Home | ARTS | Business Environment and Law
|
Crossing Of Cheques: - Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881
Business Environment and Law-The Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881
Crossing Of Cheques: - Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881
Posted On :
Crossing of a cheque is a direction to the paying banker by the drawer that payment should not be made across the counter. The payment on a crossed cheque can be collected only through a banker.
Crossing Of Cheques:
Crossing of a cheque is a direction to the paying banker by the drawer that payment should not be made across the counter. The payment on a crossed cheque can be collected only through a banker.
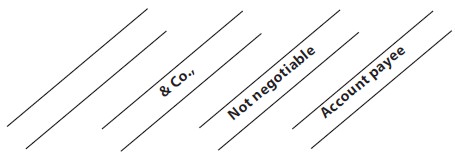
Section 123, defines crossing as, “Where a cheque bears across its face an addition of the words ‘and company’ or any abbreviation thereof, between two parallel transverse lines, or of two parallel transverse lines simply, either with or without the words ‘not negotiable’, that addition shall be deemed a crossing and the cheque shall be deemed to be crossed generally. A cheque having the cross mark such as ‘X’ is not generally regarded as a crossed cheque. A cheque that is not crossed is called an open cheque.
Payment cannot be claimed across the counter on a crossed cheque, crossing of cheques serves as a measure of safety against theft or loss of cheques in transit. By crossing a cheque, a person, who is not entitled to receive its payment, is prevented from getting the cheque encashed at the counter of the paying banker.
Types Of Crossing:
Crossing may be either (1) General or (2) Special.
Crossing of a cheque is a direction to the paying banker by the drawer that payment should not be made across the counter. The payment on a crossed cheque can be collected only through a banker.
Section 123, defines crossing as, “Where a cheque bears across its face an addition of the words ‘and company’ or any abbreviation thereof, between two parallel transverse lines, or of two parallel transverse lines simply, either with or without the words ‘not negotiable’, that addition shall be deemed a crossing and the cheque shall be deemed to be crossed generally. A cheque having the cross mark such as ‘X’ is not generally regarded as a crossed cheque. A cheque that is not crossed is called an open cheque.
Significance Of Crossing:
Payment cannot be claimed across the counter on a crossed cheque, crossing of cheques serves as a measure of safety against theft or loss of cheques in transit. By crossing a cheque, a person, who is not entitled to receive its payment, is prevented from getting the cheque encashed at the counter of the paying banker.
Types Of Crossing:
Crossing may be either (1) General or (2) Special.
General Crossing:
The
term general crossing implies the addition
of two parallel transverse lines.

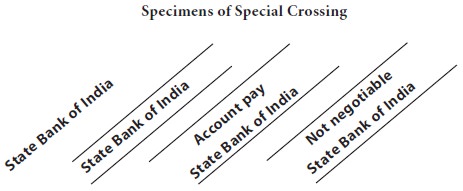
Special Crossing:
‘Special Crossing’ implies the specification of the name of the banker on the face of the
cheque. Section 124 in this regard, reads: Where a cheque bears across its
face, an addition of the name of a bank, either with or without the words ‘not
negotiable’, that addition shall be deemed a crossing, and the cheque shall be
deemed to be crossed to that banker.” The object of special crossing is to
direct the drawee banker to pay the cheque, only if it is presented through the
particular bank mentioned therein. Thus, it makes the cheque system still
safer.

Not Negotiable Crossing:
By
including the words ‘not negotiable’, the
cheque is deprived of its special feature of negotiability. Such a cheque is
like any other goods where the title of the transferee is always subject to the
title of the transferor. A bank, therefore, should be extra careful in paying
such cheques.
Account Payee Crossing (A/c Payee Crossing):
An A/c payee crossing
signifies that the drawer intends the payment to be credited only to the
payee’s account and in none else. The addition of ‘A/c payee’ to a crossing has
no legal sanctity and the paying banker may ignore such a direction without
being liable for any damages.
Not Negotiable, A/c Payee Crossing:
The
instrument is rendered not
negotiable, plus A/c payee crossing directs the collecting banker to collect it
for the payee only and warns that if the amount is collected for someone else,
he may be held liable for damages.
Tags : Business Environment and Law-The Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881
Last 30 days 1010 views












