Accounting For Managers - Cost Estimation And Control-Standard Costing And Variance Analysis
Direct Material Cost Variance
Posted On :
It is the difference between the standard cost of material specified for the output achieved and the actual cost of materials used.
Direct
Material Cost Variance
It is the difference between the standard cost of material specified for the output achieved and the actual cost of materials used. The standard cost materials is computed by multiplying the standard price with the standard quantity for actual output and the actual cost is obtained by multiplying the actual price with actual quantity. The formula is:
= Standard Cost For Actual Output – Actual Cost or
DMCV = (Standard Price × Standard Quantity For Actual Output) – (Actual Price × Actual Quantity)
= (SP × SQ) – (AP × AQ).
Example 1.
The standard cost of material for manufacturing a unit of a particular product is estimated as under :
16 kg of raw materials @ rs. 1 per kg. On completion of the unit it was found that 20 kg. Of raw material costing rs. 1.50 per kg. Have been consumed. Compute material cost variance:
DMCV= (SP × SQ) – (AP × AQ)
= (16 × 1) – (20 × 1.50)
= Rs. 14 (Adverse)
It is that portion of material cost variance which is due to the difference between the standard prices specified and the actual price paid. This variance may be due to a number of reasons: change in price, inefficient buying, standard quality of materials not purchased, favorable discounts not obtained etc. The formula is:
Dmpv = actual quantity (standard price – actual price)
If the actual price is more than the standard price, the variance would be adverse and in case the standard price is more than the actual price, it would result in a favourable variance.
Example 2.
Use the information given in example 1 and compute the material price variance.
DMPV = AQ (SP – AP)
= 20 (1 – 1.50)
= Rs. (10) Adverse.
It is the difference between the standard quantity specified and the actual quantity used. This variance may arise because of: careless handling of materials, wastage, spoilage, theft, pilferage, changes in product design, use of inferior materials, defective tools and equipment etc. The formula is:
DMUV = Standard Price (Standard Quantity For Actual Output – Actual Quantity)
= SP (SQ – AQ).
Example 3.
Use the information given in example 1 and compute the material usage variance.
DMUV = SP (SQ – AQ)
= 1 (16 – 20)
= Rs. 4 (Adverse)
Note. The total of material price and usage variances is equal to material cost variance. Thus,
DMCV = DMPV + DMUV
in the example that has been used so far, let us verify this:
DMCV = DMPV + DMUV
Rs. 14 (A) = Rs. 10 (A) + Rs. 4 (A)
Illustration 1.
A manufacturing concern which had adopted standard costing furnishes the following information.
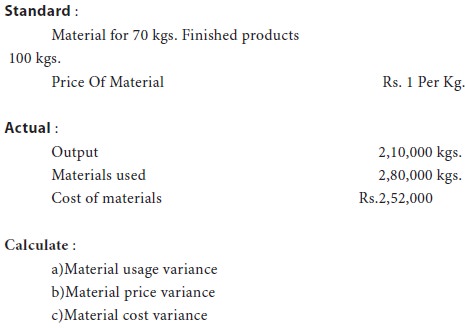
Solution:
For an output of Rs.70 kgs. Of finished products, standard quantity of material output is 100 kgs.
Therefore for the output of 2,10,000 kgs., standard quantity of material input should be = {100/70 × 2,10,000}= 3,00,000 kgs. Actual price per kg. = 2,52,000 / 2,80,000 = .90 paise
(a) Material usage variance :
= Standard Price (Standard Quantity – Actual Quantity)
= Rs.1 (3,00,000 – 2,80,000) = Rs. 20,000 (Favorable)
(b) Material price variance :
= Actual Quantity (Standard Price – Actual Price)
= 2,80,000 (1- .90) = Rs. 28,000 (Favorable)
(c) Material cost variance :
= Standard Quantity × Standard Price – Actual Quantity × Actual Price
= (3,00,000 × 1) – (2,52,000)
= Rs. 48,000 (Favorable)
Verification:
Material cost variance = material price variance + material usage variance.
Rs.48,000 (Favorable) = Rs.28,000 (Favorable) + Rs.20,000 (Favorable).
Illustration 2.
From the following particulars calculate :
ՖՖ Total materials cost variance;
ՖՖ Material price variance; and
ՖՖ Material usage variance.
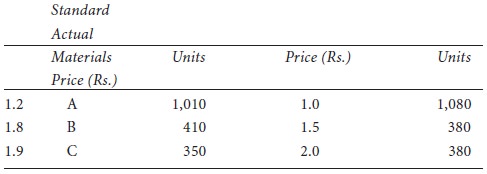
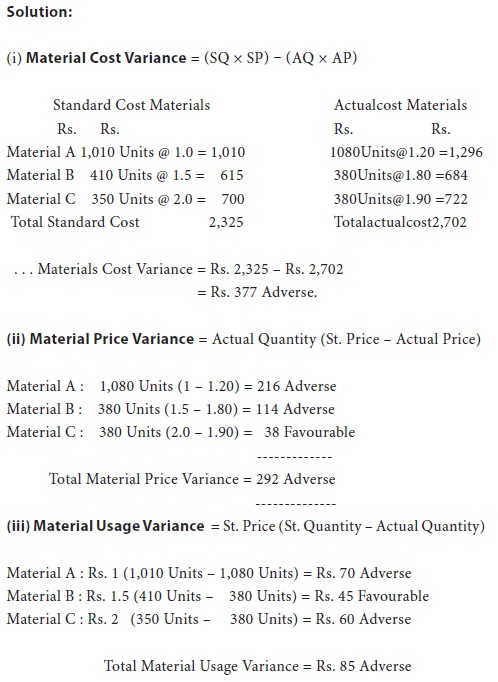

