bookstores or Pizza Corners in multiplexes.
These are retail institutions owned by consumers and this is mainly because of dissatisfied customers whose needs were never fulfilled by the existing retailers. Some of these are either owned by the government or backed by government. This helps in price negotiations and is one of the prime players when price quality is considered as an important parameter. We find Farmers cooperatives, Mahila cooperatives and employee cooperatives in different locations.
These are relatively small stores near residential area and are open for long hours. They carry limited line of high turnover products and have self-service formats. This format is emerging in India and they work seven days a week. BP’s In&Out, HP Speed mart fall under this category.
These stores are relatively large and operate on low costs, low margins, high volume and offering a self-service format. The store houses food, laundry, and household maintenance products. Some examples for this format are Nilgiris and Food World.
Has it’s origins in the US, these are stores that have a space of about 80,000 to 2,20,000 sq ft. the combine supermarket, discount stores and the warehouse principles in setting up them. They are usually situated on the outskirts of big cities and towns. In India the size is proportional and is not too big. Big bazaar is considered as a hypermarket.
They are characterized by narrow line, with deep assortments in that particular product line. For the speciality stores a well-defined target market is essential. Personal attention, store ambience, customer service are
important to the retailers. Music World, Gautier
Furniture’s are examples of this type of retailers. A new form of speciality
stores have emerged and are called the category killers, who offer products
from a single product line at economical prices. This particular concept has
found tremendous appeal with the Indian market. Toys kemp in Bangalore is a
classic example of this type of stores
This format originated in the mid-nineteenth century and is popular in many parts. They are large scaled retail outlets whose merchandise offer runs across different product lines. Apparel and home furnishing are the most common categories found in the departmental stores. The size of an average Indian departmental store varies between 20,000-40,000 sq ft, while that of the western stores are around 75,000 + sq ft. Some of the big players in this format are Life style, Globus, Ebony and so on.
In this format, the merchandise is sold less than the MRP. The retailers buy manufacturer’s seconds or overruns as a result of which the merchandise may be in odd sizes or may be minor defects. Some off-price retail stores are manufacturer run and are called the factory outlets and sell the manufacturer’s products at lesser prices compared to other retailers. Mega Mart, Levi’s factory outlets are some of the examples of this format.
They are retailers who specialize in goods like jewellery, electronics. Customers have to check through a catalogue and then order the product they need. This concept s still in the nascent stage in the Indian market
A form that is gaining ground in the non-store retailing, in this type of retailing the customers have a direct relationship with the retailers. The non-store retailing is broadly classified into direct selling and direct response marketing, which incorporates mail orders, television shopping and electronic shopping
This form of retailing is common for products like cosmetics, food products, educational materials and basic home appliances where the consumer will be in his place while the marketer brings the products to his doorsteps. Over the last decade the concept has grown leaps and bounds and according to the direct selling industry in India, there has been a 60-65 percent growth in sales turnover from this industry alone every year.
Using the telephone to sell directly to consumers has become the major direct marketing tool. Marketers use outbound telephone charges to help sell their products and services. Some telemarketing systems are fully automated. Marketers also use inbound toll-free numbers to receive orders arising from interactive marketing done through television and radio ads, direct mail or catalogs. Telemarketing is used in industrial as well as consumer marketing. The recent explosion in unsolicited telephone marketing has annoyed many consumers who object to the almost daily junk phone calls that pull them away from their normal routines. Today mobile companies, insurance companies and banks are using this technique.
This form eliminates personal selling and the physical store operations. This format is appropriate to specialty products or narrow product lines and where the target market is well defined. The main advantage of this type of retailing is the convenience they offer to the customers. In India, long since book publishers (Prentice –Hall, Tata McGraw Hill, Sultan chand etc. )are using this method of selling.
Television Shopping- the television based retailing has received fair amount of success in India. With players like Asian Sky shop, TSN products are advertised on televisions with features, warranties and prices discounts. Phone numbers are given for different cities where the customers have to give a call to the nearest place and order the products. The products are then home delivered.
The fastest growing medium to do retailing is electronic medium. Every brick and motor retailers are looking for click only models whereby customers can order products at the click of a button. This format virtually eliminates the physical infrastructure needed and can help in reducing the cost of operations. An effective supply chain is what these players need. It has been estimated that the Indian online shopping market is worth Rs.150 crores with 25% growth in 2005-06. The industry is expected to grow in the next 3-5 years. E-bay, rediff.com are some of the online shopping portals in the country.
Pantaloon: Fashion by Pantaloon
Pantaloon is the company’s departmental store and part of life style retail format. In fact, PRIL took its very initial steps in the retail journey by setting up the first Pantaloon store in Kolkata in 1997. In a short time Pantaloon has been able to carve a special place for it self in the hearts and minds of the aspirational Indian customers. The company has depth of offering for both men and women at affordable prices. A striking characteristic of Pantaloon has been the strength of its private label programme. John Miller, Ajile. Scottsvile, Lombard, Annabelle are some of the successful brands created by the company.
