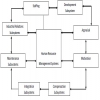
Human Resources Management - HRM-Systems Perspective
Staffing - HRM-Systems Perspective
Posted On :
Under this subsystem the job of recruitment, selection and placement are undertaken. Following are the principles of recruitment policy.
Staffing
Under this subsystem the job of recruitment, selection and placement are undertaken. Following are the principles of recruitment policy.
1. Internal
2. External to the organization.
1. Lack of adequately qualified and experienced persons within the organization.
2. Inducting persons of specialized knowledge.
3. Inducting persons well exposed in successful units.
1. Campus Recruitment.
2. Personnel Consultants.
3. Professional Bodies.
4. Private Recruitment Agencies.
5. Employment Exchange.
6. Trade Unions.
7. Recommendations of Existing Employees.
8. Solicited Application.
9. Unsolicited Application.
1. Details of Vacancy.
2. Number of Vacancies.
3. Scale of pay.
4. Minimum qualification.
5. Minimum Experience.
7. Reservation of vacancies.
8. Mode of applying – last date.
1. Short listing.
2. Application blank.
3. Tests.
4. Interviews.
6. Medical Examination
7. Final Selection.
To improve knowledge regarding organization, its objectives, philosophy, policies, procedures and practices.
To increase technical skill and update the knowledge.
To improve their aptitude and abilities on the job.
To help supervisors to increase their management skill especially in their human relations and planning the work.
To assist managers to improve their personality, sharpen their intelligence and to increase their conceptual skill.
To prepare managers to take higher responsibility and position by updating their professional knowledge.
Orientation training
On the job-training
Simulation (vestibule) training.
Class room training
Apprenticeship training
Industrial training
The principles involved are
Wage plan should be linked to the productivity
Should be related to job requirement skill and job
Should have incentive content to motivate workers to put up their best efforts.
Wages to be fixed for different categories based on job evaluation.
Wage plan should have a guaranteed minimum wage.
It should be comparable with wages of other similar industries in similar locations
It should attract talented personnel to join the organization
It should be flexible enough to bring about changes as and when found necessary.
The other functions of staffing sub system are:
Job evaluation is the evaluation rating of jobs to determine their positions in job hierarchy. The evaluation may be achieved through assignment of points or the use of some other systematic rating method for essential job requirement such as skill, experience and responsibility.
The various steps of job evaluation are
1. Job Analysis
2. Job Description
3. Job Grading
4. Job Pricing
Job Evaluation Techniques
1. Qualitative Method
a. Ranking Job comparison method
b. Job classification / Grading method
2. Quantitative method
a. Factor comparison method
b. Point comparison method.
Under this subsystem the job of recruitment, selection and placement are undertaken. Following are the principles of recruitment policy.
1. Centralized recruitment policy.
2. Recruitment compatible with personnel policy of the
organization.
3. Merit is to be the basis.
4. Qualification and experience compatible with job
analysis.
5. Rules and procedure to be transparent and adequately
published through circular, notices and newspaper advertisements.
6. Proper mix of internal and external candidates.
7. Statutory policies are to be followed.
8. Recruitment policy is to be flexible enough to bring
necessary amendments.
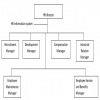
Sources of Recruitment
1. Internal
2. External to the organization.
Need for External Recruitment
1. Lack of adequately qualified and experienced persons within the organization.
2. Inducting persons of specialized knowledge.
3. Inducting persons well exposed in successful units.
Source for External Recruitment
1. Campus Recruitment.
2. Personnel Consultants.
3. Professional Bodies.
4. Private Recruitment Agencies.
5. Employment Exchange.
6. Trade Unions.
7. Recommendations of Existing Employees.
8. Solicited Application.
9. Unsolicited Application.
Advertisements
1. Details of Vacancy.
2. Number of Vacancies.
3. Scale of pay.
4. Minimum qualification.
5. Minimum Experience.
6. Desirable qualities.
7. Reservation of vacancies.
8. Mode of applying – last date.
Selection process
1. Short listing.
2. Application blank.
3. Tests.
4. Interviews.
5. References
6. Medical Examination
7. Final Selection.
Training and Development
To improve knowledge regarding organization, its objectives, philosophy, policies, procedures and practices.
To increase technical skill and update the knowledge.
To improve their aptitude and abilities on the job.
To assist employees to perform better and earn
more.
To help supervisors to increase their management skill especially in their human relations and planning the work.
To assist managers to improve their personality, sharpen their intelligence and to increase their conceptual skill.
To prepare managers to take higher responsibility and position by updating their professional knowledge.
To assist in an overall improvement and development of
individual employees.
To increase the contribution of employees to the
organization.
Method of Training
Orientation training
On the job-training
Simulation (vestibule) training.
Class room training
Apprenticeship training
Industrial training
Wage and Salary Administration
The principles involved are
Wage plan should be linked to the productivity
Should be related to job requirement skill and job
Should have incentive content to motivate workers to put up their best efforts.
Wages to be fixed for different categories based on job evaluation.
Wage plan should have a guaranteed minimum wage.
It should be comparable with wages of other similar industries in similar locations
It should attract talented personnel to join the organization
It should be flexible enough to bring about changes as and when found necessary.
The other functions of staffing sub system are:
Job Evaluation
Job evaluation is the evaluation rating of jobs to determine their positions in job hierarchy. The evaluation may be achieved through assignment of points or the use of some other systematic rating method for essential job requirement such as skill, experience and responsibility.
The various steps of job evaluation are
1. Job Analysis
2. Job Description
3. Job Grading
4. Job Pricing
Job Evaluation Techniques
1. Qualitative Method
a. Ranking Job comparison method
b. Job classification / Grading method
2. Quantitative method
a. Factor comparison method
b. Point comparison method.
Tags : Human Resources Management - HRM-Systems Perspective
Last 30 days 918 views