Home | ARTS | Marketing Management
|
Pricing in industrial (business-to-business) markets - Pricing Policies and Constraints
MARKETING MANAGEMENT - Pricing Policies and Constraints
Pricing in industrial (business-to-business) markets - Pricing Policies and Constraints
Posted On :
As Lesson 1.1 outlined the differences between consumer marketing and industrial marketing, those differences can further be explained based on the distinguishing characteristics of industrial pricing. Some of those characteristics are listed below:
Pricing in industrial (business-to-business) markets
As Lesson 1.1 outlined the differences between consumer marketing and industrial marketing, those differences can further be explained based on the distinguishing characteristics of industrial pricing. Some of those characteristics are listed below:
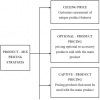
1. The true price as industrial customer pays is often different from the list price because of factors like delivery and installation costs, discounts, training costs, trade-in allowance, financing costs and so on.
2. Pricing is not an independent variable. It is highly intertwined with product, promotion and distribution strategies.
3. Price for industrial products cannot be set out without considering other products that are compliments or substitutes sold by the firm. Cross elasticities exist, where the price of one item affects sales of other items.
4. Prices can be changed in numerous ways such as changing the quantity of goods and services provided by the seller, changing the premiums and discounts that are offered, changing the time and place of payment, and so on. This implies that pricing is often a more flexible decision than product or distribution decisions.
5. Industrial prices are established, in many cases, by competitive bidding on a project-by-project basis. In a number of cases, prices are resolved through negotiation.
6. Industrial pricing is often characterized by an emphasis on fairness. Industrial buyers, who are experienced and able to estimate the
7. Industrial prices are affected by a host of economic factors such as inflation, interest rate changes, exchange rate fluctuations and so on. This problem is particularly critical for the marketer locked into a long term contract with no escalation cause.
As Lesson 1.1 outlined the differences between consumer marketing and industrial marketing, those differences can further be explained based on the distinguishing characteristics of industrial pricing. Some of those characteristics are listed below:
1. The true price as industrial customer pays is often different from the list price because of factors like delivery and installation costs, discounts, training costs, trade-in allowance, financing costs and so on.
2. Pricing is not an independent variable. It is highly intertwined with product, promotion and distribution strategies.
3. Price for industrial products cannot be set out without considering other products that are compliments or substitutes sold by the firm. Cross elasticities exist, where the price of one item affects sales of other items.
4. Prices can be changed in numerous ways such as changing the quantity of goods and services provided by the seller, changing the premiums and discounts that are offered, changing the time and place of payment, and so on. This implies that pricing is often a more flexible decision than product or distribution decisions.
5. Industrial prices are established, in many cases, by competitive bidding on a project-by-project basis. In a number of cases, prices are resolved through negotiation.
6. Industrial pricing is often characterized by an emphasis on fairness. Industrial buyers, who are experienced and able to estimate the
7. Industrial prices are affected by a host of economic factors such as inflation, interest rate changes, exchange rate fluctuations and so on. This problem is particularly critical for the marketer locked into a long term contract with no escalation cause.
Tags : MARKETING MANAGEMENT - Pricing Policies and Constraints
Last 30 days 524 views