Operations Management - Game Theory, Goal Programming & Queuing Theory
Graphical Solution - 2 X N Zero-Sum Games
Posted On :
Now we consider the graphical method of solution to the given game.
Graphical Solution
Now we consider the graphical method of solution to the given game.
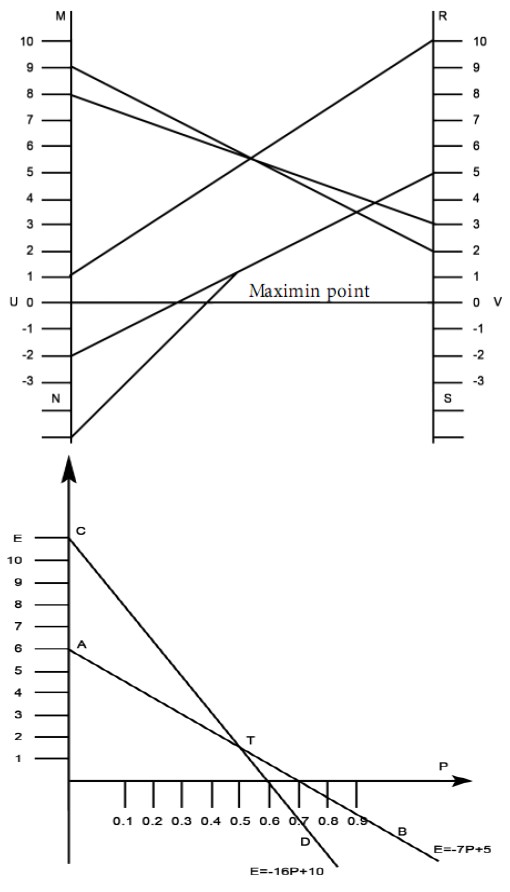
Draw two vertical lines MN and RS. Note that they are parallel to each other. Draw UV perpendicular to MN as well as RS. Take U as the origin on the line MN. Take V as the origin on the line RS.
Mark units on MN and RS with equal scale. The units on the two lines MN and RS are taken as the payoff numbers. The payoffs in the first row of the given matrix are taken along the line MN while the payoffs in the second row are taken along the line RS.
We have to plot the following points: (8, 3), (-2, 5), (-6, 10), (9, 2). The points 8, -2, -6, 9 are marked on MN. The points 3, 5, 10, 2 are marked on RS.
Join a point on MN with the corresponding point on RS by a straight line. For example, join the point 8 on MN with the point 3 on RS. We have 4 such straight lines. They represent the 4 moves of the second player. They intersect in 6 points. Take the lowermost point of intersection of the straight lines. It is called the Maximin point. With the help of this point, identify the optimal strategies for the second player. This point corresponds to the points –2 and –6 on MN and 5 and 10 on RS. They correspond to the sub game with the matrix .
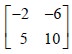
The points –2 and –6 on MN
correspond to the second and third strategies of the second player. Therefore,
the graphical method implies that, in the long run, the second player will
retain his strategies 2 and 3 and give up his strategies 1 and 4.
We graphically solve the sub game with the above matrix. We have to solve the two equations E = -7 p + 5 and E = - 16 p + 10. Represent the two equations by two straight lines AB and CD on the graph sheet. Take the point of intersection of AB and CD as T. For this point, we have p =5/9 and E = 10/9 . Therefore, the value V of the game is 10/9 . We see that the

Now we consider the graphical method of solution to the given game.
Draw two vertical lines MN and RS. Note that they are parallel to each other. Draw UV perpendicular to MN as well as RS. Take U as the origin on the line MN. Take V as the origin on the line RS.
Mark units on MN and RS with equal scale. The units on the two lines MN and RS are taken as the payoff numbers. The payoffs in the first row of the given matrix are taken along the line MN while the payoffs in the second row are taken along the line RS.
We have to plot the following points: (8, 3), (-2, 5), (-6, 10), (9, 2). The points 8, -2, -6, 9 are marked on MN. The points 3, 5, 10, 2 are marked on RS.
Join a point on MN with the corresponding point on RS by a straight line. For example, join the point 8 on MN with the point 3 on RS. We have 4 such straight lines. They represent the 4 moves of the second player. They intersect in 6 points. Take the lowermost point of intersection of the straight lines. It is called the Maximin point. With the help of this point, identify the optimal strategies for the second player. This point corresponds to the points –2 and –6 on MN and 5 and 10 on RS. They correspond to the sub game with the matrix .
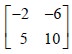
We graphically solve the sub game with the above matrix. We have to solve the two equations E = -7 p + 5 and E = - 16 p + 10. Represent the two equations by two straight lines AB and CD on the graph sheet. Take the point of intersection of AB and CD as T. For this point, we have p =5/9 and E = 10/9 . Therefore, the value V of the game is 10/9 . We see that the


Tags : Operations Management - Game Theory, Goal Programming & Queuing Theory
Last 30 days 972 views












