Financial Management - WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT
Tandon Committee - Working Capital And Banking Policy
Posted On :
A study group under the chairmanship of Shri P.L. Tandon was constituted in 1974 by the RBI in order to frame guidelines for bank credit.
Tandon
Committee
A study group under the chairmanship of Shri P.L. Tandon was constituted in 1974 by the RBI in order to frame guidelines for bank credit. The terms of reference of the committee were as follows.
1. To suggest guidelines for commercial banks to follow up and supervise credit from the point of view of ensuring proper end-use of funds and keeping a watch on the safety of advances.
2. To make recommendations for obtaining periodical information that may be obtained by banks from the borrower.
3. To make suggestions for prescribing inventory norms for different industries.
4. To suggest criteria regarding satisfactory capital structure and sound financial basis in relation to borrowings.
5. To suggest whether the existing patterns of financing working capital requirements by cash credit / overdraft system, etc. are required to be modified, if so, to suggest modifications.
On the basis of the reference given above, the committee studied the existing system of working capital finance provided to industry and identified the following as its major weaknesses.
1. The banks do not have any credit appraisal or planning. It is the borrower who decides how much he would borrow.
2. The security-based approach to lending has led to division of funds to purchase of fixed assets.
3. Bank credit is treated as the first source of finance rather than being taken as a supplementary to other sources of finance.
4. The working capital finance should be made available only for a short period, as it has otherwise, led to accumulation of inventories with the industry.
The report was submitted on 9th August 1975 and it is a landmark in the history of financing working capital by commercial banks in India. The Tandon Committee made comprehensive recommendation regarding the bank lending practices, which can be broadly classified into four groups’. Important features of the Tandon Committee recommendations based on the fixation of norms for bank lending to industry are as follows.
The borrowers are allowed to keep reasonable current assets particularly inventory and debtors. The normal current assets based on economic ordering levels and certain level of safety should be financed by banker. Finance to borrower in the form of working capital should not be made available for profit making or to keep excess inventory. Similarly the bank should finance the bills receivable, which are in line with the practices of the borrower’s industry. The norms have been worked out according to the time element. The limit of the raw materials is expressed as so many months of total consumption in the year. The work-in-progress limit determined as so many months of cost of production, the finished goods and bills receivable limits are determined by cost of sales and credit sales respectively. The Tandon Committee has suggested norms for fifteen industries.
Tandon Committee introduced the concept of MPBF in the working capital finance by banker. The Committee suggested that bank should attempt to supplement the borrowers’ resources in financing the current assets. It has recommended that the current assets first should be
In the first method, 25% of the Working Capital Gap (CA-(CL excluding bank borrowing)) should be contributed by borrower through long-term funds and remaining 75% can be financed from bank borrowings. This method will give a minimum current ratio of 1.17:1. The term working capital gap refers to the total of CA less CL other than bank borrowings. This can be understood with the help of the following examples.