Big Bazaar: Is se sasta aur acha kahin nahin
Big bazaar is the company’s foray into the world of hypermarket discount stores, the first of its kind in India. Price and the wide array of products are the USP’s of Big Bazaar. Close to two lakhs products are available under one roof at prices lower by 2 to 60 per cent over the corresponding market prices. The high quality of service, good ambience, implicit guarantees and continuous discount programmes have helped in changing the face of the Indian retailing industry. A leading foreign broking house compared the rush at Big Bazaar to that of a local suburban train Food Bazaar – Wholesale prices
Food Bazaar’s core concept is to create a blend of a typical Indian Bazaar and International supermarket atmosphere with the objective of giving the customer all the advantages of Quality, Range and Price associated with large format stores and also the comfort to See, Touch and Feel the products. The company has recently launched an aggressive private label programme with its own brands of tea, salt, spices, pulses, jams, ketchups etc. With unbeatable prices and vast variety (there are
Retailers
have changed dramatically according to the changing trends and the evolving
needs of the consumers. Different retail format have emerged over the years and
each have been an improvisation over the earlier formats. Retail stores can be
classified broadly based on store based and non-store based, the store based is
otherwise the brick and the motor stores while the non-store based are those,
which do not use the traditional format. Ownership in store based is further
divided based on ownership and merchandise. This section discusses some of the
prominent formats under each classification

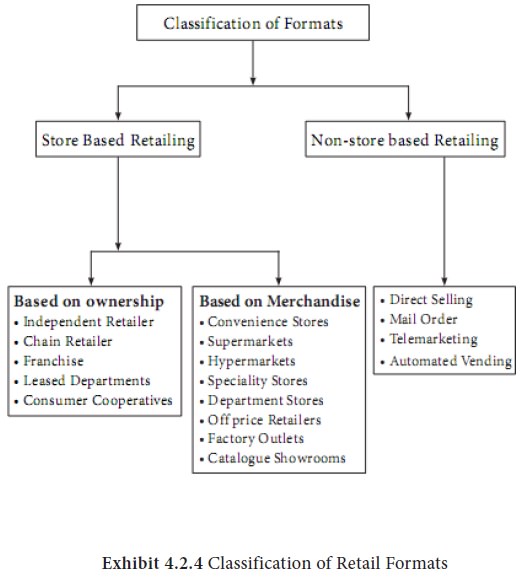
Retail formats are broadly classified into store based and non-store based retail formats. The store based formats are the traditional models where you have brick and motor stores while a direct relationship with the customer is the trust area of the non-store based. The store based is further divided based on the ownership and the merchandise held by the stores.
Classification Based On Ownership
An independent Retailer- these are retail stores which owns only one retail outlet. Usually the format is passed from generation to generation and this is has a proprietor who owns the store. 80 percent of the retail stores fall under this class in our country. From the paan shops to the kirana stores we find this type of stores in our country. Saravana stores is a good example.
A Chain Retailer
They are otherwise known as the corporate chain where we find two or more outlets under a common ownership. These stores have commonality in merchandise, store layout, ambience etc. The advantage of this particular type of format is the economies of scale they enjoy. Here since they are scattered all over consumer preference may not be given greater importance. Some of the chain retailers are Mega mart and Nilgris.
Franchising
This is a contractual agreement between two parties where the franchiser allows the franchisee to conduct the business under an established name in return for a fee. Some of the well-known franchisers are Mc Donald’s, Archie’s stores, Pizza Hut etc
Leased Departments
These is otherwise known as shops in shops. In this particular type a portion of a store is rented or leased to a third party. We see Coffee Day having outlets in Crossword bookstores or Pizza Corners in multiplexes.
Consumer Cooperatives
These are retail institutions owned by consumers and this is mainly because of dissatisfied customers whose needs were never fulfilled by the existing retailers. Some of these are either owned by the government or backed by government. This helps in price negotiations and is one of the prime players when price quality is considered as an important parameter. We find Farmers cooperatives, Mahila cooperatives and employee cooperatives in different locations.
Classification Based On Merchandise
Convenience Stores
These are relatively small stores near residential area and are open for long hours. They carry limited line of high turnover products and have self-service formats. This format is emerging in India and they work seven days a week. BP’s In&Out, HP Speed mart fall under this category.
Supermarkets
These stores are relatively large and operate on low costs, low margins, high volume and offering a self-service format. The store houses food, laundry, and household maintenance products. Some examples for this format are Nilgiris and Food World.
Hypermarkets
Has it’s origins in the US, these are stores that have a space of about 80,000 to 2,20,000 sq ft. the combine supermarket, discount stores and the warehouse principles in setting up them. They are usually situated on the outskirts of big cities and towns. In India the size is proportional and is not too big. Big bazaar is considered as a hypermarket.
