Business Environment and Law-Industrial Disputes Act, 1947
Types Of Strike - Industrial Disputes Act, 1947
Posted On :
It means the failure, refusal or inability of an employer on account of the shortage of coal, power or raw material or the accumulation of stocks or the breakdown of machinery or natural calamity or for any other connected reason to give employment to a workman whose name is borne on the muster rolls of his industrial establishment and who has not been retrenched.
Types Of Strike
1. Stay-in, Sit-down, Pen-down or Tool-down Strike :In all such cases, the workmen after taking their seats, refuse to do work. All such acts on the part of the workmen acting in combination, amount to a strike.
1. Stay-in, Sit-down, Pen-down or Tool-down Strike :In all such cases, the workmen after taking their seats, refuse to do work. All such acts on the part of the workmen acting in combination, amount to a strike.
2. Go-slow : Go-slow does not amount
to strike, but it is a serious case of misconduct.
3. Sympathetic Strike : Cessation of work in the support of the demands of workmen belonging to other employer is called a sympathetic strike. The management can take disciplinary action for the absence of workmen. However, in Ramalingam Vs. Indian Metallurgical Corporation, Madras, 1964-I L.L.J.81, it was held that such cessation of work will not amount to a strike since there is no intention to use the strike against the management.
5. Work-to-rule : Since there is no
cessation of work, it does not constitute a strike.
It means the failure, refusal or inability of an employer on account of the shortage of coal, power or raw material or the accumulation of stocks or the breakdown of machinery or natural calamity or for any other connected reason to give employment to a workman whose name is borne on the muster rolls of his industrial establishment and who has not been retrenched.
Lay-off does not involve alteration in the conditions of service. A lay-off is not the same, this as the order of dismissal. It is more akin to an order of suspension.
It means temporary closing of a place of employment or the suspension of work or the refusal by an employer to continue to employ any number of persons employed by him. Under the present definition, two alternative acts of the employer constitute a lockout:
Essentials of Lock-out :
The essentials of a lock-out are as follows:
1. There is a temporary closing of the place of employment, or suspension or withholding of the work by the employer in some form.
2. There is an element of demands for which the place of employment is locked-out or closed.
There is an intention to re-employ the workers, if they accept the demands.
Section 2(1) defines lock-out thus: “Lock-out” means temporary closing of a place of employment, or the suspension of work, or the refusal by an employer to continue to employ any number of persons employed by him. The requirements of lock-out, according to this definition are:
Temporary closure of the place of employment;
1. Suspension of work;
2. Refusal to employ;
3. By an employer; and
4. To continue to employ any number of persons employed by him.
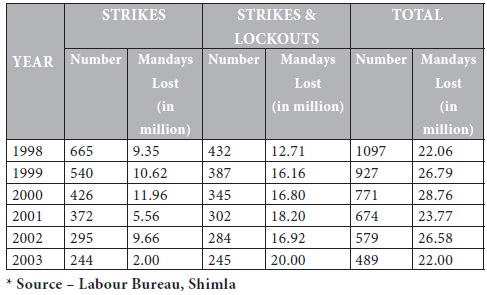
The total Mandays lost on account of strikes and lockouts have declined by 4.80 million in 2003
3. Sympathetic Strike : Cessation of work in the support of the demands of workmen belonging to other employer is called a sympathetic strike. The management can take disciplinary action for the absence of workmen. However, in Ramalingam Vs. Indian Metallurgical Corporation, Madras, 1964-I L.L.J.81, it was held that such cessation of work will not amount to a strike since there is no intention to use the strike against the management.
4. Hunger Strike : Some workers may
resort to fast on or near the place of work or residence of the employer. If it
is peaceful and does not result in cessation of work, it will not constitute a
strike. But if due to such an act, even those present for work, could not be
given work, it will amount to strike (Pepariach Sugar Mills Ltd. Vs. Their
Workmen).
Lay-Off [Sec.2 (Kkk0]
It means the failure, refusal or inability of an employer on account of the shortage of coal, power or raw material or the accumulation of stocks or the breakdown of machinery or natural calamity or for any other connected reason to give employment to a workman whose name is borne on the muster rolls of his industrial establishment and who has not been retrenched.
Lay-off does not involve alteration in the conditions of service. A lay-off is not the same, this as the order of dismissal. It is more akin to an order of suspension.
Lock-Out
It means temporary closing of a place of employment or the suspension of work or the refusal by an employer to continue to employ any number of persons employed by him. Under the present definition, two alternative acts of the employer constitute a lockout:
1. Temporary closing of a place of employment or
suspension of work; or
2. Refusal to continue to employ any number of persons
employed by him.
Essentials of Lock-out :
The essentials of a lock-out are as follows:
1. There is a temporary closing of the place of employment, or suspension or withholding of the work by the employer in some form.
2. There is an element of demands for which the place of employment is locked-out or closed.
There is an intention to re-employ the workers, if they accept the demands.
Meaning of Lock-out
Section 2(1) defines lock-out thus: “Lock-out” means temporary closing of a place of employment, or the suspension of work, or the refusal by an employer to continue to employ any number of persons employed by him. The requirements of lock-out, according to this definition are:
1. Suspension of work;
2. Refusal to employ;
3. By an employer; and
4. To continue to employ any number of persons employed by him.
The total Mandays lost on account of strikes and lockouts have declined by 4.80 million in 2003

Tags : Business Environment and Law-Industrial Disputes Act, 1947
Last 30 days 1256 views