Example 1
Amount of maximum permissible bank borrowings as per the first method can be ascertained as follows:

Under this method the borrower should provide 25% of the total current assets through long-term funds and this will give a current ratio of 1.33:1
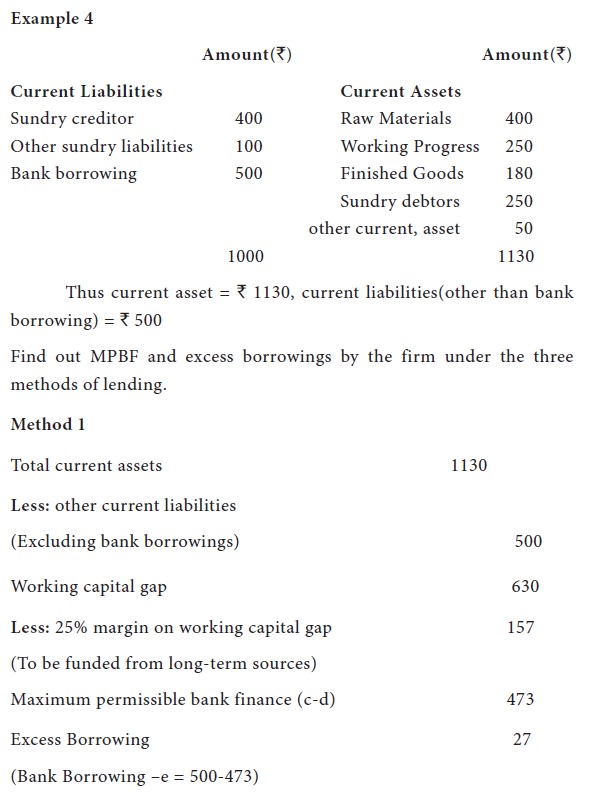
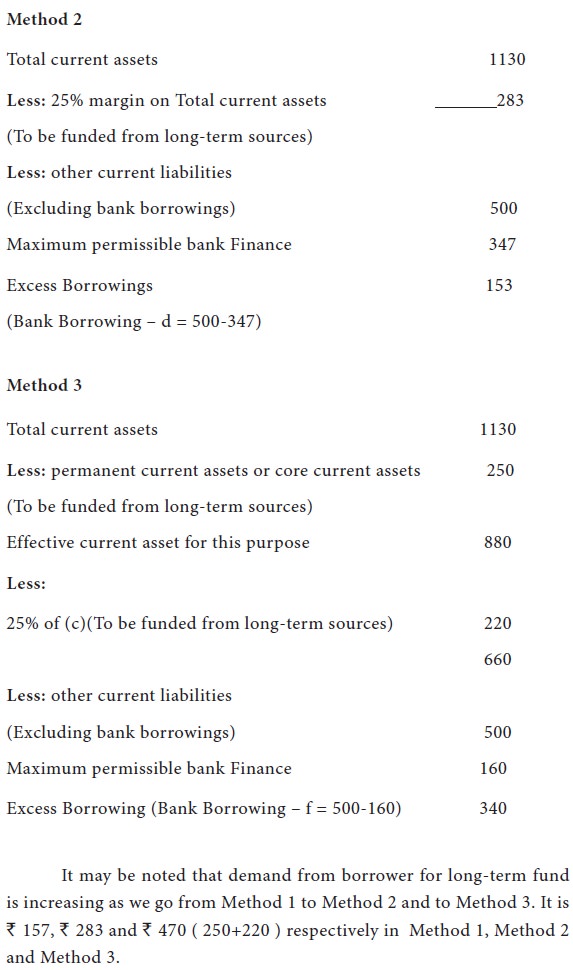
Example 2
The maximum permissible bank borrowings as per second method can be ascertained as follows:

In this method the borrower should contribute from long-term sources to the extent of core current assets (Fixed Current assets) and 25% of the balance of the current assets. The remaining of the working capital gap can be met from bank borrowings. This method will further strengthen the current ratio.
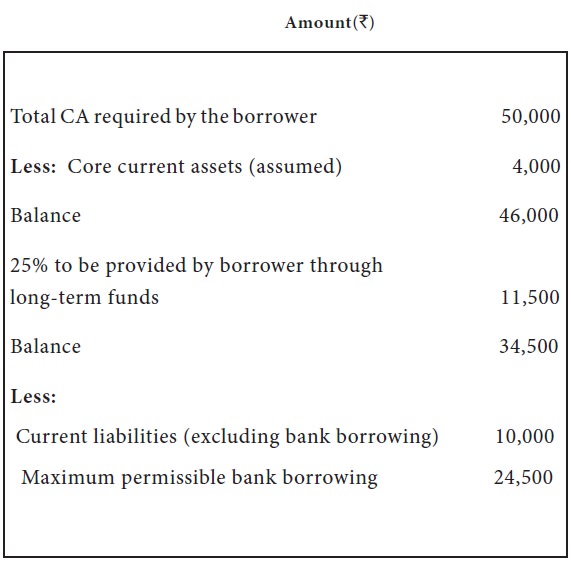
Example 3
The maximum permissible bank borrowings as per the third method can be ascertained as follows:
The committee recommended the first method mainly as a stop-gap method till borrowers get used to the new approach of lending. The borrowers who are already in the second method would not be allowed to revert to the first stage.