Stores
They are characterized by narrow line, with deep assortments in that particular product line. For the speciality stores a well-defined target market is essential. Personal attention, store ambience, customer service are
Departmental Stores
This format originated in the mid-nineteenth century and is popular in many parts. They are large scaled retail outlets whose merchandise offer runs across different product lines. Apparel and home furnishing are the most common categories found in the departmental stores. The size of an average Indian departmental store varies between 20,000-40,000 sq ft, while that of the western stores are around 75,000 + sq ft. Some of the big players in this format are Life style, Globus, Ebony and so on.
Off-price Retailers
In this format, the merchandise is sold less than the MRP. The retailers buy manufacturer’s seconds or overruns as a result of which the merchandise may be in odd sizes or may be minor defects. Some off-price retail stores are manufacturer run and are called the factory outlets and sell the manufacturer’s products at lesser prices compared to other retailers. Mega Mart, Levi’s factory outlets are some of the examples of this format.
Catalogue showrooms
They are retailers who specialize in goods like jewellery, electronics. Customers have to check through a catalogue and then order the product they need. This concept s still in the nascent stage in the Indian market
Non-Store Retailing
A form that is gaining ground in the non-store retailing, in this type of retailing the customers have a direct relationship with the retailers. The non-store retailing is broadly classified into direct selling and direct response marketing, which incorporates mail orders, television shopping and electronic shopping
Direct selling
This form of retailing is common for products like cosmetics, food products, educational materials and basic home appliances where the consumer will be in his place while the marketer brings the products to his doorsteps. Over the last decade the concept has grown leaps and bounds and according to the direct selling industry in India, there has been a 60-65 percent growth in sales turnover from this industry alone every year.
Telemarketing
Using the telephone to sell directly to consumers has become the major direct marketing tool. Marketers use outbound telephone charges to help sell their products and services. Some telemarketing systems are fully automated. Marketers also use inbound toll-free numbers to receive orders arising from interactive marketing done through television and radio ads, direct mail or catalogs. Telemarketing is used in industrial as well as consumer marketing. The recent explosion in unsolicited telephone marketing has annoyed many consumers who object to the almost daily junk phone calls that pull them away from their normal routines. Today mobile companies, insurance companies and banks are using this technique.
Mail order Retailing
This form eliminates personal selling and the physical store operations. This format is appropriate to specialty products or narrow product lines and where the target market is well defined. The main advantage of this type of retailing is the convenience they offer to the customers. In India, long since book publishers (Prentice –Hall, Tata McGraw Hill, Sultan chand etc. )are using this method of selling.
Television Shopping- the television based retailing has received fair amount of success in India. With players like Asian Sky shop, TSN products are advertised on televisions with features, warranties and prices discounts. Phone numbers are given for different cities where the customers have to give a call to the nearest place and order the products. The products are then home delivered.
Electronic Shopping
The fastest growing medium to do retailing is electronic medium. Every brick and motor retailers are looking for click only models whereby customers can order products at the click of a button. This format virtually eliminates the physical infrastructure needed and can help in reducing the cost of operations. An effective supply chain is what these players need. It has been estimated that the Indian online shopping market is worth Rs.150 crores with 25% growth in 2005-06. The industry is expected to grow in the next 3-5 years. E-bay, rediff.com are some of the online shopping portals in the country.
Pantaloon: Fashion by Pantaloon
Pantaloon is the company’s departmental store and part of life style retail format. In fact, PRIL took its very initial steps in the retail journey by setting up the first Pantaloon store in Kolkata in 1997. In a short time Pantaloon has been able to carve a special place for it self in the hearts and minds of the aspirational Indian customers. The company has depth of offering for both men and women at affordable prices. A striking characteristic of Pantaloon has been the strength of its private label programme. John Miller, Ajile. Scottsvile, Lombard, Annabelle are some of the successful brands created by the company.
Big Bazaar: Is se sasta aur acha kahin nahin
Big bazaar is the company’s foray into the world of hypermarket discount stores, the first of its kind in India. Price and the wide array of products are the USP’s of Big Bazaar. Close to two lakhs products are available under one roof at prices lower by 2 to 60 per cent over the corresponding market prices. The high quality of service, good ambience, implicit guarantees and continuous discount programmes have helped in changing the face of the Indian retailing industry. A leading foreign broking house compared the rush at Big Bazaar to that of a local suburban train Food Bazaar – Wholesale prices
Food Bazaar’s core concept is to create a blend of a typical Indian Bazaar and International supermarket atmosphere with the objective of giving the customer all the advantages of Quality, Range and Price associated with large format stores and also the comfort to See, Touch and Feel the products. The company has recently launched an aggressive private label programme with its own brands of tea, salt, spices, pulses, jams, ketchups etc. With unbeatable prices and vast variety (there are
Tags : MARKETING MANAGEMENT - Retailers And Wholesalers
Last 30 days 10464 views














