Financial Management - CAPITAL STRUCTURE THEORIES
Net operating income approach - CAPITAL STRUCTURE THEORIES
Posted On :
Net Operating Income or NOI is equal to yearly gross income less operating expenses.
Net operating income
approach
Net Operating Income or NOI is equal to yearly gross income less operating expenses. Gross income includes all income earned by the company. Operating expenses are costs incurred during the operation and maintenance of the company. Net operating income or NOI is used in two very important ratios. It is an essential ingredient in the Capitalization Rate (Cap Rate) calculation. We would estimate the value of company like this
Debt
Coverage Ratio = Net Operating Income / Debt Service
Debt service is the total of all interest and principal paid in a given year. The Net Operating Income is an important ingredient in several ratios which include the Capitalization Rate, Net Income Multiplier and the Debt Service Coverage Ratio. According to net operating income approach in the capital structure, the overall capitalization rate and the cost of debt remain constant for all degrees of financial leverage.
As we have seen under net income approach the average cost of capital is measured as under
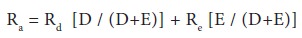
Ra and Rd are constant for all degrees of leverage. Given this, the cost of equity can be ascertained as under:
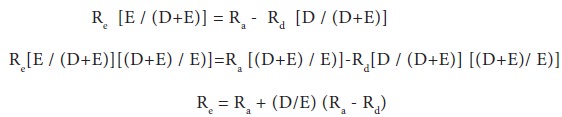
The critical assumption of this approach is that the market capitalizes the company as a whole at a discount rate which is independent of the company’s debt-equity ratio. As a result, the division between debt and equity is considered irrelevant. Any increase in the use of debt capital which is cheaper and it is offset by an increase in the equity capitalization rate. This is obvious because the equity investors seek higher return as they are exposed to greater risk which in turn arises from the increase in the financial leverage.
This net operating income approach has been propounded by David Durand. He concluded that the market value of a company depends on its net operating income and business risk.
The changes in the degree of leverage employed by a company cannot change these underlying factors. They merely change the distribution of income and risk between debt capital and equity capital without affecting the total income and risk which influence the market value of the company.
Net Operating Income or NOI is equal to yearly gross income less operating expenses. Gross income includes all income earned by the company. Operating expenses are costs incurred during the operation and maintenance of the company. Net operating income or NOI is used in two very important ratios. It is an essential ingredient in the Capitalization Rate (Cap Rate) calculation. We would estimate the value of company like this
Estimated
Value = Net Operating Income /Capitalization Rate
Another important ratio that is used is the Debt Coverage Ratio or DCR. The NOI is a key ingredient in this important ratio also. Lenders and investors use the debt coverage ratio to measure a company’s ability to pay its’ operating expenses. A debt coverage ratio of 1 is break even. From a bank’s perspective and an investor’s perspective, the larger the debt coverage ratio is better. Debt coverage ratio is calculated like this
Another important ratio that is used is the Debt Coverage Ratio or DCR. The NOI is a key ingredient in this important ratio also. Lenders and investors use the debt coverage ratio to measure a company’s ability to pay its’ operating expenses. A debt coverage ratio of 1 is break even. From a bank’s perspective and an investor’s perspective, the larger the debt coverage ratio is better. Debt coverage ratio is calculated like this
Debt service is the total of all interest and principal paid in a given year. The Net Operating Income is an important ingredient in several ratios which include the Capitalization Rate, Net Income Multiplier and the Debt Service Coverage Ratio. According to net operating income approach in the capital structure, the overall capitalization rate and the cost of debt remain constant for all degrees of financial leverage.
As we have seen under net income approach the average cost of capital is measured as under
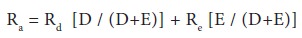
Ra and Rd are constant for all degrees of leverage. Given this, the cost of equity can be ascertained as under:
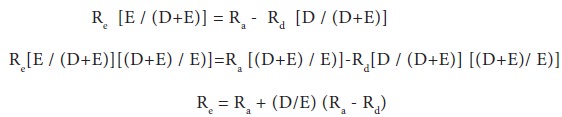
The critical assumption of this approach is that the market capitalizes the company as a whole at a discount rate which is independent of the company’s debt-equity ratio. As a result, the division between debt and equity is considered irrelevant. Any increase in the use of debt capital which is cheaper and it is offset by an increase in the equity capitalization rate. This is obvious because the equity investors seek higher return as they are exposed to greater risk which in turn arises from the increase in the financial leverage.
This net operating income approach has been propounded by David Durand. He concluded that the market value of a company depends on its net operating income and business risk.
The changes in the degree of leverage employed by a company cannot change these underlying factors. They merely change the distribution of income and risk between debt capital and equity capital without affecting the total income and risk which influence the market value of the company.
Tags : Financial Management - CAPITAL STRUCTURE THEORIES
Last 30 days 1207 views












