Home | ARTS | Financial Management
|
Determining the ratio of current assets to sales level - Working Capital Management Dimension Of Working Capital Management
Financial Management - WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT
Determining the ratio of current assets to sales level - Working Capital Management Dimension Of Working Capital Management
Posted On :
As already said, there is an inevitable relationship between the sales and the current assets.
Dimension 2 : Determining the ratio of current assets to sales level
As already said, there is an inevitable relationship between the sales and the current assets. The actual and the forecast sales have a major impact on the amount of current assets, which the firm must maintain. So, depending upon the sales forecast, the financial manager should also estimate the requirement of current assets. This uncertainty may result in spontaneous increase in current assets in line with the increase in sales level, and may bring the firm to a face-to-face tight working capital position. In order to overcome this uncertainty, the financial manager may establish a minimum level as well as a safety component for each of the current asset for different levels of sales. But how much should this safety component be? It may be noted that in fact, this safety component determines the type of working capital policy a firm is pursuing. There are three types of working capital policies which a firm may adopt i.e. conservative, moderate and aggressive working capital policy. These policies describe the relationship between sales level and the level of current asset and have been shown in figure
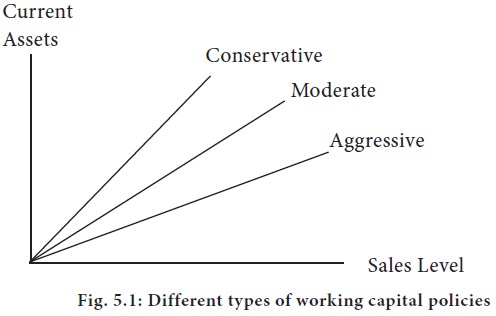
The figure 5.1 shows that in case of moderate working capital policy, the increase in sales level will be coupled with proportionate increase in level of current asset also e.g., if the sales increase or are expected to increase by 10%, then the level of current assets will also increase by 10%. In case of conservative working capital policy, the firm does not like to take risk. For every increase in sales, the level of current assets will be increased more than proportionately. Such a policy tends to reduce the risks of shortage of working capital by increasing the safety component of current assets. The conservative working capital policy also reduces the risk of non-payment to liabilities.
On the other hand, a firm is said to have adopted an aggressive working capital policy, if the increase in sales does not result in proportionate increase in current assets. For example, for 10% increase in sales the level of current asset is increased by 7% only. This type of aggressive policy has many implications. First, the risk of insolvency of the firm increases as the firm maintains lower liquidity. Second, the firm is exposed to greater risk as it may not be able to face unexpected change in market and, third, reduced investment in current assets will result in increase in profitability of the firm.
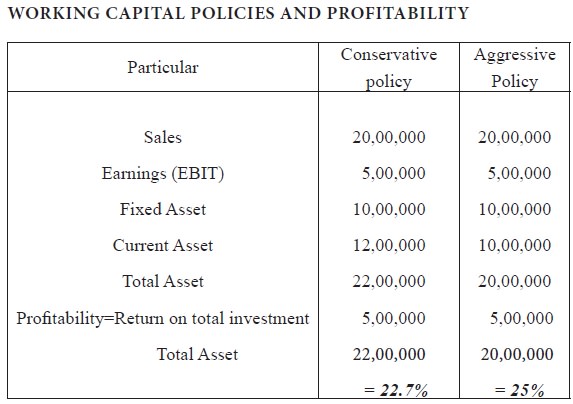
The effect of working capital policies on the profitability of a firm is illustrated below:
As already said, there is an inevitable relationship between the sales and the current assets. The actual and the forecast sales have a major impact on the amount of current assets, which the firm must maintain. So, depending upon the sales forecast, the financial manager should also estimate the requirement of current assets. This uncertainty may result in spontaneous increase in current assets in line with the increase in sales level, and may bring the firm to a face-to-face tight working capital position. In order to overcome this uncertainty, the financial manager may establish a minimum level as well as a safety component for each of the current asset for different levels of sales. But how much should this safety component be? It may be noted that in fact, this safety component determines the type of working capital policy a firm is pursuing. There are three types of working capital policies which a firm may adopt i.e. conservative, moderate and aggressive working capital policy. These policies describe the relationship between sales level and the level of current asset and have been shown in figure

The figure 5.1 shows that in case of moderate working capital policy, the increase in sales level will be coupled with proportionate increase in level of current asset also e.g., if the sales increase or are expected to increase by 10%, then the level of current assets will also increase by 10%. In case of conservative working capital policy, the firm does not like to take risk. For every increase in sales, the level of current assets will be increased more than proportionately. Such a policy tends to reduce the risks of shortage of working capital by increasing the safety component of current assets. The conservative working capital policy also reduces the risk of non-payment to liabilities.
On the other hand, a firm is said to have adopted an aggressive working capital policy, if the increase in sales does not result in proportionate increase in current assets. For example, for 10% increase in sales the level of current asset is increased by 7% only. This type of aggressive policy has many implications. First, the risk of insolvency of the firm increases as the firm maintains lower liquidity. Second, the firm is exposed to greater risk as it may not be able to face unexpected change in market and, third, reduced investment in current assets will result in increase in profitability of the firm.
The effect of working capital policies on the profitability of a firm is illustrated below:

In the conservative policy the firm has more current
assets, which results in high liquidity, low risk and low return
(22.7%), where as in the aggressive policy the firm has less current assets,
which result in low liquidity, high risk and high return (25%).
Tags : Financial Management - WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT
Last 30 days 1417 views













