Managerial Economics - Demand Analysis
Demand Forecasting - Demand Analysis
Posted On :
All organizations operate in an atmosphere of uncertainty but decisions must be made today that affect the future of the organization.
Demand
Forecasting
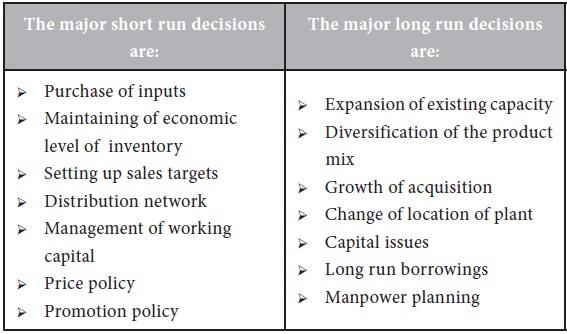
All organizations operate in an atmosphere of uncertainty but decisions must be made today that affect the future of the organization. There are various ways of making forecasts that rely on logical methods of manipulating the data that have been generated by historical events. A forecast is a prediction or estimation of a future situation, under given conditions. Demand forecast will help the manager to take the following decisions effectively.
The steps to be followed:
1. Identification of objectives
2. Nature of product and market
3. Determinants of demand
4. Analysis of factors
5. Choice of technology
6. Testing the accuracy
Criteria to choose a method of forecasting are:
1. Accuracy
2. Plausibility
3. Durability
4. Flexibility
5. Availability
4.
Develop some predetermined
criteria on which the selection decision can be made.
1. Survey of buyers’ intension
2. Delphi method
3. Expert opinion
4. Collective opinion
5. Naïve model
6. Smoothing techniques
7. Time series / trend projection
8. Controlled experiments
9. Judgmental approach
The linear trend is the most commonly used method of time series analysis. The following are various trend projections used under various circumstances.
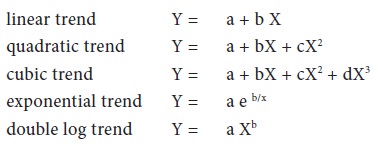
Y = a + b
X
Y = demand
X = time period
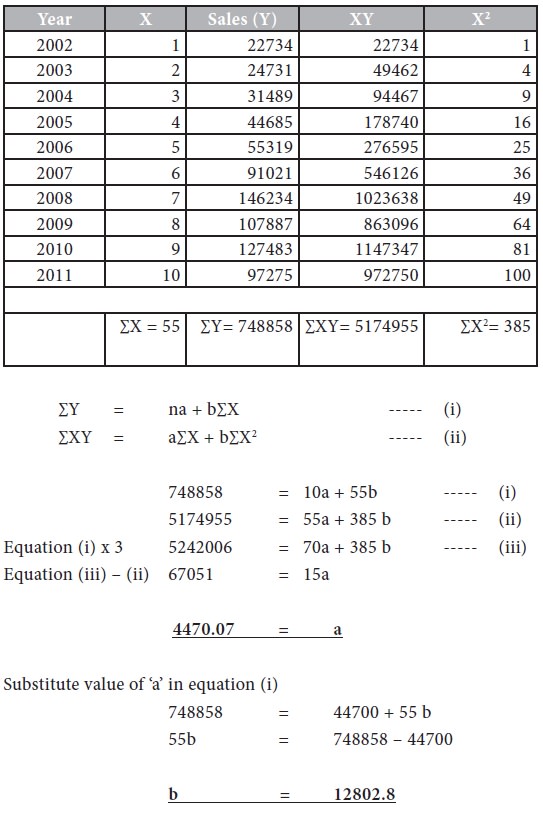
a,b constant values representing intercept and slope of the line. To calculate Y for any value of X we have to solve the following equations,
(i) and (ii). We can derive the values of ‘a’ and ‘b’ through solving these equations and by substituting the same in the above given linear trend equation we can forecast demand for ‘X’ time period.