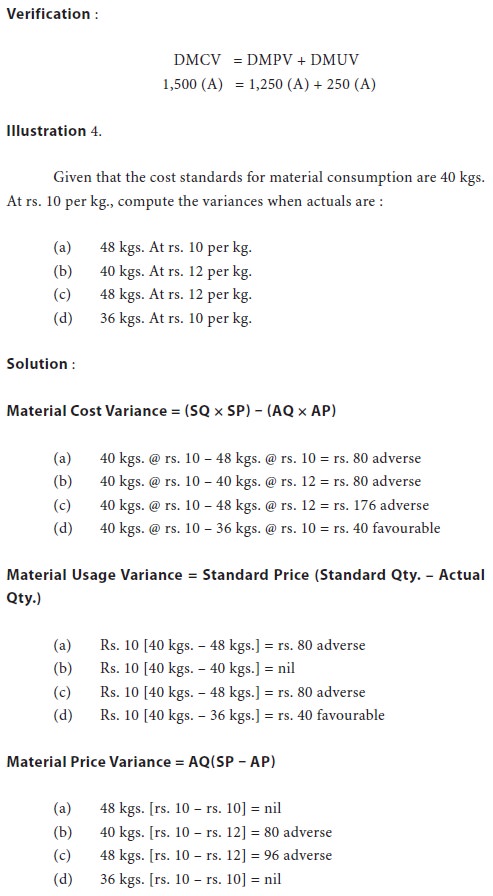
It is the difference between the standard cost of material specified for the output achieved and the actual cost of materials used. The standard cost materials is computed by multiplying the standard price with the standard quantity for actual output and the actual cost is obtained by multiplying the actual price with actual quantity. The formula is:
= Standard Cost For Actual Output – Actual Cost or
DMCV = (Standard Price × Standard Quantity For Actual Output) – (Actual Price × Actual Quantity)
= (SP × SQ) – (AP × AQ).
Example 1.
The standard cost of material for manufacturing a unit of a particular product is estimated as under :
16 kg of raw materials @ rs. 1 per kg. On completion of the unit it was found that 20 kg. Of raw material costing rs. 1.50 per kg. Have been consumed. Compute material cost variance:
DMCV= (SP × SQ) – (AP × AQ)
= (16 × 1) – (20 × 1.50)
= Rs. 14 (Adverse)
Direct Material Price Variance (DMPV)
It is that portion of material cost variance which is due to the difference between the standard prices specified and the actual price paid. This variance may be due to a number of reasons: change in price, inefficient buying, standard quality of materials not purchased, favorable discounts not obtained etc. The formula is:
Dmpv = actual quantity (standard price – actual price)
If the actual price is more than the standard price, the variance would be adverse and in case the standard price is more than the actual price, it would result in a favourable variance.
Example 2.
Use the information given in example 1 and compute the material price variance.
DMPV = AQ (SP – AP)
= 20 (1 – 1.50)
= Rs. (10) Adverse.
Direct Material Usage Or Quantity Variance (DMUV)
It is the difference between the standard quantity specified and the actual quantity used. This variance may arise because of: careless handling of materials, wastage, spoilage, theft, pilferage, changes in product design, use of inferior materials, defective tools and equipment etc. The formula is:
DMUV = Standard Price (Standard Quantity For Actual Output – Actual Quantity)
= SP (SQ – AQ).
Example 3.
Use the information given in example 1 and compute the material usage variance.
DMUV = SP (SQ – AQ)
= 1 (16 – 20)
= Rs. 4 (Adverse)
Note. The total of material price and usage variances is equal to material cost variance. Thus,
DMCV = DMPV + DMUV
in the example that has been used so far, let us verify this:
DMCV = DMPV + DMUV
Rs. 14 (A) = Rs. 10 (A) + Rs. 4 (A)
Illustration 1.
A manufacturing concern which had adopted standard costing furnishes the following information.

Solution:
For an output of Rs.70 kgs. Of finished products, standard quantity of material output is 100 kgs.
Therefore for the output of 2,10,000 kgs., standard quantity of material input should be = {100/70 × 2,10,000}= 3,00,000 kgs. Actual price per kg. = 2,52,000 / 2,80,000 = .90 paise
(a) Material usage variance :
= Standard Price (Standard Quantity – Actual Quantity)
= Rs.1 (3,00,000 – 2,80,000) = Rs. 20,000 (Favorable)
(b) Material price variance :
= Actual Quantity (Standard Price – Actual Price)
= 2,80,000 (1- .90) = Rs. 28,000 (Favorable)
(c) Material cost variance :
= Standard Quantity × Standard Price – Actual Quantity × Actual Price
= (3,00,000 × 1) – (2,52,000)
= Rs. 48,000 (Favorable)
Verification:
Material cost variance = material price variance + material usage variance.
Rs.48,000 (Favorable) = Rs.28,000 (Favorable) + Rs.20,000 (Favorable).
Illustration 2.
From the following particulars calculate :
ՖՖ Total materials cost variance;
ՖՖ Material price variance; and
ՖՖ Material usage variance.




Tags : Accounting For Managers - Cost Estimation And Control-Standard Costing And Variance Analysis
Last 30 days 3824 views












