Strategic Management - Environmental Analysis and Diagnosis
Technological Environment - Environmental Analysis
Posted On :
Technology is knowledge to create new things. Mangers need technology to design, produce, distribute and sell goods and services.
Technological Environment
Technology is knowledge to create new things. Mangers need technology to design, produce, distribute and sell goods and services. Impact of technology is mixed. Positive benefits are seen in new products, new machines, new tools, new materials and services. Benefits include greater productivity, higher living standards, more leisure time and greater variety of products. Ex: Range of cars – subcompacts, compacts, intermediates, sports, specialty, variations in engine power, steering A/c, speed control, roof etc. Negative effects include pollution, energy shortage, loss of privacy, traffic jam etc. A balanced approach is therefore needed.
Xerox dominated the world photocopier market with 93 percent of the market share. It guarded its technology with over 500 patents. Cannon was a camera company from Japan that entered into this business around 1970. It did not have the process technology to by-pass Xerox’s patents. Yet over the next three decades, Canon rewrote the rule book of how copiers were to be produced and sold. Canon’s copiers are a business of around Rs.300,000 crore in annual revenues and it sells more copiers than Xerox does. Canon succeeded, not by coping Xerox, but Canon believed that individuals and small businesses would find the product useful if only they could afford it. The technology appropriate for this product would therefore be different from Xerox’s patent protected technologies.
In 1975, revolutionary technological changes and discoveries have brought about dramatic impact of organizations. Among such discoveries mention may be made of super conductivity, computer engineering, “thinking” computers, robotics, unmanned factories, miracle drugs, fiber optics biometrics and electronic funds transfer. Superconductivity is expected to revolutionize business operations especially in such areas as transport, utility, health care, electrical and computers.
Technological Change is of Two Types
Convergent change - where incremental innovation and improvement optimizes the ability of the organization to succeed in the existing environment. In India this change occurs in 10-12 years, in western firms five to six years and in Japan it is four years. Presently
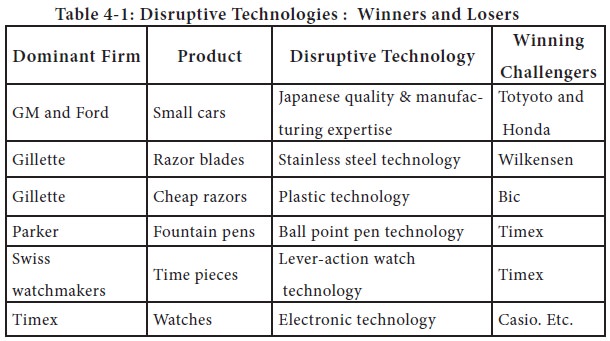
Divergent change – Involves changes where the framework of the organization undergoes discontinuities. Whether it is in response to events over which the corporation has no control, like deregulation, major shift in economic policies, nationalization or events related to radical changes in technology like product life cycle shifts, new process technologies, radical innovations, etc., these changes involve organizational re-formation or transformation. Example includes replacement of Swiss mechanical watches with high innovation by simple battery operated electronic watches. Some of the winners and losers of technological changes are given in the following Table 4-1.
Technology is knowledge to create new things. Mangers need technology to design, produce, distribute and sell goods and services. Impact of technology is mixed. Positive benefits are seen in new products, new machines, new tools, new materials and services. Benefits include greater productivity, higher living standards, more leisure time and greater variety of products. Ex: Range of cars – subcompacts, compacts, intermediates, sports, specialty, variations in engine power, steering A/c, speed control, roof etc. Negative effects include pollution, energy shortage, loss of privacy, traffic jam etc. A balanced approach is therefore needed.
Xerox dominated the world photocopier market with 93 percent of the market share. It guarded its technology with over 500 patents. Cannon was a camera company from Japan that entered into this business around 1970. It did not have the process technology to by-pass Xerox’s patents. Yet over the next three decades, Canon rewrote the rule book of how copiers were to be produced and sold. Canon’s copiers are a business of around Rs.300,000 crore in annual revenues and it sells more copiers than Xerox does. Canon succeeded, not by coping Xerox, but Canon believed that individuals and small businesses would find the product useful if only they could afford it. The technology appropriate for this product would therefore be different from Xerox’s patent protected technologies.
In 1975, revolutionary technological changes and discoveries have brought about dramatic impact of organizations. Among such discoveries mention may be made of super conductivity, computer engineering, “thinking” computers, robotics, unmanned factories, miracle drugs, fiber optics biometrics and electronic funds transfer. Superconductivity is expected to revolutionize business operations especially in such areas as transport, utility, health care, electrical and computers.
Technological Change is of Two Types
Convergent change - where incremental innovation and improvement optimizes the ability of the organization to succeed in the existing environment. In India this change occurs in 10-12 years, in western firms five to six years and in Japan it is four years. Presently
Divergent change – Involves changes where the framework of the organization undergoes discontinuities. Whether it is in response to events over which the corporation has no control, like deregulation, major shift in economic policies, nationalization or events related to radical changes in technology like product life cycle shifts, new process technologies, radical innovations, etc., these changes involve organizational re-formation or transformation. Example includes replacement of Swiss mechanical watches with high innovation by simple battery operated electronic watches. Some of the winners and losers of technological changes are given in the following Table 4-1.

Tags : Strategic Management - Environmental Analysis and Diagnosis
Last 30 days 1061 views