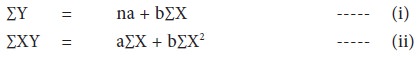
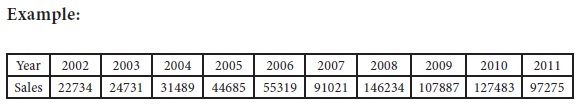
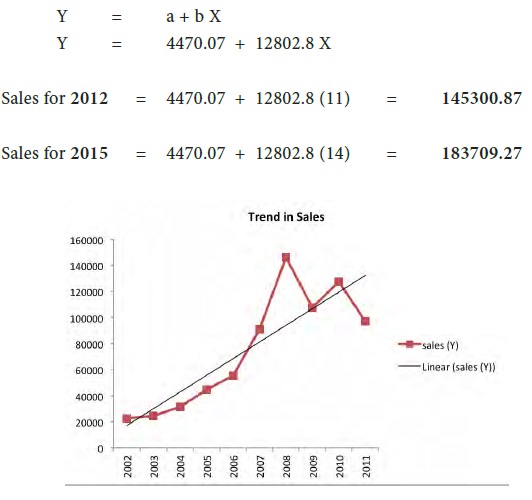
Estimate the sales for 2012, 2015 and fit a linear regression equation
and draw a trend line.
Techniques that should be used when forecasting stationary series (the demand patterns influencing the series are relatively stable) include naïve method, simple average method, moving average, and autoregressive moving average (ARMA) and Box-Jenkins method.
When forecasting trend series then, moving averages, simple regression, growth curves, exponential models and autoregressive integrated moving average (ARIMA) models and Box-Jenkins methods can be used.
For seasonal series census X-12, winter’s exponential smoothing, multiple regression and ARIMA models can be used.
When forecasting cyclical series econometric models, economic indicators, multiple regression and ARIMA models can be used.
The major forecasting techniques are: naïve, simple average, moving averages, exponential smoothing, linear exponential smoothing, quadratic exponential smoothing, seasonal exponential smoothing, adaptive filtering, simple regression, multiple regression, classical decomposition, exponential trend models, S-curve fitting, Compertz models, growth curves, census X-12, Box-Jenkins, leading indicators, econometric models and time series multiple regression may be used.
The causal forecasting models (simple, multiple regression analysis) will be useful to decide the production, personnel hiring, and facility planning in the short run. In Time series forecasting models like decomposition is suitable to decide the new plant, equipment planning. Moving average and exponential smoothing is used for operations such as inventory, scheduling and pricing decisions. The autoregressive models, Box-Jenkins techniques are used to forecast price, inventory, production, stock and sales related decisions. Neural network method is for forecasting applications in development phase of the organization.
Apart from the above mentioned statistical methods the survey methods are also commonly used. They are:
1. Complete Enumeration Method: the survey covers all the potential consumers in the market and an interview is conducted to find out the probable demand. The sum of all gives the total demand for the industry. If the number of customers is too many this method cannot be used.
All organizations operate in an atmosphere of uncertainty but decisions must be made today that affect the future of the organization. There are various ways of making forecasts that rely on logical methods of manipulating the data that have been generated by historical events. A forecast is a prediction or estimation of a future situation, under given conditions. Demand forecast will help the manager to take the following decisions effectively.

The steps to be followed:
1. Identification of objectives
2. Nature of product and market
3. Determinants of demand
4. Analysis of factors
5. Choice of technology
6. Testing the accuracy
Criteria to choose a method of forecasting are:
1. Accuracy
2. Plausibility
3. Durability
4. Flexibility
5. Availability
The following are needed for
demand forecasting:
1. Appropriate production scheduling
2. Suitable purchase policy
3. Appropriate price policy
4. Setting realistic sales targets for salesmen
5. Forecasting financial requirements
6. Business planning
7. Financial planning
8. Planning man-power requirements
To select the appropriate forecasting technique, the manager/forecaster must be able to accomplish the following:
1. Define the nature of the forecasting problem
2. Explain the nature of the data under investigation
3. Describe the capabilities and limitations of potentially useful forecasting techniques.
1. Appropriate production scheduling
2. Suitable purchase policy
3. Appropriate price policy
4. Setting realistic sales targets for salesmen
5. Forecasting financial requirements
6. Business planning
7. Financial planning
8. Planning man-power requirements
To select the appropriate forecasting technique, the manager/forecaster must be able to accomplish the following:
1. Define the nature of the forecasting problem
2. Explain the nature of the data under investigation
3. Describe the capabilities and limitations of potentially useful forecasting techniques.
Demand Forecasting Methods:
1. Survey of buyers’ intension
2. Delphi method
3. Expert opinion
4. Collective opinion
5. Naïve model
6. Smoothing techniques
7. Time series / trend projection
8. Controlled experiments
9. Judgmental approach
Time Series / Trend Projection
The linear trend is the most commonly used method of time series analysis. The following are various trend projections used under various circumstances.
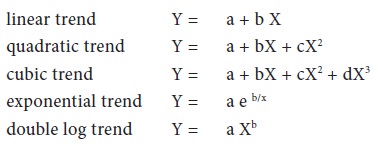
Linear Trend Equation:
Y = demand
X = time period
a,b constant values representing intercept and slope of the line. To calculate Y for any value of X we have to solve the following equations,
(i) and (ii). We can derive the values of ‘a’ and ‘b’ through solving these equations and by substituting the same in the above given linear trend equation we can forecast demand for ‘X’ time period.
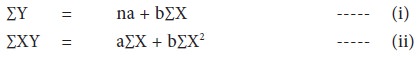



Techniques that should be used when forecasting stationary series (the demand patterns influencing the series are relatively stable) include naïve method, simple average method, moving average, and autoregressive moving average (ARMA) and Box-Jenkins method.
When forecasting trend series then, moving averages, simple regression, growth curves, exponential models and autoregressive integrated moving average (ARIMA) models and Box-Jenkins methods can be used.
For seasonal series census X-12, winter’s exponential smoothing, multiple regression and ARIMA models can be used.
When forecasting cyclical series econometric models, economic indicators, multiple regression and ARIMA models can be used.
The major forecasting techniques are: naïve, simple average, moving averages, exponential smoothing, linear exponential smoothing, quadratic exponential smoothing, seasonal exponential smoothing, adaptive filtering, simple regression, multiple regression, classical decomposition, exponential trend models, S-curve fitting, Compertz models, growth curves, census X-12, Box-Jenkins, leading indicators, econometric models and time series multiple regression may be used.
The causal forecasting models (simple, multiple regression analysis) will be useful to decide the production, personnel hiring, and facility planning in the short run. In Time series forecasting models like decomposition is suitable to decide the new plant, equipment planning. Moving average and exponential smoothing is used for operations such as inventory, scheduling and pricing decisions. The autoregressive models, Box-Jenkins techniques are used to forecast price, inventory, production, stock and sales related decisions. Neural network method is for forecasting applications in development phase of the organization.
Apart from the above mentioned statistical methods the survey methods are also commonly used. They are:
1. Complete Enumeration Method: the survey covers all the potential consumers in the market and an interview is conducted to find out the probable demand. The sum of all gives the total demand for the industry. If the number of customers is too many this method cannot be used.
2. Sample Survey Method: the
complete enumeration is not possible
always. The forecaster can go in for sample survey method. In this method, only
few (a sample) customers are selected from the total and interviewed and then
the average demand is estimated.
3. Expert’s Opinion: the experienced people from the same field or from marketing agents can also be taken into consideration for collecting information about the future demand.
The above discussed qualitative and quantitative methods are commonly used to forecast the future demand and based on this information firms will take production decision.
3. Expert’s Opinion: the experienced people from the same field or from marketing agents can also be taken into consideration for collecting information about the future demand.
The above discussed qualitative and quantitative methods are commonly used to forecast the future demand and based on this information firms will take production decision.
Tags : Managerial Economics - Demand Analysis
Last 30 days 1750 views