It is also known as Core current assets or fixed current assets. Any organization has to maintain minimum level of current assets throughout its existence as long as production cycle continues. They are permanent in nature. Thus a minimum amount of raw material, WIP, finished goods etc, that are required to be kept for running a company are called hard core working capital. The hard core working capital are like fixed assets such as machinery and building are for long-terms, but the difference between them is that the same machinery and building continues to exist but in case of elements of hard core working capital the level of working capital remains same but not the exact raw material, WIP on finished goods.
These are replaced continuously by other items consisting of utmost same value.
The RBI accepted the recommendations of the committee as a whole. It instructed the commercial banks in 1976 to put all the borrowers having aggregate credit limits from banking system in excess of `10 lakhs, under the first method lending.
At present, all sanctions of working capital by banks are based on Method 2. Because, the second method of lending is more acceptable to bankers since, it provides more cushion to them as far as quantum of margin is concerned compared to first method of lending. Obviously the amount of maximum permissible bank finance under the second method is lesser when compared to the first method.
The Tandon committee also suggested that total MPBF should be bifurcated into two components 1. Loan component represents the minimum level of borrowing throughout the year and 2. Demand cash credit component, which would take care of the fluctuating needs and is required to be reviewed periodically. The demand cash credit component should be charged slightly higher interest rate than the loan components. This would provide the borrower an incentive for better planning. Apart from the loan component and cash credit component, a part of the total financing requirements should also be provided by way of bills limit to finance the seller’s receivables. The proposed system of lending and the style of credit might be extended to all borrowers having credit limits in excess of ` 10 lakhs from the banking system.
In order to ensure that the borrowers do not use the cash credit facility in an unplanned manner and they keep only required level inventories and receivables, the committee suggested a new information system. Under this system the borrowers are required to submit the following documents to the bankers periodically.
1. A copy of the audited financial statements at the end of each year.
2. A copy of a projected financial statement and funds flow statement for the next year.
3. Quarterly budgeting cum reporting statements.
4. Monthly stock statement.
The Tandon committee further suggested that the information system might be introduced to start with in respect of borrowers with limit of Rs1 crore and above from the entire banking system and then extended progressively to others.
A study group under the chairmanship of Shri P.L. Tandon was constituted in 1974 by the RBI in order to frame guidelines for bank credit. The terms of reference of the committee were as follows.
Terms of reference
1. To suggest guidelines for commercial banks to follow up and supervise credit from the point of view of ensuring proper end-use of funds and keeping a watch on the safety of advances.
2. To make recommendations for obtaining periodical information that may be obtained by banks from the borrower.
3. To make suggestions for prescribing inventory norms for different industries.
4. To suggest criteria regarding satisfactory capital structure and sound financial basis in relation to borrowings.
5. To suggest whether the existing patterns of financing working capital requirements by cash credit / overdraft system, etc. are required to be modified, if so, to suggest modifications.
Findings
On the basis of the reference given above, the committee studied the existing system of working capital finance provided to industry and identified the following as its major weaknesses.
1. The banks do not have any credit appraisal or planning. It is the borrower who decides how much he would borrow.
2. The security-based approach to lending has led to division of funds to purchase of fixed assets.
3. Bank credit is treated as the first source of finance rather than being taken as a supplementary to other sources of finance.
4. The working capital finance should be made available only for a short period, as it has otherwise, led to accumulation of inventories with the industry.
Recommendations
The report was submitted on 9th August 1975 and it is a landmark in the history of financing working capital by commercial banks in India. The Tandon Committee made comprehensive recommendation regarding the bank lending practices, which can be broadly classified into four groups’. Important features of the Tandon Committee recommendations based on the fixation of norms for bank lending to industry are as follows.
Norms for Bank Lending
1. Inventory and receivable norms
The borrowers are allowed to keep reasonable current assets particularly inventory and debtors. The normal current assets based on economic ordering levels and certain level of safety should be financed by banker. Finance to borrower in the form of working capital should not be made available for profit making or to keep excess inventory. Similarly the bank should finance the bills receivable, which are in line with the practices of the borrower’s industry. The norms have been worked out according to the time element. The limit of the raw materials is expressed as so many months of total consumption in the year. The work-in-progress limit determined as so many months of cost of production, the finished goods and bills receivable limits are determined by cost of sales and credit sales respectively. The Tandon Committee has suggested norms for fifteen industries.
2. Lending norms or Maximum Permissible Bank Finance (MPBF)
Tandon Committee introduced the concept of MPBF in the working capital finance by banker. The Committee suggested that bank should attempt to supplement the borrowers’ resources in financing the current assets. It has recommended that the current assets first should be
First method
In the first method, 25% of the Working Capital Gap (CA-(CL excluding bank borrowing)) should be contributed by borrower through long-term funds and remaining 75% can be financed from bank borrowings. This method will give a minimum current ratio of 1.17:1. The term working capital gap refers to the total of CA less CL other than bank borrowings. This can be understood with the help of the following examples.
Example 1
Amount of maximum permissible bank borrowings as per the first method can be ascertained as follows:

Second method
Under this method the borrower should provide 25% of the total current assets through long-term funds and this will give a current ratio of 1.33:1
Example 2
The maximum permissible bank borrowings as per second method can be ascertained as follows:

Third method
In this method the borrower should contribute from long-term sources to the extent of core current assets (Fixed Current assets) and 25% of the balance of the current assets. The remaining of the working capital gap can be met from bank borrowings. This method will further strengthen the current ratio.
The maximum permissible bank borrowings as per the third method can be ascertained as follows:

The committee recommended the first method mainly as a stop-gap method till borrowers get used to the new approach of lending. The borrowers who are already in the second method would not be allowed to revert to the first stage.
Hard Core Working Capital
It is also known as Core current assets or fixed current assets. Any organization has to maintain minimum level of current assets throughout its existence as long as production cycle continues. They are permanent in nature. Thus a minimum amount of raw material, WIP, finished goods etc, that are required to be kept for running a company are called hard core working capital. The hard core working capital are like fixed assets such as machinery and building are for long-terms, but the difference between them is that the same machinery and building continues to exist but in case of elements of hard core working capital the level of working capital remains same but not the exact raw material, WIP on finished goods.
These are replaced continuously by other items consisting of utmost same value.
Reserve Bank’s Direction
The RBI accepted the recommendations of the committee as a whole. It instructed the commercial banks in 1976 to put all the borrowers having aggregate credit limits from banking system in excess of `10 lakhs, under the first method lending.


Suitability of lending method to bankers
At present, all sanctions of working capital by banks are based on Method 2. Because, the second method of lending is more acceptable to bankers since, it provides more cushion to them as far as quantum of margin is concerned compared to first method of lending. Obviously the amount of maximum permissible bank finance under the second method is lesser when compared to the first method.
3. Style of Credit
The Tandon committee also suggested that total MPBF should be bifurcated into two components 1. Loan component represents the minimum level of borrowing throughout the year and 2. Demand cash credit component, which would take care of the fluctuating needs and is required to be reviewed periodically. The demand cash credit component should be charged slightly higher interest rate than the loan components. This would provide the borrower an incentive for better planning. Apart from the loan component and cash credit component, a part of the total financing requirements should also be provided by way of bills limit to finance the seller’s receivables. The proposed system of lending and the style of credit might be extended to all borrowers having credit limits in excess of ` 10 lakhs from the banking system.
4. Information and Reporting System
In order to ensure that the borrowers do not use the cash credit facility in an unplanned manner and they keep only required level inventories and receivables, the committee suggested a new information system. Under this system the borrowers are required to submit the following documents to the bankers periodically.
1. A copy of the audited financial statements at the end of each year.
2. A copy of a projected financial statement and funds flow statement for the next year.
3. Quarterly budgeting cum reporting statements.
4. Monthly stock statement.
The Tandon committee further suggested that the information system might be introduced to start with in respect of borrowers with limit of Rs1 crore and above from the entire banking system and then extended progressively to others.
Tags : Financial Management - WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT
Last 30 days 18883 views












